(Press-News.org) Cigarette smokers, cigar smokers, and non-smokers each have distinct personality profiles, according to a study published July 3, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Dritjon Gruda from Universidade Catolica Portuguesa, Portugal, and Jim McCleskey from Western Governors University, USA.
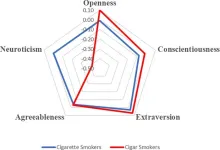
Tobacco use remains a formidable global public health challenge, responsible for more than 8 million deaths annually, including those attributed to second-hand smoke exposure. Emerging research underscores the critical role of psychological factors, including personality traits, in shaping tobacco consumption patterns. To further explore this issue, Gruda and McCleskey examined the association between Big Five personality traits (openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, and neuroticism) and cigar or cigarette smoking in a sample of 9,918 older adults across 11 European countries.
The results showed that smoking is associated with lower scores in conscientiousness and agreeableness and higher extraversion scores than not smoking. The authors speculate that relatively low conscientiousness among smokers may reflect a lack of self-discipline and disregard for long-term health risks, characteristic of more impulsive behaviors, while reduced agreeableness could help explain why smokers often persist despite societal disapproval. They also suggest that the higher extraversion observed may suggest that these individuals enjoy the social nature of smoking.
The analysis also determined personality differences between types of smokers, finding that cigar smokers tend to exhibit lower neuroticism and higher openness compared to both cigarette smokers and non-smokers, underlining that the motivations and contexts of tobacco use are varied.
These findings suggest that personality traits are antecedents of smoking behavior, with implications for targeted public health interventions and social policies aimed at combating the global tobacco epidemic. According to the authors, future research should explore these relationships in younger cohorts, potentially informing early intervention strategies that preempt the onset of smoking based on predisposition to certain personality types. Further studies could also expand the scope to include other forms of tobacco products such as chewing tobacco or more recent smoking trends such as e-cigarettes and vaping.
The authors add: “Basically what we found is: 'tell me what you smoke, and I'll tell you who you are.’”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0305634
Citation: Gruda D, McCleskey JA (2024) Hit me with your best puff: Personality predicts preference for cigar vs. cigarette smoking. PLoS ONE 19(7): e0305634. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0305634
Author Countries: Portugal, Ireland, USA
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work.
END
Smoking behavior is linked to personality traits
Smokers are on average more extraverted, but less conscientious and agreeable
2024-07-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Minority status, social origin, gender, and weight can all count against a German kid’s grades
2024-07-03
A new study done in more than 14,000 ninth graders in Germany has revealed that students experience grading bias based on their gender, body size, ethnicity and parental socio-economic status. These negative biases stack on each other, meaning that students with multiple intersectional identities get significantly lower grades than their peers regardless of their true abilities. Richard Nennstiel and Sandra Gilgen of the University of Bern and University of Zurich in Switzerland present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on July 3, ...
Dengue linked to heightened short- and long-term risk of depression in Taiwan
2024-07-03
Analysis of the medical records of nearly 50,000 people who experienced dengue fever in Taiwan suggests that this disease is associated with elevated short- and long-term risk of depression. Hsin-I Shih and colleagues of National Cheng Kung University and National Health Research Institutes, Taiwan present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases.
People may develop dengue fever after being bitten by a mosquito carrying the dengue virus. Dengue fever can be mild, but it can also progress ...
Fighting COVID-19 with a cancer drug
2024-07-03
Twelve years ago, cancer researchers at University of California San Diego identified a molecule that helps cancer cells survive by shuttling damaging inflammatory cells into tumor tissue. In new research, they show that the same molecule does the same thing in lung tissue infected with COVID-19 — and that the molecule can be suppressed with a repurposed cancer drug. The work, published in Science Translational Medicine, represents a new approach to preventing irreversible organ damage in infectious diseases like COVID-19 and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
The two key players in this scenario are inflammatory cells called myeloid ...
From ‘hit to vial’: Discovery and optimization of a promising vaccine adjuvant
2024-07-03
Many vaccines are only partially effective, have waning efficacy, or do not work well in the very young or the very old. For more than a decade, Ofer Levy, MD, PhD, and David Dowling, PhD, in the Precision Vaccines Program at Boston Children’s Hospital, have tried improving vaccines by adding compounds known as adjuvants to boost vaccine recipients’ immune responses.
Now, under a large Adjuvant Discovery Program contract from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases ...
