(Press-News.org) Highlights:
• In late March 2024, H5N1 bird flu was detected in dairy cattle and then in raw milk.
• Researchers tested hundreds of milk products from dozens of states for the virus.
• No infectious virus was found in pasteurized milk products.
• Non-infectious traces of viral genetic material were found in 20% of samples.
Washington, D.C.—In March 2024, dairy cows in Texas were found to be infected with highly pathogenic avian flu, or H5N1 bird flu, in the first known case of the virus spreading to cattle. Since then, H5N1 has been found in about 200 animals—and 3 people—across 12 states, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The virus was soon detected in raw milk, leading researchers to investigate whether dairy products pose a risk to consumers.
“How far is the virus getting through?” asked Erica Spackman, Ph.D., a virologist at the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) in Athens, Ga. To find out, she and her collaborators tested nearly 300 milk products from 132 processors.
The researchers found no infectious virus in the samples, Spackman and her collaborators report this week in the Journal of Virology, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology. “Milk is safe,” she said. “Just like bacterial pathogens that occur in milk, or other viruses that could occur in milk, the sanitation processes that are in place are getting rid of the pathogens.”
The milk processing pipeline includes multiple layers of protection, Spackman said. Microbiological surveillance of milk products can identify pathogens, and milk from cows with mastitis or other disease conditions does not enter the food supply. Finally, heating during the pasteurization process can destroy H5N1 and other, more common bacterial pathogens.
Bird flu primarily infects and spreads among migratory birds and can be transmitted to domestic poultry, but the virus has been detected in other animals as well. Recently, those have included cats, dogs and juvenile goats, as well as a polar bear in Alaska and elephant and fur seals in the Antarctic. However, the discovery of H5N1 on dairy farms in March was a surprise—the virus had never been found in dairy cattle before.
Soon after the discovery, diagnostic testing revealed that an infectious form of the virus was present in raw milk, suggesting the virus passes from cow to milk. That finding led the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the USDA to investigate whether pasteurization effectively eliminated risks posed to consumers. Between April 18 and April 22, 2024, researchers used real-time PCR to analyze 297 samples of pasteurized retail milk products, including 23 types of products, collected from 17 states.
“We did a viability assay to detect live virus and went as sensitive as we could to get even the least little bit of virus, but couldn’t detect anything,” Spackman said. Using PCR, the researchers did identify viral genetic material in 20% of samples. “It looks like the virus is just totally inactivated,” she said.
Spackman said the new findings “give us reassurance that what we have been doing— pasteurization—is keeping us safe from what we don’t know about.”
###
The American Society for Microbiology is one of the largest professional societies dedicated to the life sciences and is composed of 32,000 scientists and health practitioners. ASM's mission is to promote and advance the microbial sciences.
ASM advances the microbial sciences through conferences, publications, certifications, educational opportunities and advocacy efforts. It enhances laboratory capacity around the globe through training and resources. It provides a network for scientists in academia, industry and clinical settings. Additionally, ASM promotes a deeper understanding of the microbial sciences to diverse audiences.
END
Pasteurization inactivates highly infectious avian flu in milk
2024-07-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
KIER develops 'viologen redox flow battery' to replace vanadium’
2024-07-03
A technology has been developed to replace the active material in large-capacity ESS 'redox flow batteries' with a more affordable substance.
*Redox Flow Battery: A term synthesized from Reduction, Oxidation, and Flow. It is a battery that stores electrical energy as chemical energy through oxidation and reduction reactions of active materials in the electrolyte at the electrode surface and converts it back to electrical energy when needed. It is capable of large-scale storage, can be used long-term through periodic replacement of the electrolyte, and its major advantage is the absence of fire risk.
Dr. Seunghae Hwang’s ...
Chemists synthesize an improved building block for medicines
2024-07-03
Chemists have overcome a major hurdle in synthesizing a more stable form of heterocycle—a family of organic compounds that are a common component of most modern pharmaceuticals.
The research, which could expand the toolkit available to drug developers in improving the safety profiles of medications and reducing side effects, was published in Science by organic chemists at the University of British Columbia (UBC), the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), and the University of Michigan.
“Azetidines ...
