(Press-News.org) About The Study: This comparative effectiveness research study demonstrated that self-fit over-the-counter hearing aids can offer comparable long-term benefits to audiologist-fit hearing aids for individuals with mild to moderate hearing loss.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Karina C. De Sousa, Ph.D., email karina.swanepoel@up.ac.za.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2024.1825)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaotolaryngology/fullarticle/10.1001/jamaoto.2024.1825?guestAccessKey=69c42de1-36ed-4955-a13b-062387141bed&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=071124
END
Long-term outcomes of self-fit vs audiologist-fit hearing aids
JAMA Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery
2024-07-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Second-hand vaping exposure very low compared to second-hand smoking
2024-07-11
Children exposed to vaping indoors absorb less than one seventh the amount of nicotine as children who are exposed to indoor smoking, but more than those exposed to neither, according to a new study led by UCL researchers.
The study, published in JAMA Network Open and funded by Cancer Research UK, looked at blood tests and survey data for 1,777 children aged three to 11 in the United States.
The researchers said that second-hand exposure to harmful substances in e-cigarettes would likely be much lower still, as e-cigarettes deliver similar levels of nicotine to tobacco but contain only a fraction of the toxicants and ...
Biological science helps fuel the future of electric air travel
2024-07-11
– By William Ferguson
When it comes to figuring out why electric aircraft batteries lose power over time, one typically wouldn’t think to turn to a decades-old approach biologists use to study the structure and function of components in living organisms. However, it turns out that omics, a field that helped scientists unravel the secrets of the human genome, could also soon play a key role in making carbon-free air travel a reality.
In a new study in the journal Joule, a team of researchers led ...
Electric aviation: Batteries that stay strong for the flight duration
2024-07-11
Images
A battery component innovation could help keep power delivery high when electric aircraft land with low charge, according to a study led by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory with expertise from the University of Michigan.
The research provides a solution to a problem identified in 2018 in a study led by Venkat Viswanathan, a professor of aerospace engineering at U-M and a coauthor of the new work published in Joule.
"Both takeoff and landing require high power, and landing is more challenging because you’re not fully charged," Viswanathan said. "To get high power you ...
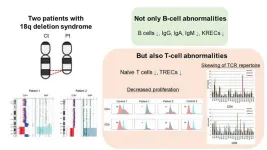
Uncovering late-onset combined immune deficiency in chromosome 18q deletion syndrome
2024-07-11
Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) researchers have discovered that patients with 18q deletion syndrome can experience both cellular and humoral immunodeficiency
Tokyo, Japan – Chromosome 18q deletion (18q del) syndromeis a rare genetic condition disorder, affecting approximately 1 in 40,000 to 55,000 individuals, caused by the deletion of genetic material on the long arm of chromosome 18. This genetic anomaly disrupts normal growth and development, and critically, can impair the immune system's functionality. Patients with 18q del syndrome often exhibit humoral immunodeficiency or a common ...
SciOpen, an international digital publishing platform for STM journals, unveils new updates
2024-07-11
On June 30, 2024, SciOpen 2.0 was officially launched. Developed by Tsinghua University Press, SciOpen initially made its debut in June 2022 as an international digital publishing platform for STM journals. After two years of global operation and continuous iterative upgrades, SciOpen 2.0 has fully embraced the best practices of mainstream publishing models. SciOpen has completed a comprehensive upgrade of its interactive system design and has integrated advanced large-model AI reading capabilities, marking a significant leap forward in its functionality.
These updates steer SciOpen towards ...
JMIR Bioinformatics and Biotechnology is inviting submissions for a new theme issue titled “Artificial Intelligence in Oncology”
2024-07-11
(Toronto, July 11, 2024) JMIR Publications invites submissions to a new theme issue titled “Artificial Intelligence in Oncology” in its premier open access journal JMIR Bioinformatics and Biotechnology indexed in PubMed Central and PubMed, SCOPUS, Sherpa/Romeo, DOAJ and EBSCO/EBSCO Essentials.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to revolutionize oncology by enhancing diagnostic accuracy, personalizing treatment plans, predicting patient outcomes, and accelerating drug discovery. Researchers, clinicians, and industry experts are invited ...
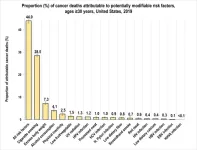
New study finds 40-percent of cancer cases and almost half of all deaths in the US linked to modifiable risk factors
2024-07-11
A new study led by researchers at the American Cancer Society (ACS) finds four in 10 cancer cases and about one-half of all cancer deaths in adults 30 years old and older in the United States (or 713,340 cancer cases and 262,120 cancer deaths in 2019) could be attributed to modifiable risk factors, including cigarette smoking, excess body weight, alcohol consumption, physical inactivity, diet, and infections. Cigarette smoking was by far the leading risk factor, contributing to nearly 20% of all cancer cases and 30% of all cancer deaths. The findings are ...
Pathogen prioritization for wastewater surveillance ahead of the Paris 2024 Olympic and Paralympic Games, France
2024-07-11
The study by researchers from the French national public health institute aimed to identify priority pathogens that could be suitable for wastewater surveillance (WWS) during the Paris 2024 Olympic and Paralympic Games taking place from 26 July to 11 August and 28 August to 8 September, respectively. The pathogens were evaluated using a Delphi method which integrated evidence from peer-reviewed publications and expert opinion.
WWS has become more prominent due to its role during the COVID-19 pandemic. As a non-intrusive, cost-effective surveillance tool, WWS offers ...
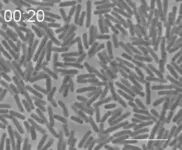
Bacteria form glasslike state
2024-07-11
Dense E.coli bacteria have several similar qualities to colloidal glass, according to new research at the University of Tokyo. Colloids are substances made up of small particles suspended within a fluid, like ink for example. When these particles become higher in density and more packed together, they form a “glassy state.” When researchers multiplied E.coli bacteria within a confined area, they found that they exhibited similar characteristics. More surprisingly, they also showed some other unique properties not typically found in glass-state materials. This study contributes to our understanding of glassy “active matter,” a relatively new field of ...
Prestigious MERIT grant funds research on how the immune system can banish HIV
2024-07-11
Weill Cornell Medicine has received $4.2 million to study how the immune system in some people infected with HIV can keep the virus under control, which could lead to novel therapeutic strategies for thwarting or eliminating HIV. Dr. Brad Jones, associate professor of immunology in medicine in the Division of Infectious Diseases at Weill Cornell Medicine, was awarded a MERIT grant from the National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) at the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
The “Method for Extending Research in Time” (MERIT) grant provides ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
[Press-News.org] Long-term outcomes of self-fit vs audiologist-fit hearing aidsJAMA Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery