(Press-News.org) For those living in cities, space to play sports outside can be a scarcity. Recently, natural grass in parks or public sports courts has often been replaced with more durable artificial turf to allow heavy consecutive use.
There are, however, downsides to this practice, both for people and for cities as a whole. Now, scientists in the Netherlands have set out to change that by integrating a subsurface water storage and capillary irrigation system under artificial turf sports fields.
“Here we show that including a subsurface water storage and capillary irrigation system in artificial turf fields can lead to significantly lower surface temperatures compared to conventional artificial turf fields,” said Dr Marjolein van Huijgevoort, a hydrologist at KWR Water Research Institute and first author of the article published in Frontiers in Sustainable Cities. “With circular on-site water management below the field, a significant evaporative cooling effect is achieved.”
Cooler turf and air
The artificial turf and subbase system includes an open water storage layer directly underneath the artificial turf and shockpad. In this water layer, rainwater is stored. This water retention system contains cylinders that transport the stored water back up to the surface of the artificial turf, where it evaporates.
“The process of evaporative cooling and capillary rise is controlled by natural processes and weather conditions, so water only evaporates when there is demand for cooling,” van Huijgevoort explained.
Conventional artificial turf can reach surface temperatures of up to 70°C on sunny days. These temperatures are high enough to cause burn injuries and trigger heat related illnesses, ranging from mild rashes to potentially life-threatening conditions like heat stroke.
In a field experiment conducted in Amsterdam, the researchers found that when conventional turf was replaced with the self-cooling turf, temperatures dropped. They reported that on a particularly hot day in June 2020, the cooled turf reached a surface temperature of 37°C – just 1.7°C higher than natural grass – whereas surface temperatures of the conventional artificial turf reached 62.5°C.
Above the plots, temperatures also differed. “We found lower air temperatures 75cm above the cooled plots compared to conventional artificial turf fields, especially during the night,” said van Huijgevoort. “This is a first indication that the cooled plots contribute less to the urban heat island effect.”
Artificial with natural advantages
The cooling turf combines advantages of artificial turf and natural grass: It is durable, keeps itself cool, and offers a healthy environment to play sports. It can also store almost as much rainwater as natural grass. The field’s rainwater retention capacity also reduces stormwater drainage, which helps mitigate urban flooding. During periods when it does not rain enough, extra water can be added directly into the system. Alternatively, it could be watered like natural grass.
Installation costs, however, can be up to twice as expensive as for conventional artificial turf. The researchers said that a full-scale cost-benefit analysis should be undertaken to find out the true value of the investment.
Further research also needs to confirm how cooling turf could impact the surrounding area and cities as a whole. Learning more about the benefits of the turf in different climates and using different storage sizes, materials, and infills is also necessary to find the optimal combination, the researchers pointed out.
Initial results, however, are promising. “People in urban areas, especially children, have a growing need for sport and play facilities,” van Huijgevoort concluded. “With this work we show the benefits of the subsurface water storage and capillary irrigation system without negative effects of artificial turf fields.”
END
Water stored under artificial turf could make cities cooler and safer to play in
Artificial turf with an integrated subsurface water storage and irrigation system could make sports courts safer and cooler while helping cities with water and flood management
2024-07-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How a plant app helps identify the consequences of climate change
2024-07-09
Plants are known to respond to seasonal changes by budding, leafing, and flowering. As climate change stands to shift these so-called phenological stages in the life cycle of plants, access to data about phenological changes – from many different locations and in different plants – can be used to draw conclusions about the actual effects of climate change. However, conducting such analyses require a large amount of data and data collection of this scale would be unthinkable without the help of citizen scientists. “The problem is that the quality of the data suffers when fewer people engage ...
Tomato triumph: genetic key to chill-proof crops unveiled
2024-07-09
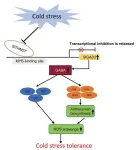
In a significant advancement for agricultural biotechnology, researchers have identified a genetic mechanism that enhances the cold tolerance of tomatoes. This breakthrough is pivotal for cultivating crops in cooler climates, ensuring stable yields and bolstering global food security. The study focuses on the SlGAD2 gene, which, when overexpressed, elevates the plant's γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) levels, boosts antioxidant activities, and stimulates anthocyanin production, collectively improving cold resilience.
Tomatoes play a vital role in global agriculture but are susceptible ...
Scientists exploring potential new treatments for glioblastoma
2024-07-09
A new approach to treating the most malignant type of brain cancer – glioblastoma – has shown strong promise in pre-clinical settings, raising hopes of increasing current average survival rates beyond 18 months.
Targeted alpha therapy (TAT) is emerging as a potential additional treatment for glioblastoma (GB), a disease which has confounded oncologists for decades due to its aggressive nature and strong resistance to existing therapies.
The current standard treatment for GB is surgery, followed by external beam radiotherapy and the chemotherapy drug, temozolomide. However, survival rates of less than 5-10% at five years have prompted researchers to explore ...
Tomato Time capsule: postharvest treatments and their role in ripening dynamics
2024-07-09
Tomato fruit ripening, a process initiated by key gene demethylation, is significantly influenced by postharvest handling practices. These practices, while extending shelf life, can alter ripening dynamics and affect fruit quality. This study explores the impact of various postharvest treatments on the fruit's methylome and transcriptome, shedding light on how physiological and molecular changes interplay to determine the final quality of tomatoes.
Postharvest handling practices, such as refrigeration and modified atmosphere storage, are commonly used to extend the shelf life of tomatoes. However, these methods can negatively impact fruit quality, ...
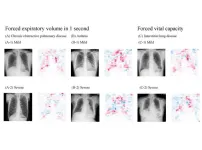
Innovative, highly accurate AI model can estimate lung function just by using chest x-rays
2024-07-09
If there is one medical exam that everyone in the world has taken, it’s a chest x-ray. Clinicians can use radiographs to tell if someone has tuberculosis, lung cancer, or other diseases, but they can’t use them to tell if the lungs are functioning well.
Until now, that is.
In findings published in The Lancet Digital Health, a research group led by Associate Professor Daiju Ueda and Professor Yukio Miki at Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Medicine has developed an artificial intelligence model that can estimate lung function from chest radiographs with high accuracy.
Conventionally, ...
University of Cincinnati, Swing Therapeutics study: Mobile app therapy leads to significant improvement in fibromyalgia management
2024-07-09
New research led by the University of Cincinnati and Swing Therapeutics found that a self-guided smartphone-based behavioral therapy led to significant improvements for patients with fibromyalgia.
The multicenter, randomized controlled trial tested Stanza, a smartphone app that delivers acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), a type of cognitive behavioral therapy recommended by international clinical guidelines for fibromyalgia management, with the results of the study published July 8 in The Lancet.
Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain condition that affects an estimated 10 million Americans, a majority ...
Anxiety and depression a more common consequence of cardiac arrest for women than for men
2024-07-09
Cardiac arrests affect around 350,000 people in Europe each year with less than 20% surviving an out of hospital cardiac arrest. Research from Amsterdam UMC shows that women who survive consequently have greater rates of anxiety and depression. Furthermore, both men and women are affected by negative population-wide changes in socioeconomic status as they age. Suggesting more support is necessary for those who have suffered a cardiac arrest. These results are published today in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality & Outcomes.
"We looked at many factors to determine the five-year consequences of a cardiac arrest, here we saw, most significantly, a 50% ...
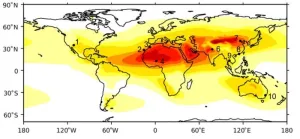
Engine wear risk as planes swallow more dust waiting to land
2024-07-09
Planes flying into one of the world's busiest airports are ingesting around 10kg of dust per 1,000 flights - with most of this dust ingested while they are waiting to land, new research has revealed.
Scientists used 17 years of ECMWF atmospheric data and data from the CALIPSO satellite to calculate the quantity of sand and dust swallowed by jet engines at ten major international airports located in desert regions or subject to seasonal dust storms.
The global study, published today (Tuesday, 9 July) in the journal Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, ...
Coral reefs: battlegrounds for survival in a changing climate
2024-07-09
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Coral reefs, those vibrant underwater cities, stand on the precipice of collapse. While rising ocean temperatures and coral bleaching grab headlines, a new essay in Current Biology reveals a hidden layer of complexity in this fight for survival: the often-overlooked roles of the reefs’ smallest inhabitants.
Scientists have long understood the vital partnership between corals and their symbiotic algae, but work by researchers at UC Santa Barbara and University of Georgia highlights how the fate of entire reefs may hinge ...
Study: Telehealth builds autonomy, trust in treating addiction
2024-07-09
Even as the nation’s opioid epidemic continues to ravage families and communities nationwide — with more than 100,000 Americans dying of drug overdoses each year — stigma remains a barrier for many people accessing treatment for addiction.
A new study from Oregon Health & Science University suggests telehealth may be an important antidote to overcoming stigma and reducing barriers for people seeking out the treatment they need.
The study, published recently in the Harm Reduction Journal, compiled in-depth interviews with 30 people treated for substance use disorder ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Water stored under artificial turf could make cities cooler and safer to play inArtificial turf with an integrated subsurface water storage and irrigation system could make sports courts safer and cooler while helping cities with water and flood management