Regorafenib synergizes with TAS102 against multiple gastrointestinal cancers
2024-07-09
(Press-News.org)
“In this study, we investigated the therapeutic effects and the underlying mechanisms of TAS-102 in combination with regorafenib against gastrointestinal cancers.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 9, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on July 2, 2024, entitled, “Regorafenib synergizes with TAS102 against multiple gastrointestinal cancers and overcomes cancer stemness, trifluridine-induced angiogenesis, ERK1/2 and STAT3 signaling regardless of KRAS or BRAF mutational status.”
Single-agent TAS102 (trifluridine/tipiracil) and regorafenib are FDA-approved treatments for metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). Researchers previously reported that regorafenib combined with a fluoropyrimidine can delay disease progression in clinical case reports of multidrug-resistant mCRC patients. In this new study, researchers Jun Zhang, Lanlan Zhou, Shuai Zhao, and Wafik S. El-Deiry from Fox Chase Cancer Center and Brown University hypothesized that the combination of TAS102 and regorafenib may be active in CRC and other gastrointestinal (GI) cancers and may in the future provide a treatment option for patients with advanced GI cancer.
“We investigated the therapeutic effect of TAS102 in combination with regorafenib in preclinical studies employing cell culture, colonosphere assays that enrich for cancer stem cells, and in vivo.”
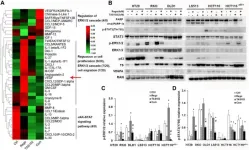
TAS102 in combination with regorafenib has synergistic activity against multiple GI cancers in vitro including colorectal and gastric cancer, but not liver cancer cells. TAS102 inhibits colonosphere formation and this effect is potentiated by regorafenib. In vivo anti-tumor effects of TAS102 plus regorafenib appear to be due to anti-proliferative effects, necrosis and angiogenesis inhibition.
Growth inhibition by TAS102 plus regorafenib occurs in xenografted tumors regardless of p53, KRAS or BRAF mutations, although more potent tumor suppression was observed with wild-type p53. Regorafenib significantly inhibits TAS102-induced angiogenesis and microvessel density in xenografted tumors, as well inhibits TAS102-induced ERK1/2 activation regardless of RAS or BRAF status in vivo. TAS102 plus regorafenib is a synergistic drug combination in preclinical models of GI cancer, with regorafenib suppressing TAS102-induced increase in microvessel density and p-ERK as contributing mechanisms.
“The TAS102 plus regorafenib drug combination may be further tested in gastric and other GI cancers.”
Continue reading: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28602
Correspondence to: Wafik S. El-Deiry
Email: wafik@brown.edu
Keywords: TAS102, regorafenib, ERK1/2, angiogenesis, microvessel density
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Oncotarget: Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
Oncotarget is indexed and archived by PubMed/Medline, PubMed Central, Scopus, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
X, formerly Twitter
Facebook
YouTube
Instagram
LinkedIn
Pinterest
Reddit
Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Street., Suite 1
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957 (option 2)
###
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-07-09
Researchers at University of California San Diego have found that the most common form of liver cancer — one with a high mortality rate — can be better targeted and treated using an innovative new stem cell-derived therapy, according to a recently published study in Cell Stem Cell.
The treatment, not yet studied in patients, involves the lab engineering of natural killer (NK) cells — white blood cells that destroy tumor cells — to more effectively battle hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), one of the most treatment-resistant types of solid tumor.
Genetically modified NK-cell therapy doesn't require ...
2024-07-09
The 17th World Congress on Polyphenols Applications, taking place on September 19-20, 2024, at Università degli Studi di Milano Statale in Milan, Italy, will gather more than 140 attendees coming from 30+ countries. More than 20 international speakers will cover the latest advances in polyphenols research and their practical applications.
Key Topics
Polyphenols Applications 2024 will cover a wide range of topics, including the challenges in demonstrating the health benefits of polyphenols, the ...
