(Press-News.org) Before a cell commits fully to the process of dividing itself into two new cells, it may ensure the appropriateness of its commitment by staying for many hours—sometimes more than a day—in a reversible intermediate state, according to a discovery by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine. Their revelation of this fundamental feature of biology includes details of its mechanisms and dynamics, which may inform the development of future therapies targeting cancers and other diseases.
In their study, published June 26 in Nature, the researchers developed new tools allowing them to track over time the activation state of E2F, a transcription factor protein long known as the master switch for initiating division in mammalian cells. They found unexpectedly that E2F, before being fully activated, can remain in a potentially lengthy state of partial and reversible activation that may end in full commitment to cell division or a reversion to the usual, non-dividing, “quiescent” state.
Although the role of this pre-commitment state of cell division is not yet entirely clear, it appears to be a safety mechanism to avoid inappropriate cell division, and may also activate DNA-repair functions. In any case, it appears to be a basic—and until now undiscovered—aspect of cell biology, with likely implications for understanding cancer, wound healing, and other cell division-related processes.
“We suspect, for example, that some types of cancer cell linger in this intermediate, pre-division state to improve their chances of survival,” said study senior author Dr. Tobias Meyer, the Joseph Hinsey Professor of Cell & Developmental Biology and a professor of biochemistry at Weill Cornell Medicine.
The study’s first author—and co-corresponding author with Dr. Meyer—is Dr. Yumi Konagaya, a postdoctoral researcher in the Meyer Laboratory during the study, now a principal investigator at Riken, a national research institute in Japan.
Cell division is the basic process underlying the growth and development of living things, and even in adult organisms is necessary for the repair of wounds and the general maintenance of tissues. While it has been known that the division process starts in a cell when various input signals trigger the activation of E2F, how this works has always been something of a mystery. The activation process is, in principle, highly sensitive to input signals, yet these signals are very prone to fluctuate—so how does the cell avoid constant, inappropriate E2F activations and cell divisions?
To answer this question, Dr. Konagaya developed the first-ever set of methods for tracking, in individual cells, the detailed activation status of E2F and its signaling partners as the cells move from their usual quiescent state into the division process. With these new tools, she observed that E2F, which is activated by multiple chemical modifications called phosphorylations, often remains in an extended, partial-activation, “primed” state in which some but not all of the necessary phosphorylations have occurred.
“It became clear that cells can stall in this primed state for more than a day before returning to quiescence or advancing to cell division,” Dr. Konagaya said.
It seems likely, according to the researchers, that this intermediate primed state allows cells time to sense and integrate the usual, fluctuating cell division input signals, smoothing this “noise” and reducing the chance of inappropriate division. But the researchers suspect that this state has other functions too, including to facilitate DNA repair, since cells in this state show signs of activated DNA-repair processes. A DNA-repair function could benefit cancer cells as well as healthy cells, Dr. Meyer noted.
“Cancer cells often die when they divide because of the DNA damage they have accumulated, but this intermediate state induces DNA damage-repair machinery, so maybe some cancers use this state to repair themselves before dividing,” he said.
The researchers plan to follow up in part by exploring the role of this intermediate pre-division state in cancers. In principle, having learned the tell-tale phosphorylation pattern of this intermediate state, they could develop tests for identifying cancers in this state, which could help in optimizing treatments.
END
Cell division: Before commitment, a very long engagement
2024-06-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New tool enables faster, more cost-effective genome editing of traits to improve agriculture sustainability
2024-06-26
ST. LOUIS, MO, June 26, 2024 – With the goal of reducing the time and cost it takes to bring an improved crop to the marketplace, research conducted in the laboratory of Keith Slotkin, PhD, and his colleagues in the Plant Transformation Facility at the Donald Danforth Plant Science Center, was recently published in the scientific journal Nature. The publication Transposase-assisted target site integration for efficient plant genome engineering focuses on technology called TATSI (Transposase-Assisted Target Site Integration), which uses transposable elements to integrate custom DNA into specific sites in plant genomes.
The ...
Unlocking the world of bacteria
2024-06-26
Bacteria populate virtually every habitat on Earth, including within and on our own bodies. Understanding and engineering bacteria can lead to new methods for diagnosing, treating, and preventing infections. Additionally, it presents opportunities to protect crops from disease and create sustainable cell factories for chemical production, reducing environmental impact — just a few of the many benefits to society. To unlock these advantages, scientists need the ability to manipulate the genetic content of these bacteria. However, a longstanding bottleneck in genetically engineering bacteria has been the efficient ...
