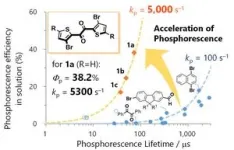
(Press-News.org) A research team led by Osaka University discovered that the new organic molecule thienyl diketone shows high-efficiency phosphorescence. It achieved phosphorescence that is more than ten times faster than traditional materials, allowing the team to elucidate this mechanism.
Osaka, Japan – Phosphorescence is a valuable optical function used in applications such as organic EL displays (OLEDs) and cancer diagnostics. Until now, achieving high-efficiency phosphorescence without using rare metals such as iridium and platinum has been a significant challenge. Phosphorescence, which occurs when a molecule transitions from a high-energy state to a low-energy state, often competes with non-radiative processes where the molecule loses energy as heat.
This competition can lead to slow phosphorescence and lower efficiency. While previous research indicated that incorporating certain structural elements into organic molecules could speed up phosphorescence, these efforts have not matched the speed and efficiency of rare metal-based materials.
The research team’s breakthrough with the new organic molecule thienyl diketone represents a significant advancement in the field. Yosuke Tani, senior author of the study, remarked, "We discovered this molecule by chance and initially did not understand why it demonstrated such superior performance. However, as our research progressed, we began to connect the pieces and deepen our understanding."
"Our research has led to a clearer understanding of the mechanism behind this molecule’s performance than any previous organic phosphorescent material,” explains Dr. Tani. “Nonetheless, we believe there is still much to explore, and we are excited about its potential applications."
This research provides new design guidelines for developing organic phosphorescent materials that do not rely on rare metals, offering the potential to surpass and replace these materials in various applications. The findings promise significant advancements in the fields of OLEDs, lighting, and medical diagnostics, among others.
###
The article, “Fast, efficient, narrowband room-temperature phosphorescence from metal-free 1,2-diketones: rational design and mechanism,” was published in Chemical Science at DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SC02841D
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and is now one of Japan's leading comprehensive universities with a broad disciplinary spectrum. This strength is coupled with a singular drive for innovation that extends throughout the scientific process, from fundamental research to the creation of applied technology with positive economic impacts. Its commitment to innovation has been recognized in Japan and around the world. Now, Osaka University is leveraging its role as a Designated National University Corporation selected by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to contribute to innovation for human welfare, sustainable development of society, and social transformation.
Website: https://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en
END
New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications
2024-07-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
International summit of experts in nuclear physics at the University of Barcelona
2024-07-04
More than two hundred international experts will take part in the 10th International Conference on Quarks and Nuclear Physics (QNP2024), a scientific summit organized by the UB Institute of Cosmos Sciences (ICCUB), which will be held in the Aula Magna of the Faculty of Biology at the University of Barcelona from 8 to 12 July. This meeting, hosted by the UB for the first time, will bring together world experts in the fields of nuclear physics and hadronic physics to discuss the latest advances in theory, experimentation and technology ...
Clever pupils don’t need to attend academically selective schools to thrive, study finds
2024-07-04
Findings published in a new peer-reviewed paper in the British Journal of Educational Studies challenges the idea that academically selective schools are necessary for clever pupils to achieve good outcomes.
Selective schools are government-funded schools that enrol only the highest performing students. Pupils take a standardized entrance exam, from which the best-scoring are enrolled.
Some argue that selective schools are necessary for bright pupils to reach their full academic potential. Selective schools can ...
Searching for dark matter with the coldest quantum detectors in the world
2024-07-04
One of the greatest mysteries of science could be one step closer to being solved.
Approximately 80% of the matter in the universe is dark, meaning that it cannot be seen. In fact, dark matter is passing through us constantly – possibly at a rate of trillions of particles per second.
We know it exists because we can see the effects of its gravity, but experiments to date have so far failed to detect it.
Taking advantage of the most advanced quantum technologies, scientists from Lancaster University, the University of Oxford, and Royal Holloway, ...
UNSW Sydney's Dr Vaishnavi Ananthanarayanan receives RMS Award for Life Sciences
2024-07-04
This accolade highlights her pioneering research in the use of a diverse array of advanced microscopy techniques to uncover fundamental biophysical processes.
