(Press-News.org) Poverty and mental illness are not only linked, but there is also a causal relationship. This is the conclusion of researchers from Amsterdam UMC, the University of Edinburgh and the University of Modena. Their study shows that while certain mental health issues can hinder financial stability, poverty is also one of the causal factors leading to mental health problems. This study was published today in Nature Human Behaviour.
"This study indicates that certain mental health problems can make a person's financial situation uncertain. But conversely, we also see that poverty can lead to mental health problems," says Marco Boks, psychiatrist at Amsterdam UMC
Previous research has shown a strong correlation between poverty and mental illness, but disentanglement between cause and effect proved difficult. The consequences of mental illness can affect a person's financial situation, for example, if this person is unable to work as well or has higher healthcare costs. But difficult financial circumstances can also cause psychological problems.
Complex relationship
The researchers used data from the UK Biobank and the international Psychiatric Genomic Consortium. "We discovered that schizophrenia and ADHD causally contribute to poverty. Conversely, poverty contributes to major depressive disorder and schizophrenia. The risk of anorexia nervosa is actually reduced when there is poverty," says Boks.
Firstly, a measure of poverty was determined on the basis of household income, occupational income and social deprivation. Researchers then used the participants' genetic information using a special technique called Mendelian randomisation to untangle the relationship. Mendelian randomisation is a method of determining the influence of risk factors on a disease, by measuring the variation of genes that are more common in certain traits.
“We were able to capture aspects of poverty shared between the individual, the household, and the area in which one lives. This enabled us to better identify the causal effects of poverty on mental illness,” says David Hill, statistical geneticist at the University of Edinburgh.
Vicious circle
The findings of this research are important for policy and the approach to both poverty and mental illness. By recognising the reciprocal influence between poverty and mental health, policymakers can develop more effective interventions aimed at breaking the cycle of poverty and mental health problems. "The research provides robust evidence for the need to also look at social factors such as poverty, when you delve into the development of mental illness," says Boks.
"Our findings suggest that the reduction of inequalities could lead to substantial public mental health gain," adds Mattia Marchi, psychiatrist at the University of Modena.
"There is often confusion about the use of genetic data to investigate the relationship between poverty and mental illness. We emphasise that this does not mean that poverty is genetic. On the contrary, with genetic data, we were able to identify poverty as a modifiable environmental factor for mental health," concludes Boks.
END
Living in poverty due to mental health problems or developing mental health problems because of poverty? It's both.
2024-07-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Atlas of proteins reveals inner workings of cells
2024-07-10
Scientists at the University of Cambridge have developed an atlas of proteins describing how they behave inside human cells. This tool could be used to search for the origins of diseases which are related to proteins misbehaving such as dementia and many cancers.
The atlas, which is published in Nature Communications, has allowed the researchers to find new proteins inside cells that are responsible for a range of important bodily functions. The team focuses on a droplet-like part of the cell called a condensate ...
Discovery of a new defense mechanism in bacteria
2024-07-10
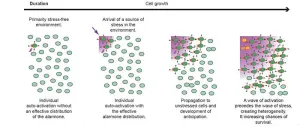
When confronted with an antibiotic, toxic substance, or other source of considerable stress, bacteria are able to activate a defence mechanism using cell-to-cell communication to ‘warn’ unaffected bacteria, which can then anticipate, shield themselves and spread the warning signal. This mechanism1 has just been described for the first time by a team of scientists2 from CNRS and Université de Toulouse III – Paul Sabatier. It paves the way for the development of new, more effective antibiotic treatments that can target this bacterial communication system.
When they perceive a source of stress, bacteria spring into action, inducing changes in the expression of certain ...
Mozambican Woodlands could store more than double the carbon previously estimated
2024-07-10
The capacity of Mozambican woodlands to capture and store carbon is underestimated and potentially undervalued for their protection and restoration, finds new research from an international team of scientists including UCL researchers and led by carbon data provider Sylvera.
