(Press-News.org) Perceived warmth and competence predict the influence of race, gender and age on callback decisions, suggesting social perceptions might underlie such hiring bias. The meta-analysis of North American correspondence studies is published July 10, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Carina Hausladen from the California Institute of Technology and ETH Zürich, Marcos Gallo from the California Institute of Technology, and colleagues.
In the labor market, applicants from marginalized groups continue to face disparate treatment. To examine hiring bias, researchers use experimental studies known as correspondence studies, in which they present employers with sets of artificial résumés, identical except for one detail that may indicate identity. Researchers can then use callback decisions to identify patterns of discrimination.
Hausladen and colleagues examined the potential link between social perceptions of candidates and callback decisions, asking if different social perceptions associated with stereotypes of particular identities might explain observed differences in callback rates. They draw upon the social perception dimensions warmth (good intentions) and competence (capability to carry out one’s intentions) to measure the major ways in which people categorize each other.
The researchers analyzed callback rates from 21 US and Canadian correspondence studies which varied either the applicants’ names or attributes to signal identity (e.g., “Sarah Davis” may be perceived as a white female, while volunteering at a church may signal religious affiliation). Participants, selected to demographically resemble North American hiring managers, rated the applicants’ characteristics on their perceived warmth and competence.
Analysis revealed that in studies where names were varied to signal race, gender, and age, warmth and competence ratings predicted callback differences between identities. The applicants' characteristics which experienced lower callback rates tended to be rated as less warm and competent, and the reverse was also true. One explanation might be that identity signals trigger specific warmth and competence perceptions according to stereotypes, which then influence callback decisions. However, for studies varying attributes to signal other categories (e.g. sexuality and disability), the influence of social perception on callbacks was inconsistent.
Social perceptions may vary across cultures, and the sample sizes of some correspondence studies were also fairly small, making it harder to draw broad conclusions from the study. The researchers encourage future research to include intersectional studies that expand and diversify the attributes measured.
The researchers aim to harness this link between perceived warmth and competence and callback rates to further understand hiring discrimination and even to correct biases in the Large Language Models increasingly used for evaluating résumés.
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0304723
Citation: Gallo M, Hausladen CI, Hsu M, Jenkins AC, Ona V, Camerer CF (2024) Perceived warmth and competence predict callback rates in meta-analyzed North American labor market experiments. PLoS ONE 19(7): e0304723. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0304723
Author Countries: USA, Switzerland
Funding: NSF DRMS grants 1851879 (ACJ), 1851745 (CFC), 1851902 (MH), and a Tianqiao and Chrissy Chen Graduate Fellowship (MG).
END
Perceived warmth, competence predict callback decisions in meta-analysis of hiring experiments
Differences in callback rates which signal bias by race, gender, age can be predicted from social perceptions of applicants
2024-07-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Microproteins found in tumors could lead to cancer vaccines
2024-07-10
A study led by the Hospital del Mar Research Institute, with Cima University of Navarra and Pompeu Fabra University, has identified a group of small molecules exclusive to liver tumors that could be key to developing cancer vaccines. These are microproteins, very small proteins expressed only by tumor cells. This can result in the activation of immune cells against the tumor. The study is published in Science Advances.
By integrating data from tumors and healthy tissue from over one hundred liver cancer ...
Mount Sinai and City of Hope scientists first to demonstrate a combination treatment can increase human insulin-producing cells in vivo
2024-07-10
NEW YORK and LOS ANGELES — In preclinical studies, a team of researchers from Mount Sinai Health System in New York City and City of Hope in Los Angeles report new findings on a therapeutic combination that regenerated human insulin-producing beta cells, providing a possible new treatment for diabetes. The findings were published today in Science Translational Medicine.
This work, led by Andrew F. Stewart, MD, Irene and Dr. Arthur M. Fishberg Professor of Medicine and Director of the Mount Sinai Diabetes, Obesity ...
City of Hope and Mount Sinai scientists first to demonstrate a combination treatment can increase human insulin-producing cells in vivo
2024-07-10
LOS ANGELES and NEW YORK — In preclinical studies, a team of researchers from City of Hope® in Los Angeles and Mount Sinai Health System in New York reports new findings on a therapeutic combination that regenerated human insulin-producing beta cells, providing a possible new treatment for diabetes. The findings were published today in Science Translational Medicine.