Why do you keep your house so cold? Science says: Ask your parents
2024-07-03
Childhood home temperature and community connectedness can help predict how U.S. residents set their thermostats, offering new ways to encourage energy conservation and combat climate change, according to a study published July 3 in the open-access journal PLOS Climate by Dritjon Gruda from the National University of Ireland Maynooth and Paul Hanges from the University of Maryland.
Half of U.S. households’ annual electricity use goes to heating and cooling, but less than half of homeowners tweak their thermostats to save energy ...
Texas A&M center receives $7.6 million grant to promote research in environmental health
2024-07-03
The Texas A&M Center for Environmental Health (TiCER), a National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS) Environmental Health Sciences Core Center, will be returning to the Texas A&M School of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences (VMBS) with a $7.6 million grant for the center’s new funding cycle.
Under the new leadership of Dr. Weston Porter, a VMBS professor in the Department of Veterinary Physiology and Pharmacology, the center will promote research in four areas of environmental health — climate ...
Deep machine-learning speeds assessment of fruit fly heart aging and disease, a model for human disease
2024-07-03
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – Drosophila — commonly known as fruit flies — are a valuable model for human heart pathophysiology, including cardiac aging and cardiomyopathy. However, a choke point in evaluating fruit fly hearts is the need for human intervention to measure the heart at moments of its largest expansion or its greatest contraction, measurements that allow calculations of cardiac dynamics.
Researchers at the University of Alabama at Birmingham now show a way to significantly cut the time needed ...
U.S. Department of Energy issues request for proposals for contractor to manage and operate Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility
2024-07-03
Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced the issuance of a Request for Proposals (RFPs) for the competitive selection of a management and operating contractor for the Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility (TJNAF).
TJNAF is a DOE national laboratory and DOE-sponsored Federally Funded Research and Development Center that has a mission focused on delivering breakthrough science and technology in nuclear physics.
DOE expects to award the contract before the current agreement with Jefferson Science Associates, LLC expires on May 31, 2025, allowing for an anticipated three-month transition. DOE expects the selected ...
Survivorship standards help address the distinct needs of adult cancer survivors
2024-07-03
Key Takeaways
More people are surviving cancer than ever before and living longer. This growing population of adult cancer survivors requires distinct survivorship services focused on long-term well-being.
Survey study demonstrates the value of American College of Surgeons’ survivorship accreditation standards, though specialized services in fertility and sexual health are less accessible.
CHICAGO — With the number of adult cancer survivors in the United States expected to reach 23 million by 2032,* the long-term needs of this ...
Mighty floods of the Nile River during warmer and wetter climates
2024-07-03
Summary
Global warming as well as recent droughts and floods threaten large populations along the Nile Valley. Understanding how such a large river will respond to an invigorated hydrological cycle is therefore a pressing issue. Insights can be gained by studying past periods with wetter and warmer conditions, such as the North African Humid Period eleven to six thousand years ago. A research team of the German Research Centre for Geosciences GFZ, led by Cécile Blanchet, together with colleagues ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Heart attack deaths rose between 2011 and 2022 among adults younger than age 55
Will melting glaciers slow climate change? A prevailing theory is on shaky ground
New treatment may dramatically improve survival for those with deadly brain cancer
Here we grow: chondrocytes’ behavior reveals novel targets for bone growth disorders
Leaping puddles create new rules for water physics
Scientists identify key protein that stops malaria parasite growth
Wildfire smoke linked to rise in violent assaults, new 11-year study finds
New technology could use sunlight to break down ‘forever chemicals’
Green hydrogen without forever chemicals and iridium
Billion-DKK grant for research in green transformation of the built environment
For solar power to truly provide affordable energy access, we need to deploy it better
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
Scientists create the most detailed molecular map to date of the developing Down syndrome brain
Nutrient uptake gets to the root of roots
Aspirin not a quick fix for preventing bowel cancer
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
Solved: New analysis of Apollo Moon samples finally settles debate about lunar magnetic field
University of Birmingham to host national computing center
Play nicely: Children who are not friends connect better through play when given a goal
Surviving the extreme temperatures of the climate crisis calls for a revolution in home and building design
The wild can be ‘death trap’ for rescued animals
New research: Nighttime road traffic noise stresses the heart and blood vessels
Meningococcal B vaccination does not reduce gonorrhoea, trial results show
[Press-News.org] Smoking behavior is linked to personality traitsSmokers are on average more extraverted, but less conscientious and agreeable