2024-07-09
A new study published today in Current Biology, "Oceanic Seabirds Chase Tropical Cyclones," reveals that the rare Desertas Petrels (Pterodroma deserta), a wide-ranging seabird in the North Atlantic, exhibit unique foraging behaviors during hurricane season. Contrary to other pelagic seabirds, these petrels do not avoid intense tropical cyclones but instead exploit the dynamic conditions for their benefit, providing new insights into the impact of cyclones on open ocean marine life.
"Initial studies suggested that seabirds either circumnavigate cyclones or seek refuge in the calm eye of the storm. However, the Desertas Petrels we tracked did neither; instead, one-third of ...
2024-07-09
During his recent yearlong sabbatical, Daniel Laughlin led a study that found trees can sustain life in temperatures higher or lower than where they are currently growing.
While tree species appear to prefer distinct climatic conditions, the true nature of these preferences is obscured by species interactions and dispersal, which limit tree species’ ranges.
“We were amazed. The result was crystal clear, and that doesn’t always happen in ecology,” says Laughlin, a professor in the University of Wyoming Department of Botany. “We found that tree species could grow and survive at one common moderate temperature, even though many ...
2024-07-09
CHARLOTTE, N.C. – Advocate Health has been selected by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) to participate in the Guiding an Improved Dementia Experience (GUIDE) Model, aimed to support advanced dementia patients and their caregivers in bridging the gaps associated with inequalities in dementia care. Following years of neurocognitive disorders research pioneered by Advocate Health's academic core, Wake Forest University School of Medicine, patients across the health system’s footprint now will benefit from the GUIDE Model’s new standardized approach to care for patients with dementia and their caregivers. Only 400 health organizations ...
2024-07-09
A team of researchers at Baylor College of Medicine, Texas Children’s Hospital, the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto and collaborating institutions has identified and located a population of stem-like cells that initiates and maintains Group 3 medulloblastoma (Gr3-MB) in the developing brain. Gr3-MB is one of the most aggressive forms of brain cancer in children and is associated with metastatic spread and poor survival.
The researchers showed that eliminating the small population of stem-like ...
2024-07-09
A study from the University of Michigan has identified a potential new treatment for food allergies in inulin, a naturally occurring plant fiber commonly used as a supplement, a prebiotic in soda, a replacement for sweeteners and for other products and purposes.
In what appears to be a major advancement that offers the promise of relief to food allergy sufferers around the world, the paper published in Nature Materials describes inulin gel-based oral immunotherapy's success in stopping allergic reactions in mice by, in part, targeting bacteria in the gut. The gel prevented severe allergic reactions ...
2024-07-09
Researchers from Emlyon Business School and HEC Montreal published a new Journal of Marketing study that examines the new breed of volunteers who often show a weaker sense of affiliation with organizations and how best to engage them for mutual benefit.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Managing Brand Relationship Plurality: Insights from the Nonprofit Sector” and is authored by Verena Gruber and Jonathan Deschênes.
Volunteers stand as vital pillars in the operation and survival of nonprofit organizations. Across ...
2024-07-09
Gendered Social Innovation: Social Change and Female Entrepreneurship in Tourism
Gendered social innovation is a crucial process that intertwines social change with female entrepreneurship, empowerment, and the evolution of work among women in the tourism industry.
Questioning Common Perceptions
Why question the usual perceptions about the role and status of women entrepreneurs in a globalized and capitalist industry? Where does power, creativity, and innovation truly reside in tourism development?
Often, discussions about gender equality in tourism revolve around a vision that confines women to the role of service providers, perpetuating stereotypes ...
2024-07-09
FAIRFAX, Va. (July 9, 2024)— Among women who have personally been diagnosed with uterine fibroids, more than half (53%) were presented with a hysterectomy, while fewer than 1 in 5 (20%) were presented with other less invasive options such as over-the-counter NSAIDs (19%), uterine fibroid embolization (17%), oral contraceptives (17%), and endometrial ablation (17%), according to new survey data by The Harris Poll on behalf of the Society of Interventional Radiology. Moreover, some women (17%) mistakenly ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Regorafenib synergizes with TAS102 against multiple gastrointestinal cancers