This work, led by Andrew F. Stewart, M.D., Irene and Dr. Arthur M. Fishberg Professor of Medicine and Director of the Mount Sinai Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism Institute, began at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in 2015. The studies were a team effort. Adolfo ...
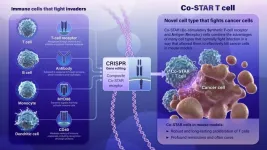
New Co-STAR receptor shows promise treating cancers in laboratory study
2024-07-10
Using genetic engineering techniques, investigators at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and its Ludwig Center, the Lustgarten Laboratory and Bloomberg~Kimmel Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy have designed a novel type of cell to recognize and fight cancer.
To produce the cells, called Co-STAR (Co-stimulatory Synthetic T-cell receptor and Antigen Receptor) cells, the researchers combined genetic components of four types of cells that the body normally uses to defend against invaders to make ...
Novel genome editing approach restores hearing in adult preclinical models with genetic deafness
2024-07-10
The study also looked at safety of the AAV-mediated genome editing approach and found it had a good safety profile that includes little off-target effect and no detectable long-term integration of the AAV vector in the genome. “Our research suggested minimal potential risk and supports the feasibility of future clinical applications in humans,” said Wenliang Zhu, PhD, and physician-scientist Wan Du, MD, PhD, members of Chen’s lab at Mass Eye and Ear and first authors on the paper.
The study, led by Zheng-Yi Chen, DPhil, an associate scientist in the Eaton-Peabody Laboratories at Mass Eye and Ear (a member of the ...
Rice’s Omid Veiseh elected to the Controlled Release Society College of Fellows
2024-07-10
HOUSTON – (July 10, 2024) – The Controlled Release Society (CRS), the premier international, multidisciplinary society dedicated to the science and technology of drug delivery, has elected Rice University bioengineer Omid Veiseh to its College of Fellows.
The recognition is a prestigious acknowledgement of “outstanding and sustained contributions in the field of delivery science and technology,” according to the organization website.
“I am deeply honored to be elected to the CRS College ...
Bringing quantum tools to high school classrooms
2024-07-10
More than 70 high school students and science teachers gathered at Young Middle School in Arlington this summer to learn about quantum information science (QIS). The annual workshop and camp are part of a national pilot program called Quantum for All led by Karen Jo Matsler, assistant professor in practice and master teacher in the UTeach program at The University of Texas at Arlington.
“Just the word ‘quantum’ scares people, which is why many teachers and school administrators ...
Novel pre-treatment process enhances PFAs removal from drinking water
2024-07-10
In a groundbreaking effort to tackle the pervasive issue of PFAS contamination in drinking water, a research team at New Jersey Institute of Technology has received funding from the Bureau of Reclamation's Desalination and Water Purification Research program.
This highly competitive grant, awarded to only eight projects out of over eighty applicants, supports their innovative project titled "Enhanced Coagulation for the Removal of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances using Hydrophobic Ion Pairing Approach Project."
Arjun Venkatesan, associate ...
NASA’s Hubble finds strong evidence for intermediate-mass black hole in Omega Centauri
2024-07-10
Most known black holes are either extremely massive, like the supermassive black holes that lie at the cores of large galaxies, or relatively lightweight, with a mass of under 100 times that of the Sun. Intermediate-mass black holes (IMBHs) are scarce, however, and are considered rare "missing links" in black hole evolution.
Now, an international team of astronomers has used more than 500 images from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope — spanning two decades of observations — to search for evidence of an intermediate-mass black hole by following the motion of seven ...
The Society for Nutrition Education and Behavior (SNEB) issues its position on how to address emergency food and nutrition needs in disaster preparedness
2024-07-10
Philadelphia, July 10, 2024 – Despite escalating disaster frequency and severity, guidance for addressing emergency food and nutrition needs is limited. However, existing literature offers insights on how to effectively address emergency food and nutrition assistance. A recent position paper issued by the Society for Nutrition Education and Behavior (SNEB) in the Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior, published by Elsevier, states that for effective recovery from and resilience to disasters, it is essential that impacted individuals and communities have access to safe, nutritious, and culturally and contextually appropriate foods and beverages, and receive emergency-related ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Perceived warmth, competence predict callback decisions in meta-analysis of hiring experimentsDifferences in callback rates which signal bias by race, gender, age can be predicted from social perceptions of applicants