(Press-News.org) As a leader in innovative health solutions, George Mason University’s College of Public Health received a National Institutes of Health (NIH) AIM-AHEAD program grant to pilot an artificial intelligence (AI) chatbot for Black and African Americans with depression. Health Informatics Professor Farrokh Alemi will enhance his first-of-its-kind, evidence-based artificial intelligence tool to address the medication needs of African Americans with depression.
The existing AI tool recommends antidepressants for 16,775 general-population patient subgroups, each representing a unique combination of medical history. For each of these subgroups, the current project will analyze the effectiveness and appropriateness of the recommendations for African Americans, using the NIH All of Us database and existing published literature.
To the researchers' knowledge, this is the first research focused on developing and evaluating an antidepressant recommendation system for Black and African American people.
“Antidepressant medications are a first-line treatment for depression; however, a majority of depressed patients do not experience improvement with their first antidepressant. Additionally, minority populations, including Black and African Americans, are not well represented in antidepressant studies, contributing to reduced antidepressant effectiveness in these populations,” said Alemi. “There is a significant need to synthesize available evidence regarding antidepressant effectiveness and provide personalized treatment recommendations, and this project addresses a major gap in the management of Black and African Americans with depression.”
Researchers will develop a Knowledge-enhanced Antidepressant Recommendation Dialogue System (KARDS), which will engage users in a back-and-forth conversation to acquire the patient information needed to identify the appropriate antidepressant medication. The AI will provide the patient with a list of recommended medications, list of the relevant studies, and an explanation for the medication decisions. The system will automatically send the patient’s clinician a brief point-of-care recommendation and explanation, with an option to examine a complete record of the conversation and the supporting evidence.
“Chatbots—or patient-facing dialogue systems like the one we will create—hold transformative potential for the health care sector and are increasingly prominent in psychiatric applications, predominantly through therapy-bot implementations,” said Alemi. “Our chatbot will help improve the detailed, time-consuming, medical history intake process, and provide point-of-care summary and prescription recommendations to the patients’ clinicians. The chatbot will make patients more comfortable because the natural language modality provides an intuitive, empathetic, stigma-free interface.”
Once the AI chatbot is developed, the team will test the dialogue system with Black and African American patients to evaluate system functionality and user preferences. Additionally, the project will train a Black or African American doctoral or master’s student in AI, expanding the available workforce and building the community’s capacity to address AI.
Alemi will lead the research team, which includes Janusz Wojtusiak, a George Mason professor of Health Informatics and the director of the Machine Learning and Inference Laboratory, and Kevin Lybarger, a George Mason assistant professor in the Department of Information Sciences and Technology in the College of Engineering and Computing. All three members have collaborated previously to diagnose COVID at home from presenting symptoms.
The $70,906 grant is part of the NIH’s AIM-AHEAD (Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning Consortium to Advance Health Equity and Researcher Diversity) program, which aims “to establish mutually beneficial and coordinated partnerships to increase the participation and representation of researchers and communities currently underrepresented in the development of AI/machine learning models and enhance the capabilities of this emerging technology, beginning with electronic health record data.”
END
College of Public Health receives NIH grant to pilot AI chatbot for African Americans with depression
George Mason University Researcher to pilot first-of-its-kind, evidence-based artificial intelligence tool to address the medication needs of Black and African American people with depression
2024-07-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
RCMAR Annual Meeting promotes mentorship and research on aging
2024-07-08
The latest Annual Meeting convened by the Resource Centers for Minority Aging Research (RCMAR) National Coordinating Center, held in Arlington, Virginia, from June 26 to 28, centered on the theme of transforming diverse aging research through inspiring and mentoring scientists.
Current and former RCMAR scientists presented research findings from completed pilot studies and progress updates for ongoing research. The meeting included several professional development sessions for the scientists and members of RCMAR ...
Exploring distress experiences of patients with sickle cell disease
2024-07-08
COLUMBUS, Ohio – While distress is well-documented in patients with sickle cell disease, sources of distress and how patients manage distress have not been well explored.
“Our study found that the most profound source of distress for patient with sickle cell disease in a home visit program was anticipating and going to acute care centers to manage their acute pain,” said senior study author Maryanna Klatt, PhD, director of the Center for Integrative Health at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center.
Study findings are published ...
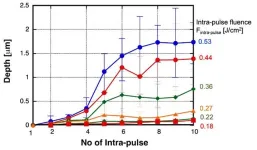
Super-resolution machining of single crystalline sapphire by GHz burst mode femtosecond laser-induced plasma assisted ablation
2024-07-08
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2024.240029 , discusses super-resolution machining of single crystalline sapphire by GHz burst mode femtosecond laser-induced plasma assisted ablation.
