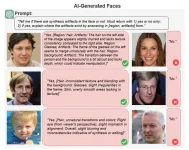
(Press-News.org) BUFFALO, N.Y. — When most people think of artificial intelligence, they’re probably thinking of — and worrying about — ChatGPT and deepfakes. AI-generated text and images dominate our social media feeds and the other websites we visit, sometimes without us knowing it, and are often used to spread unreliable and misleading information.
But what if text-generating models like ChatGPT could actually spot deepfake images?
A University at Buffalo-led research team has applied large language models (LLMs), including OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Google’s Gemini, toward spotting deepfakes of human faces. Their study, presented last week at the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition, found that LLMs' performance lagged behind that of state-of-the-art deepfake detection algorithms, but their natural language processing may actually make them the more practical detection tool in the future.
“What sets LLMs apart from existing detection methods is the ability to explain their findings in a way that’s comprehensible to humans, like identifying an incorrect shadow or a mismatched pair of earrings,” says the study’s lead author, Siwei Lyu, PhD, SUNY Empire Innovation Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, within the UB School of Engineering and Applied Sciences. “LLMs were not designed or trained for deepfake detection, but their semantic knowledge makes them well suited for it, so we expect to see more efforts toward this application.”
Collaborators on the study include the University at Albany and the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen. The work was supported by the National Science Foundation.
How language models understand images
Trained on much of the available text on the internet — amounting to some 300 billion words — ChatGPT finds statistical patterns and relationships between words in order to generate responses.
The latest versions of ChatGPT and other LLMs can also analyze images. These multimodal LLMs use large databases of captioned photos to find the relationships between words and images.
“Humans do this as well. Whether it be a stop sign or a viral meme, we constantly assign a semantic description to images,” says the study’s first author, Shan Jai, assistant lab director in the UB Media Forensic Lab. “In this way, images become their own language.”
The Media Forensics Lab team decided to test if GPT-4 with vision (GPT-4V) and Gemini 1.0 could tell the difference between real faces and faces generated by AI. They gave it thousands of images of both real and deepfake faces and asked it to identify any potential signs of manipulation, or synthetic artifacts.
ChatGPT advantages
ChatGPT was accurate 79.5% of the time on detecting synthetic artifacts in images generated by latent diffusion, and 77.2% of the time on StyleGAN-generated images.
“This is comparable to earlier deepfake detection methods, so with proper prompt guidance, ChatGPT can do a fairly decent job at detecting AI-generated images,” says Lyu, who is also co-director of UB’s Center for Information Integrity.
More crucially, ChatGPT could explain its decision making in plain language. When provided an AI-generated photo of a man with glasses, the model correctly pointed out that “the hair on the left side of the image slightly blurs” and “the transition between the person and the background is a bit abrupt and lacks depth.”
“Existing deepfake detection models will tell us the probability of an image being real or fake, but they will very rarely tell us why they came to this conclusion. And even if we look into the model’s underlying mechanisms, there will be features that we simply can’t understand,” Lyu says. “Meanwhile, everything ChatGPT outputs is understandable to humans.”
That’s because ChatGPT bases its analysis on semantic knowledge alone. Whereas traditional deepfake detection algorithms distinguish real from fake by training on large datasets of images labeled real or fake, LLMs’ natural language abilities give them something of a common sense understanding of reality — at least when they’re not hallucinating — including the typical symmetry of human faces and the look of real photographs.
“Once the vision component of ChatGPT understands an image as a human face, the language component can make the inference that a face will typically have two eyes, and so on,” Lyu says. “The language component provides a deeper connection between visual and verbal concepts.”
ChatGPT’s semantic knowledge and natural language processing make it a more user-friendly deepfake tool for both users and developers, the study concluded.
“Typically, we take insights about detecting deepfakes and convert them into programming language. Now, all this knowledge is present within a single model and we need only use natural language to bring out that knowledge,” Lyu says.
ChatGPT drawbacks
ChatGPT’s performance was well below the latest deepfake detection algorithms, which have accuracy rates in the mid- to high-90s.
This was partly because LLMs can’t catch signal-level statistical differences that are invisible to the human eye but often used by detection algorithms to spot AI-generated images.
“ChatGPT focused only on semantic-level abnormalities,” Lyu says. “In this way, the semantic intuitiveness of the ChatGPT’s results may actually be a double-edged sword for deepfake detection.”
And other LLMs may not be as effective at explaining their analysis. Despite performing comparatively to ChatGPT at guessing the presence of synthetic artifacts, Gemini’s supporting evidence was often nonsensical, like pointing out nonexistent moles.
Another drawback is that LLMs often refused to analyze images. When asked directly whether a photo was generated by AI, ChatGPT typically replied with, “Sorry, I can’t assist with that request.”
“The model is programmed not to answer when it doesn’t reach a certain confidence level,” Lyu says. “We know that ChatGPT has information relevant to deepfake detection, but, again, a human operator is needed to excite that part of its knowledge base. Prompt engineering is effective, but not very efficient, so the next step is going one level down and actually fine tuning LLMs for this task specifically.”
END
Is ChatGPT the key to stopping deepfakes? Study asks LLMs to spot AI-generated images
Large language models perform below state-of-the-art detectors, but their ability to plainly explain their analysis holds promise
2024-06-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NIH funds critical center in Detroit to lead efforts to investigate and mitigate health impacts of community-voiced chemical and non-chemical stressors
2024-06-27
DETROIT — Wayne State University received a four-year, $5.2 million P30 environmental health sciences core center (EHSCC) grant from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS) of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in support of the “Center for Urban Responses to Environmental Stressors (CURES).”
