(Press-News.org) People tend to become less narcissistic as they age from childhood through older adulthood, according to a study published by the American Psychological Association. However, differences among individuals remain stable over time -- people who are more narcissistic than their peers as children tend to remain that way as adults, the study found.
“These findings have important implications given that high levels of narcissism influence people’s lives in many ways -- both the lives of the narcissistic individuals themselves and, maybe even more, the lives of their families and friends,” said lead author Ulrich Orth, PhD, of the University of Bern in Switzerland.
The research was published in the journal Psychological Bulletin.
Orth and his colleagues analyzed data from 51 longitudinal studies, all of which measured how participants’ levels of narcissism changed over time. The studies comprised 37,247 participants (52% female and 48% male) ranging in age from 8 to 77. Some of the studies followed participants for decades. Most were conducted in the U.S., Canada and Western Europe, with one in China and one in New Zealand.
The researchers coded whether each study measured one or more of three different types of narcissism: agentic, antagonistic and neurotic. Agentic narcissism includes feelings of grandiosity or superiority and a strong need for admiration; antagonistic narcissism includes arrogance, entitlement, callousness and low empathy; and neurotic narcissism involves emotional dysregulation and hypersensitivity.
Overall, the researchers found that all three types of narcissism declined from childhood through old age, with a small decline for agentic narcissism and a moderate decline for antagonistic and neurotic narcissism.
The researchers also found, however, that people’s narcissism relative to that of their peers did not change significantly over time. In other words, people who were more narcissistic than average as children remained more narcissistic than average as adults.
“This was true even across very long periods of time, which suggests that narcissism is a stable personality trait,” Orth said.
Most of the data analyzed in the study were from the United States and Western Europe, so future research should examine narcissism across a broader range of countries and cultures, Orth said.
Future research should also aim to explore the reasons that narcissism declines with age, according to Orth. “One theory suggests that the social roles we take on in adulthood, for example as a partner, a parent, an employee and so on, lead to the development of more mature personality characteristics, including lower levels of narcissism,” he said.
ARTICLE: “Development of Narcissism Across the Life Span: A Meta-Analytic Review of Longitudinal Studies,” by Ulrich Orth, PhD, and Samantha Krauss, PhD, University of Bern; and Mitja D. Back, PhD, University of Münster. Psychological Bulletin,published online July 11, 2024.
CONTACT: Orth can be reached at ulrich.orth@unibe.ch.
The American Psychological Association, in Washington, D.C., is the largest scientific and professional organization representing psychology in the United States. APA’s membership includes over 157,000 researchers, educators, clinicians, consultants and students. Through its divisions in 54 subfields of psychology and affiliations with 60 state, territorial and Canadian provincial associations, APA works to advance the creation, communication and application of psychological knowledge to benefit society and improve lives.
END
Narcissism decreases with age, study finds
But people who are more narcissistic as children tend to remain so as adults
2024-07-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists call for ‘major initiative’ to study whether geoengineering should be used on glaciers
2024-07-11
A group of scientists have released a landmark report on glacial geoengineering—an emerging field studying whether technology could halt the melting of glaciers and ice sheets as climate change progresses.
The white paper represents the first public efforts by glaciologists to assess possible technological interventions that could help address catastrophic sea-level rise scenarios.
While it does not endorse any specific interventions, it calls for a “major initiative” in the next decades to research which, if any, interventions could and should be ...
Mount Sinai secures over $4 million grant from National Institutes of Health to study alopecia areata and atopic dermatitis in people with Down Syndrome
2024-07-11
New York, NY (July 11, 2024) – The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai is embarking on biomedical research aiming to set new standard-of-care protocols for treating alopecia areata and atopic dermatitis in people with Down syndrome, or trisomy 21.
Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, the Waldman Professor and Chair of Dermatology at Icahn Mount Sinai, has been awarded more than $4 million for a five-year National Institutes of Health (NIH) R61/R33 grant to evaluate the long-term safety, efficacy, and mechanisms of medications known as JAK inhibitors in patients with Down syndrome. The medications have been approved ...
How risk-averse are humans when interacting with robots?
2024-07-11
How do people like to interact with robots when navigating a crowded environment? And what algorithms should roboticists use to program robots to interact with humans?
These are the questions that a team of mechanical engineers and computer scientists at the University of California San Diego sought to answer in a study presented recently at the ICRA 2024 conference in Japan.
