(Press-News.org) An experimental study led by Pompeu Fabra University describes the mechanism whereby insulinomas, a rare type of neuroendocrine tumour that affects pancreatic beta cells. According to the study, insulinomas are the result of the accumulation of rare mutations that lead to a homogeneous change in the epigenetic profile of pancreatic beta cells. This profile change causes beta cells to express unusually high levels of oncogenes, growth and transcription factors, and genes related to insulin production.
Insulinomas are rare pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours that involve the excessive growth of beta cells, which are responsible for secreting insulin. Often, they are diagnosed because they involve excessive insulin production that usually leads to hypoglycaemia. Each year, four people in one million are diagnosed with insulinomas, and in most cases, they are benign. If detected early and surgically removed, they have a good prognosis and only about in one in ten insulinomas are malignant.
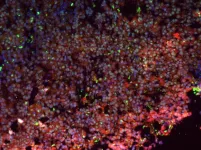
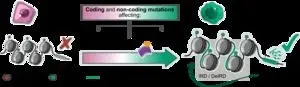
In a study published today in the journal Cell Genomics, a mechanism whereby beta cells undergo a transformation towards a neoplastic phenotype is proposed for the first time. “This is the accumulation of rare mutations that converge in a change in the epigenetic profile of beta cells”, explains Mireia Ramos, co-first author of the study.
These mutations vary among the 42 insulinomas analysed, and most accumulate in regulatory regions of the genome. “The uniqueness of insulinomas is that all of them, regardless of the mutations they have, end up acquiring the same epigenetic profile”, adds Lorenzo Pasquali, director of the UPF Endocrine Regulatory Genomics Group, who led the research.
This new epigenetic profile causes tumour beta cells to lose their repression marks and, unlike healthy beta cells, have a series of active oncogenes, growth and transcription factors and genes related to insulin production, which alter their function.
The biology of beta cells
Apart from insulinomas, pancreatic beta cells are also implicated in other disabling diseases such as diabetes mellitus. Hence, “we are especially interested in understanding how these cells lose control, upset the expression of the genes that made them function normally and end up altering insulin secretion”, Pasquali comments.
Now, the group is already working to better understand the mechanism whereby excess beta cell growth occurs, which could, in the future, have therapeutic implications in the treatment of other diseases in which beta cells are altered.
This study has also involved the Scientific Institute of Hospital San Raffaele in Milan (Italy); the University of Barcelona; IDIBELL, Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute; the University of Colorado Boulder (USA); the Parc Taulí Research and Innovation Institute, I3PT; IRB Barcelona and the Diabetes and Associated Metabolic Diseases Networking Biomedical Research Centre (CIBERDEM).
END
A study led by UPF describes how insulinomas, a rare type of pancreatic beta cell tumor, form
The cause is a change in the epigenetic pattern of the beta cells of the pancreas, which overexpress oncogenes and genes related to insulin production, thus altering their functioning. This change in pattern, a common factor in the vast majority of tumou
2024-07-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NIH researchers discover a new face-detecting brain circuit
2024-07-02
Scientists at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have uncovered a brain circuit in primates that rapidly detects faces. The findings help not only explain how primates sense and recognize faces, but could also have implications for understanding conditions such as autism, where face detection and recognition are often impaired from early childhood. The newly discovered circuit first engages an evolutionarily ancient part of the brain called the superior colliculus, which can then trigger the eyes and head to turn for a better look. This better view enables different brain areas in the temporal cortex to engage ...
Potential new target for early treatment of Alzheimer's disease
2024-07-02
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A class of proteins that regulates cell repair and enhances cell growth-signaling systems could be a promising new target for the treatment of Alzheimer's and other neurodegenerative diseases, according to a new study led by researchers at Penn State. They found that disrupting necessary sugar modifications of these proteins promotes cell repair and reverses cellular abnormalities that occur in neurodegenerative diseases.
The study appeared today (July 2) in the journal iScience, and the researchers have a patent related to this work.
“Strategies ...
Subnormal serum liver enzyme levels
2024-07-02
Liver diseases are commonly diagnosed using serum enzyme assays, particularly for aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT), and 5'-nucleotidase (5'-NT). While elevated levels of these enzymes are typically associated with liver and bile duct injuries, subnormal levels can also indicate various pathologies. This review consolidates current knowledge on diseases linked with subnormal liver enzyme levels, focusing on their pathogenesis, specificity, and treatment ...
Too much treadmill? This could help your shin splints
2024-07-02
Good news for all the treadmill runners who suffer from stubborn and painful shin splints: A little outdoor gait training may help, new research suggests.
A randomized controlled trial found that four weeks of gait training outdoors, in addition to home exercises often prescribed for shin splints, led to improved running biomechanics even when the runners were using a treadmill. These improvements included decreasing the time the runners’ feet were in contact with the ground or treadmill, a recently identified contributor to shin splints.
Based on the trial results, ...
Journal of Participatory Medicine announces new theme issue on Patient and Consumer Use of Artificial Intelligence for Health
2024-07-02
(Toronto, July 2, 2024) JMIR Publications invites submissions to a new theme issue titled “Patient and Consumer Use of Artificial Intelligence for Health” in its premier open access journal Journal of Participatory Medicine indexed in PubMed, SCOPUS, Sherpa Romeo, and DOAJ.