This grant will allow the interdisciplinary CURES team of researchers, educators and community partners to continue its ongoing quest to understand the basis for urban environmental health disparities and the human health impact of environmental exposure to complex chemical and non-chemical stressors in Detroit's urban landscape. CURES is one of ...
TREC director Jennifer Dill named editor-in-chief of Transportation Research Record
2024-06-27
Jennifer Dill, director of Portland State University's Transportation Research and Education Center (TREC), has been named the inaugural editor-in-chief of the Transportation Research Record (TRR). The TRR—the flagship journal of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine’s Transportation Research Board (TRB)—is one of the most cited and prolific transportation journals in the world, offering wide coverage of transportation-related topics.
While maintaining her current role as the director of TREC, Dill will begin her duties ...
SUNY College of Optometry focuses on diversity and inclusion in optometry
2024-06-27
New York, NY— This week, the State University of New York (SUNY) College of Optometry held a continuation of their annual webinar series, Race in Optometry which started in 2020. Aimed at fostering a national dialogue that leads to necessary changes to increase diversity in the optometric profession and education, the annual webinar focused on Headwinds: Navigating Barriers to Success. This webinar was the seventh installment in a series hosted annually around the Juneteenth holiday by the College’s Office of Continuing Professional ...
Taxing shared micromobility: How cities are responding to emerging modes, and what's next
2024-06-27
Shared micromobility (including shared electric scooters and bikes provided by private companies) is one of the newest transportation options that has come to cities in the last several decades. A new report explores the different ways cities charge shared micromobility companies to operate, and how these funds are used.
In the newly released report, John MacArthur of Portland State University, Kevin Fang of Sonoma State University and Calvin Thigpen of Lime examine data from 120 cities in 16 countries around the world. They also conducted a survey of cities’ shared micromobility ...
June research news from the Ecological Society of America
2024-06-27
The Ecological Society of America (ESA) presents a roundup of four research articles recently published across its six esteemed journals. Widely recognized for fostering innovation and advancing ecological knowledge, ESA’s journals consistently feature illuminating and impactful studies. This compilation of papers explores the potential for pines to establish in pine-free interior Alaska, internet sleuthing to assess birds’ extinction risk and more, showcasing the Society’s commitment to promoting cutting-edge research that furthers our understanding ...
Antibody-drug conjugate highly effective in preventing recurrence in patients with early stage HER2+ breast cancer, trial finds
2024-06-27
A year of treatment with a medicine made of an antibody and chemotherapy drug has proven highly effective in preventing stage 1 HER2-positive breast cancer from recurring in patients, a team led by Dana-Farber Cancer Institute researchers has found.
In a clinical trial involving 512 patients with the earliest stage of breast cancer that tested positive for the HER2 protein, 97% of those treated with trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) after surgery were alive and free of invasive cancer five years after treatment. The results, published online today in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, suggest that T-DM1 is a reasonable treatment approach for this stage 1 population, the study authors ...
Ephemeral streams, often overlooked, are major contributors to US river flow and water quality
2024-06-27
Ephemeral streams – temporary streams that only flow after rainfall or snowmelt – contribute more than 50% of the flow in downstream river systems and likely have a major influence on water quality across the United States, according to a new modeling study. The findings show how important ephemeral streams are for the transport of water and pollution into larger, more permanent water bodies. Excluding these streams from coverage under the U.S. Clean Water Act, say the authors, would significantly limit federal authority to protect downstream water quality. Ephemeral streams, which flow only in direct response to precipitation and are disconnected from groundwater sources, ...
From a Pompeii-like ash burial in Morrocco: Pristine 3D anatomy of Cambrian trilobites
2024-06-27
Thanks to being rapidly entombed in volcanic ash – in a “Pompeii-like” process – Cambrian-age trilobites’ anatomy is more discernable than ever, via exquisitely preserved fossils. The fossils uncovered in Morrocco are reported in a new study that reveals microscopic details including of trilobite appendages and the trilobite digestive system. Trilobites are perhaps the most well-known creatures that lived during the Cambrian Period. These extinct marine arthropods’ hard exoskeleton lends itself to high fossilization potential, facilitating the identification of more ...
Novel epigenic editor, CHARM, enables brain-wide prion protein silencing
2024-06-27
In a new study in mice, researchers introduce “CHARM,” a compact and versatile epigenetic editor that can be used to silence prion protein throughout the brain. The tool provides a path towards an effective first-line treatment for patients with deadly prion disease as well as other neurodegenerative diseases caused by the toxic buildup of unwanted proteins. Prion disease – a suite of devastating neurodegenerative disorders that result in rapid-onset dementia and death – is caused by misfolding of the prion protein, PrP, to form toxic aggregates that result in neuronal death. Previous research in mice has shown that removing PrP ...
A promising weapon against measles
2024-06-27
LA JOLLA, CA—What happens when measles virus meets a human cell? The viral machinery unfolds in just the right way to reveal key pieces that let it fuse itself into the host cell membrane.
Once the fusion process is complete, the host cell is a goner. It belongs to the virus now.
Scientists in the La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) Center for Vaccine Innovation are working to develop new measles vaccines and therapeutics that stop this fusion process. The researchers recently harnessed an imaging technique called cryo-electron microscopy to show—in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
[Press-News.org] Is ChatGPT the key to stopping deepfakes? Study asks LLMs to spot AI-generated imagesLarge language models perform below state-of-the-art detectors, but their ability to plainly explain their analysis holds promise