“To our knowledge, this is the first study investigating robots that infer human perception of risk for intelligent decision-making in everyday settings,” said Aamodh Suresh, first author of the study, who earned his Ph.D. in the research group of Professor Sonia Martinez Diaz ...
An unequal toll of financial stress: Poll of older adults shows different impacts related to health and age
2024-07-11
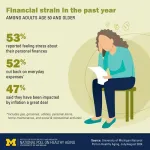
Inflation rates may have cooled off recently, but a new poll shows many older adults are experiencing financial stress – especially those who say they’re in fair or poor physical health or mental health.
Women and those age 50 to 64 are more likely than men or people over age 65 to report feeling a lot of stress related to their personal finances. So are people age 50 and older who say they’re in fair or poor physical or mental health.
In all, 47% of people age 50 and older said inflation had impacted them a great deal in the past year, and 52% said they ...
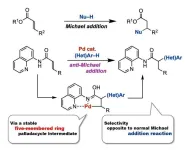
One-step synthesis of pharmaceutical building blocks: new method for anti-Michael reaction
2024-07-11
In 1887, chemist Sir Arthur Michael reported a nucleophilic addition reaction to the β-position of α,β- unsaturated carbonyl compounds. These reactions, named Michael addition reactions, have been extensively studied to date. In contrast, the anti-Michael addition reaction, referring to the nucleophilic addition reaction to the α-position, has been difficult to achieve. This is due to the higher electrophilicity of the β-position compared to the α-position. Previous attempts to overcome these difficulties have involved two main methods. The first is restricting the addition position via intramolecular reactions, ...
Urban seagulls still prefer seafood
2024-07-11
Seagull chicks raised on an “urban” diet still prefer seafood, new research shows.
University of Exeter scientists studied herring gull chicks that had been rescued after falling off roofs in towns across Cornwall, UK.
Raised in captivity (before being released), they were given either a “marine” diet consisting mainly of fish and mussels, or an “urban” diet containing mostly bread and cat food.
Every few days the gull chicks were presented with a choice of all four foods in different bowls, to test which they preferred – and all gulls strongly favoured fish.
“Our results suggest that, even when reared on an ‘urban’ ...
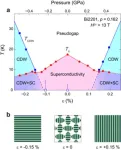
Understanding the origin of superconductivity in high-temperature copper oxide superconductors
2024-07-11
Superconductors are materials that can conduct electricity with zero resistance when cooled to a certain temperature, called the critical temperature. They have applications in many fields, including power grids, maglev trains, and medical imaging. High-temperature superconductors, which have critical temperatures higher than normal superconductors have significant potential for advancing these technologies. However, the mechanisms behind their superconductivity remain unclear.
Copper oxides or cuprates, a class of high-temperature superconductors, exhibit superconductivity ...
Shaping the future of polymer nanocarriers
2024-07-11
Scientists have taken a significant step towards the development of tailor-made chiral nanocarriers with controllable release properties. These nanocarriers, inspired by nature's helical molecules like DNA and proteins, hold immense potential for targeted drug delivery and other biomedical applications.
The study, led by Professors Emilio Quiñoá and Félix Freire at the Center for Research in Biological Chemistry and Molecular Materials (CiQUS), highlights the intricate relationship between the structure of helical polymers and their self-assembly into nanospheres. By carefully designing ...
2000th ERC Proof of Concept grant awarded
2024-07-11
The grants – each worth €150,000 – help researchers to bridge the gap between the discoveries stemming from their frontier research and the practical application of the findings, including early phases of their commercialisation.
Nanda Rea’s new project, called DeepSpacePULSE, aims to facilitate deep space exploration. Currently, to find their way, spacecraft and satellites use up a lot of energy exchanging vital navigation information with mission coordinators on Earth. Using ERC Proof of Concept funding, Prof. Nanda Rea ...
Wild plants and crops don’t make great neighbors
2024-07-11
Native plants and non-native crops do not fare well in proximity to one another, attracting pests that spread diseases in both directions, according to two new UC Riverside studies.
“We have changed the landscape, and it’s created opportunities for pathogens to thrive,” said UCR entomologist Kerry Mauck, who co-authored the studies. “We have introduced pathogens that damage native plants, and on the other side of the coin we have endemic pathogens that mutate to infect ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
[Press-News.org] Narcissism decreases with age, study findsBut people who are more narcissistic as children tend to remain so as adults