JMIR Bioinformatics and Biotechnology is inviting submissions for a new theme issue titled “Artificial Intelligence in Oncology”
2024-07-11
(Press-News.org) (Toronto, July 11, 2024) JMIR Publications invites submissions to a new theme issue titled “Artificial Intelligence in Oncology” in its premier open access journal JMIR Bioinformatics and Biotechnology indexed in PubMed Central and PubMed, SCOPUS, Sherpa/Romeo, DOAJ and EBSCO/EBSCO Essentials.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to revolutionize oncology by enhancing diagnostic accuracy, personalizing treatment plans, predicting patient outcomes, and accelerating drug discovery. Researchers, clinicians, and industry experts are invited to share their insights and pave the way for a future where AI plays a pivotal role in advancing cancer research.
The scope of this call for papers includes, but is not limited to, the following topics:
Machine learning (ML) based predictive models using genomic, electronic health record (EHR), and imaging data in oncology
Natural language processing (NLP) techniques for mining information from real-world oncology data, including EHR
Large language models (LLMs) applying real-world data in oncology research
AI applications in radiology and radiogenomics
Image analysis for tumor detection and classification
AI-driven drug discovery and development in oncology
Innovative clinical trials design using AI or ML
Patient clinical trial matching using AI or ML
Development and applications of AI or ML in digital oncology
Leveraging and learning from real-world data to advance cancer research
All submissions will undergo rigorous peer review, and accepted articles will be published as part of a special issue titled “Artificial Intelligence in Oncology.”
Read the full call for submissions to learn more.
About JMIR Publications:
JMIR Publications, celebrating its 25th anniversary in 2024, is a leading open access digital health research publisher. As a pioneer in open access publishing, JMIR Publications is committed to driving innovation in scholarly communications, advancing digital health research, and promoting open science principles. Our portfolio features 35 open access, peer-reviewed journals dedicated to the dissemination of high-quality research in the field of digital health, including the Journal of Medical Internet Research, as well as cross-disciplinary journals such as JMIR Research Protocols and the new title JMIR XR & Spatial Computing.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-07-11
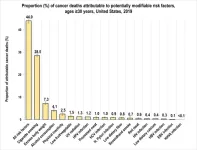
A new study led by researchers at the American Cancer Society (ACS) finds four in 10 cancer cases and about one-half of all cancer deaths in adults 30 years old and older in the United States (or 713,340 cancer cases and 262,120 cancer deaths in 2019) could be attributed to modifiable risk factors, including cigarette smoking, excess body weight, alcohol consumption, physical inactivity, diet, and infections. Cigarette smoking was by far the leading risk factor, contributing to nearly 20% of all cancer cases and 30% of all cancer deaths. The findings are ...
2024-07-11
The study by researchers from the French national public health institute aimed to identify priority pathogens that could be suitable for wastewater surveillance (WWS) during the Paris 2024 Olympic and Paralympic Games taking place from 26 July to 11 August and 28 August to 8 September, respectively. The pathogens were evaluated using a Delphi method which integrated evidence from peer-reviewed publications and expert opinion.
WWS has become more prominent due to its role during the COVID-19 pandemic. As a non-intrusive, cost-effective surveillance tool, WWS offers ...
2024-07-11
Dense E.coli bacteria have several similar qualities to colloidal glass, according to new research at the University of Tokyo. Colloids are substances made up of small particles suspended within a fluid, like ink for example. When these particles become higher in density and more packed together, they form a “glassy state.” When researchers multiplied E.coli bacteria within a confined area, they found that they exhibited similar characteristics. More surprisingly, they also showed some other unique properties not typically found in glass-state materials. This study contributes to our understanding of glassy “active matter,” a relatively new field of ...
2024-07-11
Weill Cornell Medicine has received $4.2 million to study how the immune system in some people infected with HIV can keep the virus under control, which could lead to novel therapeutic strategies for thwarting or eliminating HIV. Dr. Brad Jones, associate professor of immunology in medicine in the Division of Infectious Diseases at Weill Cornell Medicine, was awarded a MERIT grant from the National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) at the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
The “Method for Extending Research in Time” (MERIT) grant provides ...
2024-07-11
According to Science Alert, neuroscientists from Johns Hopkins University have recently discovered a new treatment for Parkinson's disease using an FDA-approved cancer drug. A recent study published in Neuroscience Bulletin reveals the genetic cause of Parkinson's disease. The study discovered that a mutation in the Cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase (CARS) gene (c.2384A>T; p.Glu795Val; E795V) is responsible, offering a new path for prevention and control of the disease. This research was conducted by a team led by Zhang Jianguo, including researcher ...
2024-07-11
People tend to become less narcissistic as they age from childhood through older adulthood, according to a study published by the American Psychological Association. However, differences among individuals remain stable over time -- people who are more narcissistic than their peers as children tend to remain that way as adults, the study found.
“These findings have important implications given that high levels of narcissism influence people’s lives in many ways -- both the lives of the narcissistic individuals themselves and, maybe even more, the lives of their families and friends,” said lead author Ulrich Orth, PhD, of the University of Bern in Switzerland.
The ...
2024-07-11
A group of scientists have released a landmark report on glacial geoengineering—an emerging field studying whether technology could halt the melting of glaciers and ice sheets as climate change progresses.
The white paper represents the first public efforts by glaciologists to assess possible technological interventions that could help address catastrophic sea-level rise scenarios.
While it does not endorse any specific interventions, it calls for a “major initiative” in the next decades to research which, if any, interventions could and should be ...
2024-07-11
New York, NY (July 11, 2024) – The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai is embarking on biomedical research aiming to set new standard-of-care protocols for treating alopecia areata and atopic dermatitis in people with Down syndrome, or trisomy 21.
Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, the Waldman Professor and Chair of Dermatology at Icahn Mount Sinai, has been awarded more than $4 million for a five-year National Institutes of Health (NIH) R61/R33 grant to evaluate the long-term safety, efficacy, and mechanisms of medications known as JAK inhibitors in patients with Down syndrome. The medications have been approved ...
2024-07-11
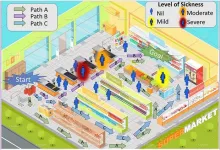
How do people like to interact with robots when navigating a crowded environment? And what algorithms should roboticists use to program robots to interact with humans?
These are the questions that a team of mechanical engineers and computer scientists at the University of California San Diego sought to answer in a study presented recently at the ICRA 2024 conference in Japan.
“To our knowledge, this is the first study investigating robots that infer human perception of risk for intelligent decision-making in everyday settings,” said Aamodh Suresh, first author of the study, who earned his Ph.D. in the research group of Professor Sonia Martinez Diaz ...
2024-07-11
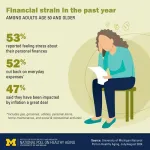
Inflation rates may have cooled off recently, but a new poll shows many older adults are experiencing financial stress – especially those who say they’re in fair or poor physical health or mental health.
Women and those age 50 to 64 are more likely than men or people over age 65 to report feeling a lot of stress related to their personal finances. So are people age 50 and older who say they’re in fair or poor physical or mental health.
In all, 47% of people age 50 and older said inflation had impacted them a great deal in the past year, and 52% said they ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] JMIR Bioinformatics and Biotechnology is inviting submissions for a new theme issue titled “Artificial Intelligence in Oncology”