(Press-News.org) Many women treated for breast cancer using taxanes, a type of cytostatic drug, often experience side effects in the nervous system. Researchers at Linköping University have developed a tool that can predict the risk level for each individual. The tool could help doctors adapt treatment to avoid persistent side effects in those at the greatest risk.
More and more people are becoming cancer survivors. But even if they have survived the disease, an increasing number still suffer from the side effects of cancer treatment. In a recent study from Linköping University, researchers studied the side effects of taxanes, a chemotherapy drug used to prevent breast cancer recurrence. The drawback of the treatment is that some patients suffer nerve damage as a side effect.
“Side effects in the form of nerve damage are very common after treatment with taxanes for breast cancer, and they often persist for several years. For those affected it is extremely stressful, and it has a major impact on quality of life. So it is a major clinical problem, which has received more attention in recent years, but there has been no way to know which individuals are at greatest risk of side effects”, says Kristina Engvall, who recently completed her PhD at Linköping University and is a doctor at the oncology clinic at Ryhov County Hospital in Jönköping.
The researchers began by carefully surveying side effects in patients treated for breast cancer with either docetaxel or paclitaxel, the two most common taxane drugs. Between two and six years had passed since treatment. 337 patients were asked to describe the severity of the nerve damage they experienced, or peripheral neuropathy as it is also called. Most common was cramps in the feet, which more than one in four patients had. Other side effects included difficulty opening a jar, numbness in feet, tingling in feet and difficulty climbing stairs.
The researchers sequenced the patients' genes and then built models that link genetic characteristics to various side effects of the taxane treatment. This allows the models to predict the risk of nerve damage. This type of model, known as a prediction model, has not previously existed for taxane-induced peripheral neuropathy. The researchers succeeded in modeling the risk of persistent numbness and tingling in feet.
The two models were able to separate the patients into two clinically relevant groups: one with a high risk of persistent side effects, and one that corresponded to the frequency of peripheral neuropathy in the normal population. The researchers used two-thirds of the data to train the models through machine learning. They were then able to use the remaining third of the patients to validate the models, which was found to work very well. Validating that the models also work in a different group is an important step.
“This is the first time a prediction model has been developed that can predict the risk of nerve damage from taxane treatment. Women who have been treated with taxanes after breast cancer surgery make up a very large group in healthcare worldwide, so this is a major and clinically relevant problem”, says Henrik Gréen, professor at Linköping University, who led the study published in the journal npj precision oncology.
“This can be a tool to individualise treatment, and not only to look at the benefits, but also to look at the risks for the individual patient. Today we are so good at treating breast cancer that we need to focus more on the risk of complications and side effects that affect the patient long after treatment”, says Kristina Engvall.
In the long term, the prediction model could be adopted as routine in healthcare. But first, research is needed in order to find out whether the prediction model also works well in other population groups than the Swedish population.
“It also emerged that three of the five symptoms we focused on are so biologically complex that we could not model them. These include, for example, difficulty opening cans. Opening a can involves both motor and sensory nerves, which makes it very difficult to predict which individuals are at greatest risk of developing that symptom”, says Henrik Gréen.
The study was funded with support from, among others, the Swedish Cancer Society, ALF funding, the Medical Research Council of Southeast Sweden (FORSS), and Futurum in Region Jönköping.
The article: Prediction models of persistent taxane-induced peripheral neuropathy among breast cancer survivors using whole-exome sequencing, Kristina Engvall, Hanna Uvdal, Niclas Björn, Elisabeth Åvall-Lundqvist and Henrik Gréen, npj precision oncology, published online 16 May 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41698-024-00594-x
END
Nerve damage from breast cancer treatment can be predicted
2024-07-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Water stored under artificial turf could make cities cooler and safer to play in
2024-07-09
For those living in cities, space to play sports outside can be a scarcity. Recently, natural grass in parks or public sports courts has often been replaced with more durable artificial turf to allow heavy consecutive use.
There are, however, downsides to this practice, both for people and for cities as a whole. Now, scientists in the Netherlands have set out to change that by integrating a subsurface water storage and capillary irrigation system under artificial turf sports fields.
“Here we show that including a subsurface water storage and capillary ...
How a plant app helps identify the consequences of climate change
2024-07-09
Plants are known to respond to seasonal changes by budding, leafing, and flowering. As climate change stands to shift these so-called phenological stages in the life cycle of plants, access to data about phenological changes – from many different locations and in different plants – can be used to draw conclusions about the actual effects of climate change. However, conducting such analyses require a large amount of data and data collection of this scale would be unthinkable without the help of citizen scientists. “The problem is that the quality of the data suffers when fewer people engage ...
Tomato triumph: genetic key to chill-proof crops unveiled
2024-07-09
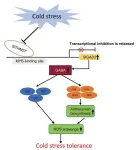
In a significant advancement for agricultural biotechnology, researchers have identified a genetic mechanism that enhances the cold tolerance of tomatoes. This breakthrough is pivotal for cultivating crops in cooler climates, ensuring stable yields and bolstering global food security. The study focuses on the SlGAD2 gene, which, when overexpressed, elevates the plant's γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) levels, boosts antioxidant activities, and stimulates anthocyanin production, collectively improving cold resilience.
Tomatoes play a vital role in global agriculture but are susceptible ...
Scientists exploring potential new treatments for glioblastoma
2024-07-09
A new approach to treating the most malignant type of brain cancer – glioblastoma – has shown strong promise in pre-clinical settings, raising hopes of increasing current average survival rates beyond 18 months.
Targeted alpha therapy (TAT) is emerging as a potential additional treatment for glioblastoma (GB), a disease which has confounded oncologists for decades due to its aggressive nature and strong resistance to existing therapies.
The current standard treatment for GB is surgery, followed by external beam radiotherapy and the chemotherapy drug, temozolomide. However, survival rates of less than 5-10% at five years have prompted researchers to explore ...
Tomato Time capsule: postharvest treatments and their role in ripening dynamics
2024-07-09
Tomato fruit ripening, a process initiated by key gene demethylation, is significantly influenced by postharvest handling practices. These practices, while extending shelf life, can alter ripening dynamics and affect fruit quality. This study explores the impact of various postharvest treatments on the fruit's methylome and transcriptome, shedding light on how physiological and molecular changes interplay to determine the final quality of tomatoes.
Postharvest handling practices, such as refrigeration and modified atmosphere storage, are commonly used to extend the shelf life of tomatoes. However, these methods can negatively impact fruit quality, ...
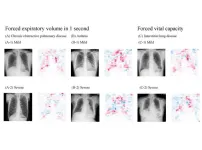
Innovative, highly accurate AI model can estimate lung function just by using chest x-rays
2024-07-09
If there is one medical exam that everyone in the world has taken, it’s a chest x-ray. Clinicians can use radiographs to tell if someone has tuberculosis, lung cancer, or other diseases, but they can’t use them to tell if the lungs are functioning well.
Until now, that is.
In findings published in The Lancet Digital Health, a research group led by Associate Professor Daiju Ueda and Professor Yukio Miki at Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Medicine has developed an artificial intelligence model that can estimate lung function from chest radiographs with high accuracy.
Conventionally, ...
University of Cincinnati, Swing Therapeutics study: Mobile app therapy leads to significant improvement in fibromyalgia management
2024-07-09
New research led by the University of Cincinnati and Swing Therapeutics found that a self-guided smartphone-based behavioral therapy led to significant improvements for patients with fibromyalgia.
The multicenter, randomized controlled trial tested Stanza, a smartphone app that delivers acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), a type of cognitive behavioral therapy recommended by international clinical guidelines for fibromyalgia management, with the results of the study published July 8 in The Lancet.
Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain condition that affects an estimated 10 million Americans, a majority ...
Anxiety and depression a more common consequence of cardiac arrest for women than for men
2024-07-09
Cardiac arrests affect around 350,000 people in Europe each year with less than 20% surviving an out of hospital cardiac arrest. Research from Amsterdam UMC shows that women who survive consequently have greater rates of anxiety and depression. Furthermore, both men and women are affected by negative population-wide changes in socioeconomic status as they age. Suggesting more support is necessary for those who have suffered a cardiac arrest. These results are published today in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality & Outcomes.
"We looked at many factors to determine the five-year consequences of a cardiac arrest, here we saw, most significantly, a 50% ...
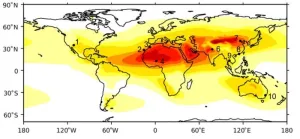
Engine wear risk as planes swallow more dust waiting to land
2024-07-09
Planes flying into one of the world's busiest airports are ingesting around 10kg of dust per 1,000 flights - with most of this dust ingested while they are waiting to land, new research has revealed.
Scientists used 17 years of ECMWF atmospheric data and data from the CALIPSO satellite to calculate the quantity of sand and dust swallowed by jet engines at ten major international airports located in desert regions or subject to seasonal dust storms.
The global study, published today (Tuesday, 9 July) in the journal Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, ...
Coral reefs: battlegrounds for survival in a changing climate
2024-07-09
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Coral reefs, those vibrant underwater cities, stand on the precipice of collapse. While rising ocean temperatures and coral bleaching grab headlines, a new essay in Current Biology reveals a hidden layer of complexity in this fight for survival: the often-overlooked roles of the reefs’ smallest inhabitants.
Scientists have long understood the vital partnership between corals and their symbiotic algae, but work by researchers at UC Santa Barbara and University of Georgia highlights how the fate of entire reefs may hinge ...