(Press-News.org) Researchers have recently developed a flexible-yet-sturdy morphing structure inspired by the starfish skeleton that exhibits 4D morphing features with promising applications for robotics, aviation, and medical devices.
“Starfish possess the remarkable ability to effortlessly hold themselves in any body posture by changing the stiffness of their endoskeleton,” says Raman, a PhD student in the Biological Structures and Biomimetics workgroup at Hochschule Bremen - City University of Applied Sciences Bremen, Germany.
Ossicles are calcite microstructures inside starfish bodies that are connected in a network by collagen fibres to form the endoskeleton. This strong but simple structure allows them to hold a wide variety of body postures with minimal energy use.
“We became fascinated with this biological solution to a complex engineering problem,” says Mr Raman. "Our goal was to unlock the secrets of their intricate skeleton and translate those principles into a novel material with similar remarkable properties."
Mr Raman and his team used a multidisciplinary approach for this project. By using high resolution X-ray CT scans, they visualised the starfish skeletal structures and used mathematical models (Finite Element Analysis and Multibody Simulations) to understand the complex interlinked mechanics of the skeletal components.
“For the first time, we are able to show the complex 3D structure of the starfish skeleton and the fine ultrastructure of the small ossicles,” says Mr Raman. “We have now used these insights for the biomimetic design process of our own morphing structure, incorporating rapid prototyping techniques for fabrication.”
Mr Raman and his team have used 3D printing to produce different working prototypes that can accomplish an impressive range of physical challenges. “Our patented starfish-inspired morphing structure shows self-locking, continuous bending, self-healing, and shape memory features,” says Mr Raman.
The scalability, low cost and relative ease of manufacture of this morphing structure provides many opportunities for industry applications, including robotics, aviation, and biomedical devices such as prosthetics and implants.
This study was funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) FHprofUnt 2018 program, project number 13FH150PX8 (JHD, SL) and the Hochschule Bremen PhD scholarship (R).
This research is being presented at the Society for Experimental Biology Annual Conference in Prague on the 2-5th July 2024.
END
Starfish skeleton inspires new 4D morphing structure
2024-07-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Eating more soy foods could improve thinking and attention in kids
2024-07-02
Chicago (July 2, 2024) — A new study found that school-aged children who consumed more isoflavones from soy foods exhibited better thinking abilities and attention. These findings pave the way for future research aimed at unraveling how soy foods can positively impact children's cognitive abilities.
Isoflavones are naturally occurring compounds found in various plants, particularly soybeans and soy products. Although previous research in adults has suggested that soy isoflavones can improve memory, the ...
Changes in emergency contraceptive fills after Massachusetts’ statewide standing order
2024-07-02
About The Study: The Massachusetts statewide standing order policy was associated with a 32% increase in emergency contraceptive fills at pharmacies versus comparison states. After the policy, fills for prescription-only ulipristal more than doubled and accounted for the observed increases in fills for emergency contraceptives.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Dima M. Qato, Pharm.D., M.P.H., Ph.D., email qato@usc.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.11715)
Editor’s ...
Bacteria detected in tattoo and permanent makeup inks
2024-07-02
Washington, D.C.—Researchers have detected anaerobic and aerobic bacteria in commercial tattoo and permanent makeup inks. The findings, reported in Applied and Environmental Microbiology, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology, demonstrate that the inks could be a source of human infections. The new study is particularly notable as it is the first to investigate the presence of anaerobic bacteria in commercial tattoo inks.
“Our findings reveal that unopened and sealed tattoo inks can harbor anaerobic bacteria, known to thrive in low-oxygen environments like ...
American Indian/Alaska Native patients less likely to undergo breast reconstruction
2024-07-02
Waltham — July 2, 2024 — American Indian/Alaska Native (AI/AN) women with breast cancer have consistently lower rates of breast reconstruction after mastectomy compared to non-Hispanic White women, reports a paper in the July issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Despite an upward trend in reconstruction, AI/AN women continue to be less likely to undergo breast reconstruction," comments Jane Hui, MD, MS, ...
Prosocial influencers can promote societal cooperation
2024-07-02
A modeling study suggests that influential neighbors can be as effective as despotic leaders at promoting social cooperation. Prosocial behaviors can be difficult to sustain in large societies over the long term, as people give into the temptation to defect to strategies that prioritize the wellbeing of themselves and their immediate family. Stefani Crabtree and colleagues constructed a general theoretical framework to explore how cooperation could arise and be maintained in a large society. The authors explore three possible ...
SRF launches the SYNGAP1 missense account with Nordmoe family donation
2024-07-02
Mill Valley, CA – June 18, 2024 SRF has established a dedicated account to support research regarding SYNGAP1 missense variants. This account is being launched with a $10,000 donation from Dennis and Janet Nordmoe. This is a cause close to their hearts, as their granddaughter Olivia was diagnosed with SYNGAP1-Related Disorder (SRD) caused by a missense variant earlier this year.
Missense Research: Neglected to Date
“Most diagnosed SYNGAP1-Related Disorder (SRD) patients have protein truncating variants (PTV) as opposed to missense variants. Virtually all PTVs are assumed to have the ...
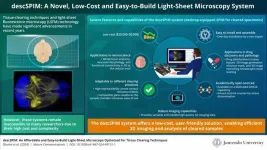
Design and development of a novel light sheet fluorescence microscope
2024-07-02
Three-dimensional (3D) imaging of organs and tissues is vital as it can provide important structural information at the cellular level. 3D imaging enables the accurate visualization of tissues and also helps in the identification of pathological conditions. However, achieving successful 3D imaging necessitates specific prerequisites, including the preparation of 'cleared' tissue samples—biological specimens rendered transparent by removing light-scattering components like lipids to ...
How to promote menstrual cups as an economic and sustainable option
2024-07-02
In recent decades, single-use plastics have pervaded modern societies, causing a significant surge in plastic pollution that exacts a heavy toll on our environment. Addressing this issue requires prioritizing sustainable alternatives to single-use plastics wherever feasible.
Disposable menstrual products are a notable contributor to plastic waste, with billions of sanitary napkins and tampons being discarded every year. Despite the availability of sustainable options like menstrual cups (MCs), consumer preference for single-use products ...
Spotted apex predator being pressured by spotted pack hunters – and it's our fault
2024-07-02
Who’s stronger? A solitary leopard or cackle of hyenas? And which is best at getting along with humans?
University of Copenhagen researchers closely studied this in a large East African natural area surrounded by rural settlements. The study demonstrates that the presence of humans has a direct impact on the competitive relationship between the two large predator species: leopards (Panthera pardus) – the iconic spotted feline and the spotted hyena (Crocuta crocuta) – a kleptoparasite and pack hunter known for its comical ...
True scale of carbon impact from long-distance travel revealed
2024-07-02
The reality of the climate impact of long-distance passenger travel has been revealed in new research from the University of Leeds.
Despite only accounting for less than 3% of all trips by UK residents, journeys of more than 50 miles (one way) are responsible for 70% of all passenger travel-related carbon emissions.
The disparity is even greater when international travel is singled-out: international journeys are only 0.4% of total trips but are responsible for 55% of emissions.
The new research, published today in the journal Nature Energy, also shows ...