This theme issue will explore the use of AI for health (AIH) from the perspectives of patients and the public. The journal is seeking papers that examine (a) the experience and impact of patients and health consumers using AI applications, and (b) the involvement of patients, caregivers, and the public in the co-design and development of AIH.
For this theme issue, the journal ...
Unveiling the genetic secrets of Musa ornata and Musa velutina: insights into pericarp dehiscence and anthocyanin biosynthesis
2024-07-02
In a pioneering study, researchers have completed the chromosome-level genome assemblies for Musa ornata and Musa velutina, shedding light on the genetic underpinnings of pericarp dehiscence and anthocyanin biosynthesis in bananas. This genetic blueprint is poised to revolutionize the enhancement of bananas' ornamental appeal and nutritional quality, unlocking mysteries that were previously obscured by limited genomic data.
Musa ornata and Musa velutina, known for their ornamental appeal, face cultivation challenges ...
Researchers achieve dual-functional supramolecular materials
2024-07-02
Versatile molecular frameworks called discrete supramolecular structures act like microscopic building blocks customizable for a wide variety of applications. The structures can serve in drug delivery, provide unique environments for catalytic reactions or plug into a molecular machine.
In their paper published June 25 in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, researchers from Yokohama National University presented a new methodology to advance self-assembly of dual-functional supramolecular materials.
Self-assembly involves the spontaneous generation of a well-defined, discrete supramolecular architecture from ...
A new target for treatment of one type of macular degeneration
2024-07-02
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new study in mice hints at the promise of an eventual alternative treatment option for the “wet” version of age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
Researchers determined in mice that an enzyme related to cell growth and division is a culprit in the blood vessel invasion in the back of the eye that causes blurred central vision in wet AMD. Targeting the enzyme, called telomerase, with an experimental drug suppressed abnormal vascular growth in the animals’ retina.
The only current treatment for wet AMD is injection into the eye of a medication that blocks the activity of a growth factor protein, called VEGF, which is ...
Australian bushfire ash is deadly for aquatic life
2024-07-02
While the impact of wildfires on terrestrial life has been well studied, only recently has research started to examine the effects of wildfire ash on aquatic organisms. New research reveals that wildfire ash can have lethal consequences on Australian water ecosystems.
Wildfires are becoming more prevalent due to the warming and drying effects of climate change, with Australia becoming especially vulnerable to dangerous bushfires. “Therefore, many Australian species may be threatened by fires,” says Miss Jenelle McCuaig, a Masters student at the University ...
Starfish skeleton inspires new 4D morphing structure
2024-07-02
Researchers have recently developed a flexible-yet-sturdy morphing structure inspired by the starfish skeleton that exhibits 4D morphing features with promising applications for robotics, aviation, and medical devices.
“Starfish possess the remarkable ability to effortlessly hold themselves in any body posture by changing the stiffness of their endoskeleton,” says Raman, a PhD student in the Biological Structures and Biomimetics workgroup at Hochschule Bremen - City University of Applied Sciences Bremen, Germany.
Ossicles are calcite microstructures inside starfish bodies that are connected in a ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Barshop Institute to receive up to $38 million from ARPA-H, anchoring UT San Antonio as a national leader in aging and healthy longevity science
Anion-cation synergistic additives solve the "performance triangle" problem in zinc-iodine batteries
Ancient diets reveal surprising survival strategies in prehistoric Poland
Pre-pregnancy parental overweight/obesity linked to next generation’s heightened fatty liver disease risk
Obstructive sleep apnoea may cost UK + US economies billions in lost productivity
Guidelines set new playbook for pediatric clinical trial reporting
Adolescent cannabis use may follow the same pattern as alcohol use
Lifespan-extending treatments increase variation in age at time of death
From ancient myths to ‘Indo-manga’: Artists in the Global South are reframing the comic
Putting some ‘muscle’ into material design
House fires release harmful compounds into the air
Novel structural insights into Phytophthora effectors challenge long-held assumptions in plant pathology
Q&A: Researchers discuss potential solutions for the feedback loop affecting scientific publishing
A new ecological model highlights how fluctuating environments push microbes to work together
Chapman University researcher warns of structural risks at Grand Renaissance Dam putting property and lives in danger
Courtship is complicated, even in fruit flies
Columbia announces ARPA-H contract to advance science of healthy aging
New NYUAD study reveals hidden stress facing coral reef fish in the Arabian Gulf
36 months later: Distance learning in the wake of COVID-19
Blaming beavers for flood damage is bad policy and bad science, Concordia research shows
The new ‘forever’ contaminant? SFU study raises alarm on marine fiberglass pollution
Shorter early-life telomere length as a predictor of survival
Why do female caribou have antlers?
How studying yeast in the gut could lead to new, better drugs
Chemists thought phosphorus had shown all its cards. It surprised them with a new move
A feedback loop of rising submissions and overburdened peer reviewers threatens the peer review system of the scientific literature
Rediscovered music may never sound the same twice, according to new Surrey study
Ochsner Baton Rouge expands specialty physicians and providers at area clinics and O’Neal hospital
New strategies aim at HIV’s last strongholds
Ambitious climate policy ensures reduction of CO2 emissions
[Press-News.org] A study led by UPF describes how insulinomas, a rare type of pancreatic beta cell tumor, formThe cause is a change in the epigenetic pattern of the beta cells of the pancreas, which overexpress oncogenes and genes related to insulin production, thus altering their functioning. This change in pattern, a common factor in the vast majority of tumou