The research, published in Nature Communications Earth & Environment, found that miombo woodlands, which span large areas of Sub-Saharan Africa, store 1.5 to 2.2 times more carbon than had previously been estimated by standard methods.
Named for the miombo trees found in the region, these biomes (geographical areas defined by their local species and ...
Cutting farm nitrous oxide emissions helps climate and ozone layer
2024-07-10
Cutting farm nitrous oxide emissions helps climate and ozone layer
Adding crushed basalt rocks and special fertilisers can reduce potent nitrous oxide (N2O) greenhouse gas emissions and safeguard the stratospheric ozone layer, which protects us from harmful UV light and reduces nitrate leaching into water bodies protecting ecosystems and human health
The new study, led by researchers at the University of Sheffield, highlights methods for reducing N2O emissions, such as enhanced weathering of agricultural soils with ...
Blood cancer drug could make radiotherapy on brain tumours more effective
2024-07-10
Drugs developed to fight blood and other cancers could also help improve the efficiency of radiotherapy in the most commonly diagnosed low-grade brain tumour in adults, a new study has found.
Meningioma account for approximately 36% of all primary brain tumours. The majority are successfully treated by surgery, but some which can’t easily be accessed need to be treated with radiotherapy. That can cause significant side effects and radiation damage to the brain, while resistance to radiotherapy can also result in tumour growth.
A new study by researchers at the Brain Tumour Research ...
Does air pollution affect lupus risk?
2024-07-10
New research published in Arthritis & Rheumatology indicates that chronic exposure to air pollutants may increase the risk of developing lupus, an autoimmune disease that affects multiple organs.
For the study, investigators analyzed data on 459,815 participants from the UK Biobank. A total of 399 lupus cases were identified during a median follow-up of 11.77 years. Air pollutant exposure was linked with a greater likelihood of developing lupus. Individuals with a high genetic risk and high air pollution exposure had the highest risk of developing ...
Can certain bacteria or fungi combat a plant pathogen that attacks common vetch?
2024-07-10
Anthracnose, a severe disease caused by the Colletotrichum spinaciae plant pathogen, often occurs in common vetch, a widely grown legume. Chemicals are not recommended for disease management because the plants are used as livestock feed. A new study published in Grassland Research reveals that treating common vetch with certain bacteria or fungi that promote plant growth may be effective for combating anthracnose.
Treating common vetch with these bacteria or fungi increased the activity of plant defense enzymes and promoted the presence of healthy bacteria that could keep Colletotrichum spinaciae at bay.
“The combined use of plant growth‐promoting rhizobacteria such as Bacillus ...
Can omega-3 fatty acid intake affect acne severity?
2024-07-10
In a study in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology that included 60 individuals with mild to moderate acne, following the Mediterranean diet and taking omega-3 fatty acid supplements led to significant reductions in inflammatory and non-inflammatory skin lesions, as well as improved quality of life.
Notably, 98.3% of participants had omega-3 fatty acid deficits at the start of the study. Acne severity lessened significantly in those who reached target omega-3 fatty acid levels during the study.
“Lifestyle interventions, including dietary recommendations, should ...
How did surge facilities impact the time to reunification for unaccompanied migrant children and their families?
2024-07-10
Unaccompanied children entering the United States without adult legal guardians and legal status account for a growing share of U.S. Border Patrol encounters along the southern border, with most fleeing extreme violence, poverty, and food insecurity. In response, emergency intake sites and influx care facilities (surge facilities) were used to promptly house unaccompanied children. A new analysis published in Economic Inquiry finds that the emergency shelters expedited the reunification of children with their families.
By analyzing data on unaccompanied minors encountered ...
Could new discovery help treat a rare and severe form of amyloidosis?
2024-07-10
In people with a rare condition called light chain amyloidosis, light chain proteins—which are a component of antibodies—mutate and build up in different organs. In new research published in The FEBS Journal, investigators have identified and characterized an antibody fragment that can bind to abnormal light chains to stabilize them and prevent their aggregation.
The findings could have an important clinical impact because the current prognosis for individuals with light chain amyloidosis is extremely poor, and current treatments, ...