Argonne to support new AI for science projects as part of the National AI Research Resource Pilot
2024-06-26
The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory will support three innovative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven science projects as part of the first round of awards from the National Artificial Intelligence Research Resource (NAIRR) Pilot.
Led by the National Science Foundation (NSF) in collaboration with DOE and several partners, the NAIRR Pilot aims to provide researchers and students with expanded access to key AI resources and data. NAIRR’s ultimate goal ...
Stress testing pension funds: Lithuanian researchers lead global innovation
2024-06-26
“We wanted to investigate how second pillar pension funds react to financial crises and how to protect them from the crises,” says Kaunas University of Technology (KTU) professor Dr Audrius Kabašinskas, who, together with his team, discovered a way to achieve this goal. The discovery in question is the development of stress tests for pension funds. Lithuanian researchers were the first in the world to come up with such an adaptation of the stress tests.
Stress tests are usually carried out on banks or other financial institutions to allow market regulators to determine and assess their ability to withstand adverse economic conditions.
According to the professor at ...
Multivitamin use and mortality risk in 3 prospective US cohorts
2024-06-26
About The Study: Multivitamin use was not associated with a mortality benefit in this cohort study of U.S. adults. Still, many adults report using multivitamins to maintain or improve health.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Erikka Loftfield, Ph.D., M.P.H., email erikka.loftfield@nih.gov.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.18729)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, ...
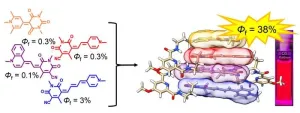
Solar technology: Innovative light-harvesting system works very efficiently
2024-06-26
In order to convert sunlight into electricity or other forms of energy as efficiently as possible, the very first step is an efficient light-harvesting system. Ideally, this should be panchromatic, i.e. absorb the entire spectrum of visible light.
The light-collecting antennae of plants and bacteria are a model for this. They capture a broad spectrum of light for photosynthesis, but are very complex in structure and require many different dyes to transmit the energy of the absorbed light and focus it on a central point.
The light-harvesting systems developed by humans to date also have disadvantages:
Although ...
Brain’s ‘escape switch’ controlled by threat sensitivity dial
2024-06-26
Neuroscientists have discovered how the brain bidirectionally controls sensitivity to threats to initiate and complete escape behaviour in mice. These findings could help unlock new directions for discovering therapies for anxiety and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
The study, published today in Current Biology, outlines how researchers at the Sainsbury Wellcome Centre at UCL studied a region of the brain called the periaqueductal gray (PAG), which is known to be hyperactive in people with anxiety and PTSD. Their ...
Improving prostate cancer screening for transgender women
2024-06-26
Transgender women are still at risk for prostate cancer. A new study led by Cedars-Sinai Cancer investigators, published in the peer-reviewed Journal of the American Medical Association, concludes that current screening guidelines could miss early-stage prostate cancer in transgender women on hormone therapy.
The prostate, a small gland that helps make semen, also produces a protein called prostate-specific antigen, or PSA. Blood levels of PSA tend to be elevated in people who have prostate cancer, and the PSA test, which measures those levels, is a common prostate ...
For healthy adults, taking multivitamins daily is not associated with a lower risk of death
2024-06-26
What: A large analysis of data from nearly 400,000 healthy U.S. adults followed for more than 20 years has found no association between regular multivitamin use and lower risk of death. The study, led by researchers at the National Institutes of Health’s National Cancer Institute, was published June 26, 2024, in JAMA Network Open.
Many adults in the United States take multivitamins with the hope of improving their health. However, the benefits and harms of regular multivitamin use remain unclear. ...
From takeoff to flight, the wiring of a fly's nervous system is mapped
2024-06-26
Work is underway on a wiring diagram of the motor circuits in the central nervous system that control muscles in fruit flies. This connectome, as the wiring diagram is called, is already providing detailed information on how the nerve coordination of leg movements differs from that controlling the wings.
Although fruit flies seem like simple creatures, the researchers said that their motor system contains “an unexpected level of complexity.”
“A typical fly motor neuron receives thousands of synapses from hundreds ...