(Press-News.org) In a study in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology that included 60 individuals with mild to moderate acne, following the Mediterranean diet and taking omega-3 fatty acid supplements led to significant reductions in inflammatory and non-inflammatory skin lesions, as well as improved quality of life.
Notably, 98.3% of participants had omega-3 fatty acid deficits at the start of the study. Acne severity lessened significantly in those who reached target omega-3 fatty acid levels during the study.
“Lifestyle interventions, including dietary recommendations, should not be considered in opposition to prescription medications, but rather as a valuable adjunct to any modern acne treatment plan,” said corresponding author Anne Guertler, MD, of the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, in Germany. “Future studies should build on the foundation laid by our current findings in a randomized, placebo-controlled design to improve dietary recommendations for acne patients.”
URL upon publication: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jocd.16434
Additional Information
NOTE: The information contained in this release is protected by copyright. Please include journal attribution in all coverage. For more information or to obtain a PDF of any study, please contact: Sara Henning-Stout, newsroom@wiley.com.
About the Journal
Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology is an open access journal that publishes high quality articles on all aspects of cosmetic dermatology to foster the highest standards of patient care. Our aim is to be share the best cosmetic science available to bring readers the most cutting-edge information.
About Wiley
Wiley is a knowledge company and a global leader in research, publishing, and knowledge solutions. Dedicated to the creation and application of knowledge, Wiley serves the world’s researchers, learners, innovators, and leaders, helping them achieve their goals and solve the world's most important challenges. For more than two centuries, Wiley has been delivering on its timeless mission to unlock human potential. Visit us at Wiley.com. Follow us on Facebook, X, LinkedIn and Instagram.
END
Can omega-3 fatty acid intake affect acne severity?
2024-07-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How did surge facilities impact the time to reunification for unaccompanied migrant children and their families?
2024-07-10
Unaccompanied children entering the United States without adult legal guardians and legal status account for a growing share of U.S. Border Patrol encounters along the southern border, with most fleeing extreme violence, poverty, and food insecurity. In response, emergency intake sites and influx care facilities (surge facilities) were used to promptly house unaccompanied children. A new analysis published in Economic Inquiry finds that the emergency shelters expedited the reunification of children with their families.
By analyzing data on unaccompanied minors encountered ...
Could new discovery help treat a rare and severe form of amyloidosis?
2024-07-10
In people with a rare condition called light chain amyloidosis, light chain proteins—which are a component of antibodies—mutate and build up in different organs. In new research published in The FEBS Journal, investigators have identified and characterized an antibody fragment that can bind to abnormal light chains to stabilize them and prevent their aggregation.
The findings could have an important clinical impact because the current prognosis for individuals with light chain amyloidosis is extremely poor, and current treatments, ...
We can’t distinguish wild coca plants from those grown to make cocaine
2024-07-10
A new paper in Molecular Biology and Evolution, published by Oxford University Press, indicates that while the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime has collected annual data on areas of coca cultivation in South America for decades – to monitor the establishment of illegal plantations and associated deforestation – scientists can’t reliably distinguish between different types of coca plants. While identification often relies on leaf shape and size, this does not reflect differences between coca varieties grown for extracting the alkaloid cocaine (the active ingredient in the recreational drug), coca cultivated for traditional purposes, ...
Chronic allergic disorder EoE’s rising incidence in Japan confirmed by large-scale data analysis
2024-07-10
Osaka, Japan — In one of the first studies of its kind in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University-led researchers uncovered the incidence and prevalence of the chronic allergic disorder eosinophilic esophagitis, or EoE.
EoE can cause difficulty in swallowing with tissue inflammation and fibrosis as eosinophils, a type of white blood cell, build up in the esophagus. EoE cases have been increasing in North America and Western Europe since the 1990s, but little has been known about the situation in Asia including Japan.
Dr. Akinari Sawada, Associate Professor Fumio Tanaka, and Professor Yasuhiro Fujiwara of OMU’s Graduate School of Medicine and colleagues analyzed a ...
Does living in America’s wealthiest communities make you safer?
2024-07-10
HERNDON, Va., July 10, 2024 -- One of the privileges the wealthiest Americans enjoy is living wherever they want. But new research published in Risk Analysis suggests they should be cautious when choosing their Shangri-La.
In their nationwide analysis, Rutgers University geographers Michael Greenberg and Dona Schneider compared the concentration of hazards and associated risks impacting the richest and poorest counties and the richest and poorest municipalities in all 50 states (200 locations).
When ...
Spectacular auroras are caused by head-on blows to Earth’s magnetic field that could damage critical infrastructure
2024-07-10
Auroras have inspired myths and portents for millennia — but only now, with modern technology dependent on electricity, are we appreciating their true power. The same forces which cause auroras also cause currents that can damage infrastructure which conducts electricity, like pipelines. Now scientists writing in Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences have demonstrated that the impact angle of interplanetary shocks is key to the currents’ strength, offering an opportunity to forecast dangerous shocks and shield critical infrastructure.
“Auroras and geomagnetically induced currents are ...
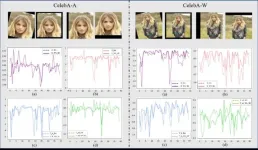
An approach for robust facial attribute classification
2024-07-10
Face attribute classification (FAC) is a high-profile problem in biometric verification and face retrieval. Although recent research has been devoted to extracting more delicate image attribute features and exploiting the inter-attribute correlations, significant challenges still remain.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Na LIU published their new research on 15 June 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer Nature.
The team proposed a scattering-based hybrid block, termed WS-SE, to incorporate frequency-domain (WST) and image-domain (CNN) features in a channel attention manner. Compared with CNN, WS-SE achieved ...
Risky drinkers most at risk: Ads from sports broadcasts significantly increase alcohol urges
2024-07-10
10 July 2024
Risky drinkers most at risk: Ads from sports broadcasts significantly increase alcohol urges
New Edith Cowan University (ECU) research shows exposure to alcohol advertisements during national sports broadcasts, particularly those that feature a preferred beverage, significantly increases cravings in people with risky drinking behaviours.
The ECU study, led by Dr Ross Hollett, analysed nationally televised finals matches from the Australian Football League (AFL) and the National Rugby League (NRL) ...
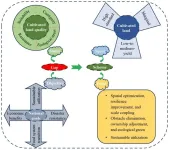
How to differentially improve the cultivated land quality in China?
2024-07-10
Quality is the core characteristic of cultivated land and is crucial for ensuring sustainable resource utilization and national food security. To meet the increasing demand for food driven by rapid population growth and the continual optimization of dietary structures, the intensity of cultivated land utilization has been steadily increasing. This trend has resulted in degradation issues such as deterioration of black soil, thinning of the cultivated land layer, reduction in organic matter content, soil salinization, acidification, and contamination by heavy metals, all of which threaten national food security. Currently, China has entered a critical period of agricultural ...
Study reveals racial disparities in Huntington’s disease diagnoses
2024-07-10
New research led by UCLA Health revealed that Black patients with Huntington's disease in the U.S. and Canada received their diagnoses, on average, one year later compared to White patients after symptoms first appear.
Huntington’s disease is a rare, incurable genetic disease that causes a gradual death of nerve cells, resulting in a variety of symptoms affecting movement, emotions and cognition. About 41,000 Americans have the disease and 200,000 are at risk of inheriting it, according to the Huntington’s Disease Society of America. Children of a parent with ...