(Press-News.org) FINDINGS
A UCLA-led team has developed a machine-learning model that can predict with a high degree of accuracy the short-term survival of dialysis patients on Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT).
BACKGROUND
CRRT is a therapy used for very sick hospitalized patients whose health status makes them ineligible for regular hemodialysis. It is a gentler therapy that provides continuous treatment over a prolonged period. About half of adults placed on CRRT, however, do not survive, rendering the treatment futile for both patients and their families.
METHOD
To help doctors decide whether a patient should start CRRT, the researchers developed a machine-learning model that uses data from thousands of patients' electronic health records to predict their chances of surviving the therapy.
IMPACT
The findings provide a data-driven tool to assist in clinical decision-making. This tool incorporates advanced machine-learning techniques to analyze a large and complex set of patient data, which was previously challenging for doctors to do. The study demonstrates how integrating machine-learning models into healthcare can improve treatment outcomes and resource management.
COMMENT
“CRRT is often used as a last resort, but many patients do not survive it, leading to wasted resources and false hope for families,” said Dr. Ira Kurtz, chief of the UCLA Division of Nephrology and the study’s senior author. “By making it possible to predict which patients will benefit, the model aims to improve patient outcomes and resource use, by serving as a basis for testing its utility in future clinical trials. Like all machine learning models, it needs to be tested in the real world to determine whether it is equally as accurate in its predictions in patients that it wasn’t trained on.”
AUTHORS
Additional authors are Davina Zamanzadeh, Jeffrey Feng, Panayiotis Petousis, Arvind Vepa, Majid Sarrafzadeh, and Alex Bui of UCLA, and S. Ananth Karumanchi of Cedars Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles.
JOURNAL
The study is published in the peer-reviewed journal Nature Communications.
FUNDING
This work was supported in part by funds by the Kidney, Urologic, and Hematologic-Advanced Research Training Program (NIH NIDDK U2C DK129496), the Medical Imaging Informatics Training Grant (NIH NIBIB T32 EB016640), the UCLA CTSI grant (NIH UL1 TR001881), the Smidt Family Foundation, the Factor Family Foundation, the Davita Allen Nissenson Research Fund, the Ralph Block Family Fund, and the Kleeman Family Fund.
Media Contact
Enrique Rivero
310-267-7120
erivero@mednet.ucla.edu
END
Poverty and mental illness are not only linked, but there is also a causal relationship. This is the conclusion of researchers from Amsterdam UMC, the University of Edinburgh and the University of Modena. Their study shows that while certain mental health issues can hinder financial stability, poverty is also one of the causal factors leading to mental health problems. This study was published today in Nature Human Behaviour.
"This study indicates that certain mental health problems can make a person's financial situation uncertain. But conversely, we also see that poverty can lead to mental health problems," ...
Scientists at the University of Cambridge have developed an atlas of proteins describing how they behave inside human cells. This tool could be used to search for the origins of diseases which are related to proteins misbehaving such as dementia and many cancers.
The atlas, which is published in Nature Communications, has allowed the researchers to find new proteins inside cells that are responsible for a range of important bodily functions. The team focuses on a droplet-like part of the cell called a condensate ...
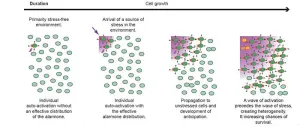
When confronted with an antibiotic, toxic substance, or other source of considerable stress, bacteria are able to activate a defence mechanism using cell-to-cell communication to ‘warn’ unaffected bacteria, which can then anticipate, shield themselves and spread the warning signal. This mechanism1 has just been described for the first time by a team of scientists2 from CNRS and Université de Toulouse III – Paul Sabatier. It paves the way for the development of new, more effective antibiotic treatments that can target this bacterial communication system.
When they perceive a source of stress, bacteria spring into action, inducing changes in the expression of certain ...
The capacity of Mozambican woodlands to capture and store carbon is underestimated and potentially undervalued for their protection and restoration, finds new research from an international team of scientists including UCL researchers and led by carbon data provider Sylvera.
The research, published in Nature Communications Earth & Environment, found that miombo woodlands, which span large areas of Sub-Saharan Africa, store 1.5 to 2.2 times more carbon than had previously been estimated by standard methods.
Named for the miombo trees found in the region, these biomes (geographical areas defined by their local species and ...
Cutting farm nitrous oxide emissions helps climate and ozone layer
Adding crushed basalt rocks and special fertilisers can reduce potent nitrous oxide (N2O) greenhouse gas emissions and safeguard the stratospheric ozone layer, which protects us from harmful UV light and reduces nitrate leaching into water bodies protecting ecosystems and human health
The new study, led by researchers at the University of Sheffield, highlights methods for reducing N2O emissions, such as enhanced weathering of agricultural soils with ...
Drugs developed to fight blood and other cancers could also help improve the efficiency of radiotherapy in the most commonly diagnosed low-grade brain tumour in adults, a new study has found.
Meningioma account for approximately 36% of all primary brain tumours. The majority are successfully treated by surgery, but some which can’t easily be accessed need to be treated with radiotherapy. That can cause significant side effects and radiation damage to the brain, while resistance to radiotherapy can also result in tumour growth.
A new study by researchers at the Brain Tumour Research ...
New research published in Arthritis & Rheumatology indicates that chronic exposure to air pollutants may increase the risk of developing lupus, an autoimmune disease that affects multiple organs.
For the study, investigators analyzed data on 459,815 participants from the UK Biobank. A total of 399 lupus cases were identified during a median follow-up of 11.77 years. Air pollutant exposure was linked with a greater likelihood of developing lupus. Individuals with a high genetic risk and high air pollution exposure had the highest risk of developing ...
Anthracnose, a severe disease caused by the Colletotrichum spinaciae plant pathogen, often occurs in common vetch, a widely grown legume. Chemicals are not recommended for disease management because the plants are used as livestock feed. A new study published in Grassland Research reveals that treating common vetch with certain bacteria or fungi that promote plant growth may be effective for combating anthracnose.
Treating common vetch with these bacteria or fungi increased the activity of plant defense enzymes and promoted the presence of healthy bacteria that could keep Colletotrichum spinaciae at bay.
“The combined use of plant growth‐promoting rhizobacteria such as Bacillus ...
In a study in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology that included 60 individuals with mild to moderate acne, following the Mediterranean diet and taking omega-3 fatty acid supplements led to significant reductions in inflammatory and non-inflammatory skin lesions, as well as improved quality of life.
Notably, 98.3% of participants had omega-3 fatty acid deficits at the start of the study. Acne severity lessened significantly in those who reached target omega-3 fatty acid levels during the study.
“Lifestyle interventions, including dietary recommendations, should ...
Unaccompanied children entering the United States without adult legal guardians and legal status account for a growing share of U.S. Border Patrol encounters along the southern border, with most fleeing extreme violence, poverty, and food insecurity. In response, emergency intake sites and influx care facilities (surge facilities) were used to promptly house unaccompanied children. A new analysis published in Economic Inquiry finds that the emergency shelters expedited the reunification of children with their families.
By analyzing data on unaccompanied minors encountered ...