(Press-News.org) The Moon’s recent discovery of energy resources, such as water ice, has refocused interest on its potential as a sustainable hub for space exploration. NASA has also announced the Artemis mission, aiming for long-term human presence on the lunar surface. However, infrastructure expansion, such as lunar base construction plays a vital role.
Yet, transporting construction materials from Earth to the lunar surface via landers incurs a significant cost of 1.2 million USD per kilogram. Weight directly translates to cost, making the transportation of construction materials from Earth to the Moon nearly impossible.
To solve this problem, Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT, President Kim, Byung-Suk), has developed technology for producing construction materials using in-situ resources from the moon.
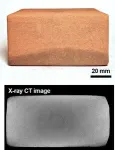
The most readily available in-situ resource on the Moon is lunar regolith, which is the Moon’s surface soil. Utilizing lunar regolith can lead to cost savings. Composed of fine particles, lunar regolith can be sintered through heat. However, in space environments, energy efficiency considerations are crucial for applying heat. And Microwaves are particularly advantageous in terms of energy efficiency.
The research team(Dr. Jangguen, Lee, Dr. Young-Jae, Kim, Dr. Hyunwoo, Jin) led by Dr. Hyu-Soung, Shin at the Future & Smart Construction Research Division of KICT, utilized microwave sintering to produce blocks from lunar regolith simulant by heating and compacting it.
When using microwaves to heat lunar regolith, localized hot & cold spots can form. These spots lead to localized thermal runaway, hindering uniform heating and sintering. To address this, a stepwise heating program with specific temperature and dwell time was established. Additionally, lunar regolith contains volatile substances, including water. Heating these volatile materials can cause internal cracks during sintering. The research team mitigated crack formation by using preheated lunar regolith simulant under vacuum conditions at 250°C.
To assess the completeness of sintered blocks intended for construction materials, the produced blocks were core-drilled at specific locations. The average density, porosity, and compressive strength of the core-drilled samples were approximately 2.11 g/cm³, 29.23%, and 13.66 MPa, respectively. The corresponding standard deviations were 0.03, 1.01, and 1.76, confirming the homogeneity of the sintered blocks.
KICT has secured technology for producing construction materials using lunar regolith. The plan is to validate this technology in space environments. By verifying it under space conditions, we can better address the increasing demand for space construction technology.
Dr. Shin said, “Many previous space construction studies related to microwave sintering technology have resulted in small or heterogeneous sintered bodies.” He further expressed plans to utilize this technology for various infrastructure construction needs on the lunar surface in the future.
###
The Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology, a government-funded research institute with 41 years of extensive research experience, is at the forefront of solving national issues that are directly related to the quality of the people’s life.
Research for this work was carried out under the KICT Research Program (project no. 20230081-001 & 20240184-001, Development of Environmental Simulator and Advanced Construction Technologies over TRL6 in Extreme Conditions) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT. An article explaining the results of this research was published in the latest issue of Journal of Building Engineering, a renowned international journal in the Civil Engineering field (IF:6.4).
END
Producing ‘space brick’ for moon base using microwave
Manufacture of the world’s largest uniform microwave-sintered lunar regolith simulant bricks
2024-07-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A simple firmware update completely hides a device’s Bluetooth fingerprint
2024-07-10
A smartphone’s unique Bluetooth fingerprint could be used to track the device’s user–until now. A team of researchers have developed a simple firmware update that can completely hide the Bluetooth fingerprint, eliminating the vulnerability.
The method was developed by a team of researchers at the University of California San Diego. The team discovered the vulnerability caused by Bluetooth fingerprints in a study they presented at the 2022 IEEE Security & Privacy conference. They presented the fix to this vulnerability two years later at the 2024 IEEE Security & Privacy conference. The math behind the update itself is complex but the implementation ...
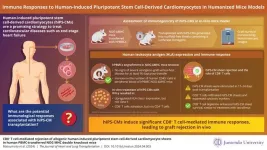
Immunogenicity of human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocyte sheets
2024-07-10
Ischemic heart disease stands as a significant global cause of morbidity and mortality. One promising avenue for treatment involves human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPS-CMs). Derived from adult somatic cells such as blood or skin cells, hiPS cells possess the capacity to differentiate into various tissues, including cardiomyocytes. These cells can potentially repair damaged heart tissue, but their clinical application is limited due to concerns about immune rejection. Understanding the immunogenicity of hiPS-CMs is crucial for advancing their ...
