Application of impedance sliding mode control combined with stiffness scheduling in rehabilitation robot systems
2024-06-27
(Press-News.org)
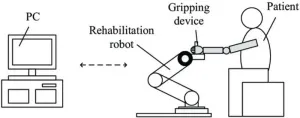
In recent years, rehabilitation robots have become increasingly popular in the field of healthcare, able to mimic the movements of a therapist and enhance patients' mobility through carefully designed control methods. A team from the Automation College of Beijing Institute of Technology, led by Kexin Hu, Zhongjing Ma, Suli Zou, Jian Li, and Haoran Ding, in collaboration with collaborators from the University College London, has recently proposed a novel impedance sliding mode control method that combines stiffness scheduling technology, which has brought significant advancements to rehabilitation robot systems.
This research has broken through the limitations of traditional rehabilitation robot control methods, which often rely on fixed or variable impedance control with no consideration for the patient's condition and health status. The proposed impedance sliding mode control combined with stiffness scheduling method is not only suitable for active and passive rehabilitation training modes, but also addresses the problem of model-based sliding mode control, reducing system uncertainty caused by limb tremors.
The innovative aspect of this method is its ability to automatically adjust the damping parameters of the rehabilitation robot based on the patient's applied force. This stiffness scheduling rule ensures that rehabilitation training is more tailored to the patient's health status, providing a more personalized and efficient rehabilitation experience. The researchers employed a model-free sliding mode control strategy to further enhance the system's robustness and adaptability.
To validate the feasibility and stability of the method, the research team conducted rehabilitation training experiments on a rehabilitation robot. Experimental results have demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed method, providing new ideas and methods for the development of rehabilitation robot systems.
The findings of this research are significant for the future development of rehabilitation robotics. By combining advanced impedance sliding mode control and stiffness scheduling technology, rehabilitation robots can provide more personalized and effective rehabilitation training, thereby improving patient outcomes and quality of life. This research also demonstrates the potential of combining advanced control techniques with rehabilitation robots to address the challenges facing the healthcare industry in providing efficient and cost-effective rehabilitation services.
The paper, "Impedance Sliding-Mode Control Based on Stiffness Scheduling for Rehabilitation Robot Systems," was published in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems on Jun 1, 2024, at DOI: https://doi/10.34133/cbsystems.0099
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-06-27
Around the time of the untimely death of Freddie Gray, a 25-year-old Black man in police custody, researchers from Johns Hopkins University were collecting data for Communities CARING, a study that examined the relationship of health behaviors among public housing residents in East and West Baltimore communities in Maryland. Led by Kristal Lyn Brown, PhD, an assistant professor in Drexel University’s College of Nursing and Health Professions, a secondary analysis of the data collected for Communities CARING examined the relationship between a high-profile event (Gray’s death) and disordered eating ...
2024-06-27
Korean researchers are strengthening South Korea’s leadership in the global market through the development of 6G, the next-generation mobile communication technology.
Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) announced that they showcased their latest research results at the “6G Symposium Spring 2024” held in Oulu, Finland, from April 9 to 11, drawing the attention of attendees.
At this symposium, ETRI particularly showcased its “service mesh” technology. This technology is a key 6G technology that addresses complex communication issues among numerous cloud-nativemobile network functions that ...
2024-06-27
Researchers have identified a protein called PFDN6 that may play a role in the development and spread of colorectal cancer (CRC). The study, published in [journal name], found that PFDN6 levels are increased in CRC patients and contribute to tumor growth. By reducing PFDN6 in lab studies, scientists were able to slow cancer cell spread and increase cell death. These findings suggest that PFDN6 could be a target for future CRC treatments.
CRC is the third most common cancer worldwide and has a poor prognosis, especially ...
2024-06-27
When operating on the heart, surgeons may find another issue in the patient. Depending on what they see, the surgical team may address on the secondary condition during the same operation.
These are sometimes called concomitant procedures.
However, two studies led by Michigan Medicine find that female patients who undergo heart surgery are less likely to have secondary ailments corrected during a procedure — despite guidelines that indicate they should.
“Across the spectrum of cardiovascular care, from medical management to transcatheter and surgical procedures, there is growing evidence that women ...
2024-06-27
LONDON, ON – A team at Lawson Health Research Institute is the first in Canada to perform a transplant using a technique called abdominal normothermic regional perfusion (A-NRP), which could lead to more organs being available for transplant. The technique was used to optimize organs from two donors in April 2024 at London Health Sciences Centre (LHSC), resulting in the successful transplantation of two kidneys and two livers to four patients.
“Organ donation after circulatory death (when the heart stops beating) has historically been less reliable than organ donation after brain death,” explained Dr. Anton Skaro, Associate Scientist ...
2024-06-27
Researchers have discovered that zinc plays a crucial role in the nitrogen fixation process of legumes. This finding, along with the transcriptional regulator Fixation Under Nitrate (FUN), could revolutionize legume-based agriculture by optimizing crop efficiency and reducing reliance on synthetic fertilizers. By understanding how zinc and FUN regulate nitrogen fixation, researchers might be able to enhance nitrogen delivery, improve crop yields, and promote more sustainable agricultural practices.
The new knowledge about zinc can change the way we cultivate crops, as plants can ...
2024-06-27
Just four per cent of talented teen academy prospects make it to the top tier of professional football, a new study has shown.
A sample of nearly 200 players, aged between 13-18, also revealed only six per cent of the budding ballers even go on to play in lower leagues.
The University of Essex researchers discovered the players who succeeded excelled in self-confidence, ball reception skills, dribbling and coaches’ subjective technical assessments.
The study – published in the International Journal ...
2024-06-27
Experts have identified 240 Chinese cities whose emission reduction are mainly benefiting from the carbon mitigation actions of other cities, whilst putting in less effort themselves.
Researchers studied the phenomenon across 309 Chinese cities using data from 2012 to 2017 – a period when China underwent economic reform and industrial transformation.
Constructing a city-level input-output model to assess carbon footprints, the researchers identified 78% of the cities as ‘outsourced beneficiaries’, ...
2024-06-27
It is widely accepted that biological interactions are stronger or more important in generating and maintaining biodiversity in the tropics than in temperate regions. However, this hypothesis has not been fully tested in ecology and evolutionary biology.
In a study published in Nature Ecology and Evolution, researchers from the Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden (XTBG) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have provided strong support for this central prediction by examining phytochemical diversity and herbivory in 60 tree communities ...
2024-06-27
Slush – water-soaked snow – makes up more than half of all meltwater on the Antarctic ice shelves during the height of summer, yet is poorly accounted for in regional climate models.
Researchers led by the University of Cambridge used artificial intelligence techniques to map slush on Antarctic ice shelves, and found that 57% of all meltwater is held in the form of slush, with the remaining amount in surface ponds and lakes.
As the climate warms, more meltwater is formed on the surface of ice shelves, the floating ice surrounding Antarctica which acts as ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Application of impedance sliding mode control combined with stiffness scheduling in rehabilitation robot systems