Chemotherapy disrupts gut microbiome in patients with breast cancer
This gut microbiome disruption is implicated in cognitive decline and inflammation
2024-06-26
(Press-News.org) COLUMBUS, Ohio – Chemotherapy is known to cause behavioral side effects, including cognitive decline. Notably, the gut microbiome communicates with the brain to affect behavior, including cognition.
“For the first time ever, our Intelligut Study found that the gut microbiome has been implicated in cognitive side effects of chemotherapy in humans,” said senior author Leah Pyter, associate professor of psychiatry and neuroscience with The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and College of Medicine. “The potential connection between the gut and the brain would allow us to create treatments for the gut to treat the brain.”
Study findings are published in the journal Brain, Behavior, and Immunity.
This clinical longitudinal observational study explored whether chemotherapy-induced disruption of the gut microbiome relates to cognitive decline and circulating inflammatory signals.
Fecal samples, blood and cognitive measures were collected from 77 patients with breast cancer before, during and after chemotherapy.
Research highlights
Chemotherapy induces microbiome disruption and inflammation.
The resulting microbiome disruption relates to cognitive decline and inflammation.
Those cognitively impaired have unique chemotherapy-induced microbiome alterations.
“We found that patients treated with chemotherapy who showed decreases in cognitive performance also had reductions in the diversity of their gut microbiome,” said Pyter, also a researcher with Ohio State’s Institute for Behavioral Medicine Research and member of the Cancer Control Research Program at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC – James).
This research builds on Pyter’s prior research in mouse models that found chemotherapy-induced shifts in the gut microbiome cause neurobiological changes and behavioral side effects.
The current study indicates that an association between gut microbiome and cognitive performance exists in humans as well.
“Side effects of chemotherapy are common and may reduce quality of life, but these side effects can be dismissed as ‘part of chemotherapy’ and therefore overlooked and under-treated,” Pyter said. “We believe that gut microbiome-focused interventions, such as fecal microbial transplantation, may improve behavioral side effects of chemotherapy.”
OSUCCC—James researchers are also conducting research studies on how the gut microbiome impacts cancer treatment effectiveness and its role in reducing or increasing cancer risk.
“Chemotherapy is a very important tool for stopping many cancers and side effects should not deter patients who would benefit from this type of therapy from pursuing it, but we know the side effects of some treatment regimens can be quite challenging for patients to complete,” said David Cohn, MD, interim chief executive officer of the OSUCCC – James. “It’s a careful tightrope of walking between effective cancer control and side effect management – and our team is working every day, in the hospital clinics and the lab, to develop ways to manage the side effects of disease treatment with an eye toward quality of life.”
Ohio State researchers collaborated with The Research Institute at Nationwide Children’s Hospital for this study.
This study was supported in part by a National Institutes of Health grant and Ohio State Wexner Medical Center.
Conflict of interest disclosure
Researcher Michael T. Bailey is a scientific cofounder and stock owner of Scioto Biosciences.
# # #
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-06-26
Engineers at the University of California San Diego have developed a pill that releases microscopic robots, or microrobots, into the colon to treat inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The experimental treatment, given orally, has shown success in mice. It significantly reduced IBD symptoms and promoted the healing of damaged colon tissue without causing toxic side effects.
The study was published June 26 in Science Robotics.
IBD, an autoimmune disorder characterized by chronic inflammation of the gut, ...
2024-06-26
Sharing false political information on social media by users may be associated with aspects of personality such as positive schizotypy, a set of traits including paranoia, suspicion and disrupted thinking patterns. It may also be linked to a motivation to increase awareness according to a study published June 26, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Tom Buchanan, University of Westminster, UK, and colleagues.
The spread of false political information on social media can tarnish trust in authentic news and even contribute to social unrest. Knowingly or not, a small portion of social media users actively share false material.
Buchanan and ...