GHz burst-mode femtosecond (fs) laser, which emits a series of pulse trains (burst pulse) with extremely short intervals of several hundred ps, offers distinct characteristics in materials processing as compared with conventional fs laser (single-pulse mode). The authors of this article have demonstrated that the GHz burst mode fs laser greatly improves ablation efficiency, quality and speed. GHz burst mode fs laser was further applied ...
Boosting UV light absorption in 2D semiconductor with quantum dot hybrids for enhanced light emission
2024-07-08
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oes.2024.240002 , discusses boosting UV Light Absorption in 2D Semiconductor with quantum dot hybrids for enhanced light emission.
Two-dimensional (2D) transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) have emerged as a promising class of materials due to their remarkable properties. These materials, such as monolayer tungsten disulfide (1L-WS2), are just a few atoms thick, yet they possess intriguing electronic and optical characteristics that make them highly attractive for various applications, from flexible electronics ...
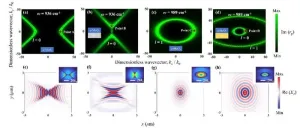
The forbidden propagation of hyperbolic phonon polaritons and applications in near-field energy transport
2024-07-08
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oes.2024.230053 , discusses forbidden propagation of hyperbolic phonon polaritons and applications in near-field energy transport.
Manipulating photons on the nanoscale to develop integrated and miniaturized optoelectronic devices as well as photonic chips has been a strong pursuit of the nanophotonics community. Among them, phonon polaritons supported by two-dimensional layered van der Waals (vdW) materials, which have emerged in recent years, have attracted much attention by virtue of their ultra-long lifetimes, ultr-low losses, and strong confinement capabilities, ...
Researchers find common immune system mechanism between pregnancy, cancer
2024-07-08
For more information, contact:
Nicole Fawcett, nfawcett@umich.edu
734-764-2220
For immediate release
ANN ARBOR, Michigan — To understand why some cancers successfully circumvent the immune system to grow unchecked, researchers turned to pregnancy.
“In pregnancy, the immune system does not reject the growing fetus, so we know there must be mechanisms active in the placenta. In cancer, it’s the same thing: the growing tumor is not rejected by the immune system. It means the cancer cells have developed strategies to suppress immune rejection, same as in pregnancy,” said Weiping ...
UC San Diego health offers novel gene therapy for bladder cancer
2024-07-08
UC San Diego Health is the first health system in San Diego County to offer a new bladder-saving gene therapy to treat localized bladder cancer.
The novel treatment is the first and only FDA-approved gene therapy delivered directly into the bladder for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC). Called nadofaragene firadenovec (Adstiladrin), the gene therapy addresses an unmet need for patients who are no longer responding to the longstanding first line of defense — bacillus calmette-guerin (BCG), a bacteria-based immunotherapy for cancer management. While BCG is a common first therapy, it can eventually stop working, ultimately leading to complete bladder removal.
The American ...
SETI Institute awards its first research and education innovation grants
2024-07-08
July 8, 2024, Mountain View, CA – Today, the SETI Institute announced the first projects it will fund with a new program to Support Technology, Research, Innovation, Development, and Education programs – or STRIDE. The SETI Institute established the $500K STRIDE fund for SETI Institute researchers and EOC (Education, Outreach, and Communications) professionals to develop innovative research and education proposals. The first five grants awarded will support projects that:
analyze Earth’s colors and climate to create detectors for studying exoplanets
develop a multi-backend capability for ...
Study reveals environmental impact of artificial sweeteners
2024-07-08
The human body’s inability to break down sucralose, an artificial sweetener found in many zero-calorie food and drink products, is well established by scientific research. The compound is so stable that it escapes wastewater treatment processing and is in drinking water and aquatic environments.
“We can't break down sucralose, and a lot of microorganisms can't break it down, either, because it's a really tough molecule that doesn't degrade easily. So there are a lot of questions about how it is affecting the environment ...
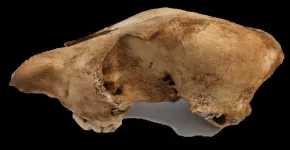
Ancient dingo DNA shows modern dingoes share little ancestry with modern dog breeds
2024-07-08
DNA from fossilised dingo remains going back 2746 years compared with modern dingoes’
Dingos arrived in Australia more than 3000 years ago
K’gari dingoes have no domestic dog ancestry – they are pure dingo
Co-lead author, paleogeneticist Dr Sally Wasef, from QUT’s School of Biomedical Sciences said this dataset gave a rare glimpse into the pre-colonial genetic landscape of dingoes, free from any mixing with modern dog breeds.
“Consequently, are behaviourally, genetically, and anatomically distinct from domestic dogs,” Dr Wasef said.
“Modern-day dingoes’ ancestors arrived in Australia more than 3000 years ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
[Press-News.org] College of Public Health receives NIH grant to pilot AI chatbot for African Americans with depressionGeorge Mason University Researcher to pilot first-of-its-kind, evidence-based artificial intelligence tool to address the medication needs of Black and African American people with depression