Currently holding a prestigious EMBL (European Molecular Biology Laboratory) Australia Group Leader fellowship, Dr Ananthanarayanan leads one of the largest and most dynamic research group in the EMBL Australia Node in Single Molecule Science, based in the Department of Molecular Medicine in the School of Biomedical Sciences.
Her research, which focuses on motor proteins and cytoskeleton dynamics, has set new standards ...
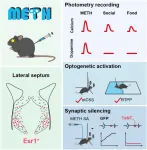
Researchers unveils a critical role of the lateral septum in drug addiction
2024-07-04
Recently, a research team led by Dr. ZHU Yingjie from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences has published a study in Neuron, the study presents a comprehensive transcriptional profile of the lateral septum (LS) at the single-cell level, elucidating the spatial distribution of its major neuronal types. The study shows that neurons expressing estrogen receptor 1 (LSEsr1), predominantly located in the ventral subregion of LS, play a crucial role in reward-seeking and methamphetamine (METH) addiction.
In 1954, psychologists Olds and Milner discovered the brain's reward system through intracranial ...
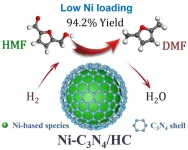
Efficient hydrogenolysis of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural over Ni-C3N4 catalysts
2024-07-04
Utilization of biomass as the basic feedstock for the production and chemicals and energy storage has been demonstrated to be an important alternative to achieve sustainable society, which has attracted increasing interests in both academic and industrial communities for decades. 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF), one of the most important bio-based platform compounds, could serve as a bridge feedstock between biomass resources and chemicals. It is possible to synthesize a series of high-value added chemicals from HMF through hydrogenation, ...
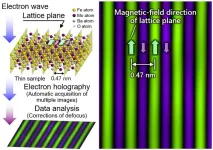
Hitachi’s holography electron microscope attains unprecedented resolution
2024-07-04
Tokyo, Japan—A research team from Japan, including scientists from Hitachi, Ltd. (TSE 6501, Hitachi), Kyushu University, RIKEN, and HREM Research Inc. (HREM), has achieved a major breakthrough in the observation of magnetic fields at unimaginably small scales. In collaboration with National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) and the National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS), the team used Hitachi’s atomic-resolution holography electron microscope—with a newly developed image acquisition technology and defocus correction algorithms—to visualize ...
An innovative test to diagnose chagas disease in newborns
2024-07-04
An innovative test that combines a DNA extraction system inspired by a modified 3D printer (PrintrLab) with loop-mediated isothermal molecular amplification (LAMP) could be used to detect T. cruzi infection -responsible for Chagas disease- in newborns. This is the conclusion of a proof-of-concept study conducted in the Bolivian Chaco, an endemic area for Chagas disease. The study was coordinated by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by "la Caixa" ...
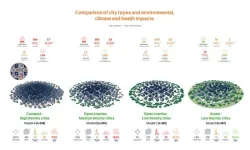
Compact cities have lower carbon emissions, but poorer air quality, less green space and higher mortality rates
2024-07-04
What types of cities exist in Europe and which are more favourable in terms of human health, environmental quality and carbon footprint? To answer these questions, a study led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation, has analysed 919 European cities. The research, published in The Lancet Planetary Health, identified four basic urban configurations on the continent: compact-high density cities, open lowrise-medium density cities, open lowrise-low density cities and green-low density cities. The results show that greener and less densely populated ...
Cuts to processed meat intake bring a range of health benefits
2024-07-04
Reducing consumption of processed meat by around one-third could prevent more than 350,000 cases of diabetes in the US over 10 years, a study suggests.
Cutting US adults’ processed meat intake by 30 per cent – the equivalent of around 10 slices of bacon a week – would also lead to tens of thousands of fewer cases of cardiovascular disease and colorectal cancer, researchers say.
A team from the University of Edinburgh’s Global Academy of Agriculture and Food Systems together with the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, has developed ...