2024-06-26
In a test of the examinations system of the University of Reading in the UK, artificial intelligence (AI)-generated submissions went almost entirely undetected, and these fake answers tended to receive higher grades than those achieved by real students. Peter Scarfe of the University of Reading and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on June 26.
In recent years, AI tools such as ChatGPT have become more advanced and widespread, leading to concerns about students using them to cheat by submitting AI-generated work as their own. Such concerns are heightened ...
2024-06-26
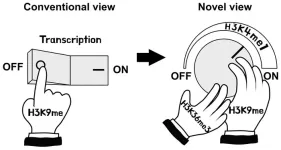
Researchers led by Kannosuke Yabe, Asuka Kamio, and Soichi Inagaki of the University of Tokyo have discovered that in thale cresses histone H3 lysine-9 (H3K9) methylation, conventionally thought to be a mark of turning off gene transcription, can also turn on gene expression via the interactions of two other proteins and histone marks. The molecular mechanisms demonstrate that rather than functioning as a simple “off switch,” H3K9 methylation is more like a “dimmer switch” that fine-tunes DNA transcription. The discovery suggests there might be similar mechanisms in other ...
2024-06-26
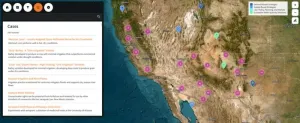
New interactive atlas of water scarcity solutions in the U.S. Southwest shares a library of case studies to help adapt to drought.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/water/article?id=10.1371/journal.pwat.0000246
Article Title: The water adaptation techniques atlas: A new geospatial library of solutions to water scarcity in the U.S. Southwest
Author Countries: United States
Funding: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist. END ...
2024-06-26
Experienced exam markers may struggle to spot answers generated by Artificial Intelligence (AI), researchers have found.
The study was conducted at the University of Reading, UK, where university leaders are working to identify potential risks and opportunities of AI for research, teaching, learning, and assessment, with updated advice already issued to staff and students as a result of their findings.
The researchers are calling for the global education sector to follow the example of Reading, and others who are also forming new ...
2024-06-26
Whether it’s a first-time visit to a zoo or when we learned to ride a bicycle, we have memories from our childhoods kept well into adult years. But what explains how these memories last nearly an entire lifetime?
A new study in the journal Science Advances, conducted by a team of international researchers, has uncovered a biological explanation for long-term memories. It centers on the discovery of the role of a molecule, KIBRA, that serves as a “glue” to other molecules, thereby solidifying memory formation.
“Previous efforts to understand ...
2024-06-26
North Carolina State University researchers have developed a kirigami-inspired mechanical computer that uses a complex structure of rigid, interconnected polymer cubes to store, retrieve and erase data without relying on electronic components. The system also includes a reversible feature that allows users to control when data editing is permitted and when data should be locked in place.
Mechanical computers are computers that operate using mechanical components rather than electronic ones. Historically, these mechanical components have been things like levers or gears. However, mechanical computers can also be made using structures that are multistable, meaning ...
2024-06-26
Genova (Italy), 26 June 2024 – Researchers at the Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT-Italian Institute of Technology) have demonstrated that under specific conditions, humans can treat robots as co-authors of the results of their actions. The condition that enables this phenomenon is that a robot behaves in a human-like, social manner. Engaging in gaze contact and participating in a common emotional experience, such as watching a movie, are the key. The study was published in Science Robotics and paves the way for understanding and designing the optimal circumstances for humans and robots to collaborate in the same environment.
The ...
2024-06-26
Scientists at the University of Konstanz in Germany have advanced ultrafast electron microscopy to unprecedented time resolution. Reporting in Science Advances, the research team presents a method for the all-optical control, compression, and characterization of electron pulses within a transmission electron microscope using terahertz light. Additionally, the researchers have discovered substantial anti-correlations in the time domain for two-electron and three-electron states, providing deeper insight into the quantum physics of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Chemotherapy disrupts gut microbiome in patients with breast cancer
This gut microbiome disruption is implicated in cognitive decline and inflammation