A genetic algorithm for phononic crystals
2024-07-03
Tokyo, Japan – The advent of quantum computers promises to revolutionize computing by solving complex problems exponentially more rapidly than classical computers. However, today's quantum computers face challenges such as maintaining stability and transporting quantum information. Phonons, which are quantized vibrations in periodic lattices, offer new ways to improve these systems by enhancing qubit interactions and providing more reliable information conversion. Phonons also facilitate better communication ...
Machine learning could aid efforts to answer long-standing astrophysical questions
2024-07-03
In an ongoing game of cosmic hide and seek, scientists have a new tool that may give them an edge. Physicists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) have developed a computer program incorporating machine learning that could help identify blobs of plasma in outer space known as plasmoids. In a novel twist, the program has been trained using simulated data.
The program will sift through reams of data gathered by spacecraft in the magnetosphere, the region of outer space strongly affected by Earth’s ...
Research spotlight: Uncovering how a cellular miscommunication leads to cognitive impairment in female patients with Alzheimer’s disease
2024-07-03
Lead author Neta Rosenzweig, PhD, of the Ann Romney Center for Neurological Diseases, and senior author Oleg Butovsky, PhD, of the Ann Romney Center and Gene Lay Institute of Immunology and Inflammation, share key messages from their paper “Sex-Dependent APOE4 Neutrophil-Microglia Interactions Drive Cognitive Impairment in Alzheimer’s Disease” published in Nature Medicine.
How would you summarize your study for a lay audience?
In this manuscript, we identify that a major genetic risk ...
AI model to improve patient response to cancer therapy
2024-07-03
A new artificial intelligence (AI) tool that can help to select the most suitable treatment for cancer patients has been developed by researchers at The Australian National University (ANU).
DeepPT, developed in collaboration with scientists at the National Cancer Institute in America and pharmaceutical company Pangea Biomed, works by predicting a patient’s messenger RNA (mRNA) profile. This mRNA - essential for protein production - is also the key molecular information for personalised cancer medicine.
According to lead author Dr Danh-Tai Hoang from ANU, when combined with a second tool called ENLIGHT, DeepPT ...
Scientists discover way to “grow” sub-nanometer sized transistors
2024-07-03
A research team led by Director JO Moon-Ho of the Center for Van der Waals Quantum Solids within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) has implemented a novel method to achieve epitaxial growth of 1D metallic materials with a width of less than 1 nm. The group applied this process to develop a new structure for 2D semiconductor logic circuits. Notably, they used the 1D metals as a gate electrode of the ultra-miniaturized transistor.
Integrated devices based on two-dimensional (2D) semiconductors, which exhibit excellent properties even at the ultimate limit of material thickness down to the atomic ...
Bath student wins national award for computer game that explores mental health
2024-07-03
A final year computer science undergraduate from the University of Bath has been named amongst the UK’s best student game developers, having won an award in the “Games with purpose” category at the Games Innovation Challenge 2024.
Salmaan Zhang competed against university and college students from across the country to win one of seven categories in the competition, which is sponsored by UNiDAYS and delivered by NSE (National Student Esports).
The challenge asked students in the UK to create the most innovative game in just eight weeks. Submitted entries were shortlisted and then judged by industry experts in several ...
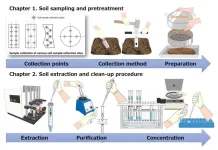
NARO developed a novel method to analyze “forever chemicals” in the soil
2024-07-03
Concern about the effects of PFAS are of increasing globally. Also there is no accurate method for analyzing multiple PFAS in soil. Hence, a team of PFAS researchers led by NARO et.al sought to develop a stable and accurate method for analyzing multicomponent PFAS in the soil (Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries -MAFF project).
Unlike the PFAS analysis method for water samples, it is difficult to ensure the extraction efficiency of the target PFAS in diverse soil samples. In Japan, there are 381 soil types, with volcanic ash soils being the predominant. Since these soils possess high carbon content, ...
Scientists pinpoint strategies that could stop cats from scratching your furniture
2024-07-03
Many cat owners are familiar with torn cushions, carpets, and couches. The feline instinct to scratch is innate but is often perceived as a behavioral problem by cat owners and sometimes leads to interventions that are not cat friendly.
Now, an international team of researchers has investigated which factors influence undesired scratching behavior in domestic cats. They published their findings in Frontiers in Veterinary Science.
“Here we show that certain factors – such as the presence of children at home, personality traits of cats, and their activity levels – significantly impact the ...