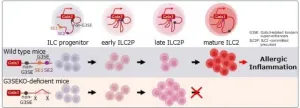
Unravelling a mechanism of Group 2 innate lymphoid immune cell development
2024-07-10
Overproduction of Group 2 innate lymphoid cells or ILC2s—a type of white blood cells—can sometimes exacerbate conditions such as bronchial asthma, chronic rhinosinusitis, atopic dermatitis, and organ fibrosis through an exaggerated immune response. Although there are immunomodulatory drugs that can suppress Type 2 helper T (Th2) cells, drugs capable of suppressing ILC2s are currently lacking.
Now, however, in a breakthrough study that could lead to the development of a new therapeutic strategy targeting ILC2s, researchers led by Associate Professor Arifumi Iwata of the Chiba University Hospital, Japan, have identified molecular ...
Award for Excellence in Natural Product Chemistry to Ricardo Riguera
2024-07-10
The Specialised Group on Chemistry of Natural Products (GQPN) of the Spanish Royal Society of Chemistry (RSEQ) has awarded its Excellence in Research Award 2023 to Professor Ricardo Riguera. The Evaluation Committee thus recognises his valuable contribution to this area of chemistry. Among other advances, his work has made it possible to describe a large number of bioactive metabolites, such as the first heptacyclopeptide and the first cyclodepsipeptide isolated from marine organisms. Riguera also identified one of the first examples of cytotoxic metabolites from marine bacteria, the first description of L-galactose as part of a natural product, and the first description ...
Researchers develop an AI model that predicts Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy survival
2024-07-10
FINDINGS
A UCLA-led team has developed a machine-learning model that can predict with a high degree of accuracy the short-term survival of dialysis patients on Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT).
BACKGROUND
CRRT is a therapy used for very sick hospitalized patients whose health status makes them ineligible for regular hemodialysis. It is a gentler therapy that provides continuous treatment over a prolonged period. About half of adults placed on CRRT, however, do not survive, rendering the treatment futile for both patients ...
Living in poverty due to mental health problems or developing mental health problems because of poverty? It's both.
2024-07-10
Poverty and mental illness are not only linked, but there is also a causal relationship. This is the conclusion of researchers from Amsterdam UMC, the University of Edinburgh and the University of Modena. Their study shows that while certain mental health issues can hinder financial stability, poverty is also one of the causal factors leading to mental health problems. This study was published today in Nature Human Behaviour.
"This study indicates that certain mental health problems can make a person's financial situation uncertain. But conversely, we also see that poverty can lead to mental health problems," ...
Atlas of proteins reveals inner workings of cells
2024-07-10
Scientists at the University of Cambridge have developed an atlas of proteins describing how they behave inside human cells. This tool could be used to search for the origins of diseases which are related to proteins misbehaving such as dementia and many cancers.
The atlas, which is published in Nature Communications, has allowed the researchers to find new proteins inside cells that are responsible for a range of important bodily functions. The team focuses on a droplet-like part of the cell called a condensate ...
Discovery of a new defense mechanism in bacteria
2024-07-10
When confronted with an antibiotic, toxic substance, or other source of considerable stress, bacteria are able to activate a defence mechanism using cell-to-cell communication to ‘warn’ unaffected bacteria, which can then anticipate, shield themselves and spread the warning signal. This mechanism1 has just been described for the first time by a team of scientists2 from CNRS and Université de Toulouse III – Paul Sabatier. It paves the way for the development of new, more effective antibiotic treatments that can target this bacterial communication system.
When they perceive a source of stress, bacteria spring into action, inducing changes in the expression of certain ...
Mozambican Woodlands could store more than double the carbon previously estimated
2024-07-10
The capacity of Mozambican woodlands to capture and store carbon is underestimated and potentially undervalued for their protection and restoration, finds new research from an international team of scientists including UCL researchers and led by carbon data provider Sylvera.
The research, published in Nature Communications Earth & Environment, found that miombo woodlands, which span large areas of Sub-Saharan Africa, store 1.5 to 2.2 times more carbon than had previously been estimated by standard methods.
Named for the miombo trees found in the region, these biomes (geographical areas defined by their local species and ...
Cutting farm nitrous oxide emissions helps climate and ozone layer
2024-07-10
Cutting farm nitrous oxide emissions helps climate and ozone layer
Adding crushed basalt rocks and special fertilisers can reduce potent nitrous oxide (N2O) greenhouse gas emissions and safeguard the stratospheric ozone layer, which protects us from harmful UV light and reduces nitrate leaching into water bodies protecting ecosystems and human health
The new study, led by researchers at the University of Sheffield, highlights methods for reducing N2O emissions, such as enhanced weathering of agricultural soils with ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
[Press-News.org] Producing ‘space brick’ for moon base using microwaveManufacture of the world’s largest uniform microwave-sintered lunar regolith simulant bricks