(Press-News.org) DURHAM, N.C. – Certain state gun laws are associated with decreased suicide rates for children under age 18, but the laws have little influence on homicide rates, according to a study from Duke Health researchers examining the relationship between gun laws and child deaths.
Since 2020, firearms rank as the leading cause of death among U.S. children ages 1-18, raising the need for research to help guide prevention efforts.
“Our analysis of suicide and homicide mortality data from 2009 to 2020 in children under 18 suggests that we do actually have some laws that work,” said Krista Haines, D.O., lead author of a study appearing July 11 in the Journal of the American College of Surgeons.
“But there are very few of these laws, and they only appear to work for suicide, not for homicide,” said Haines, an assistant professor in the departments of Surgery and Population Health Sciences at Duke University School of Medicine. “Our study clearly points to a need for more laws and controlled access to these guns, especially given the high rates of death among children in the United States.”
Haines and colleagues -- including senior author Suresh Agarwal, M.D., chief of the division of Trauma, Acute, and Critical Care Surgery at Duke -- used CDC data of pediatric firearm deaths between 2009-2020, analyzing them within the context of existing state laws governing firearms.
The study identified 36 firearm laws, including regulations for background checks, mandatory waiting periods, "stand your ground" laws that provide self-defense protections, safe storage provisions, and access prohibitions for people at risk of harming themselves or others.
From 2009-2020, there were 6,735 suicides and 10,278 homicides by firearm in the U.S., totaling 17,013 child deaths. Overlaid with the state law database, the researchers found:
States with safe storage laws and mandatory waiting periods demonstrated lower suicide mortality rates among children.
“Stand your ground” laws, prevalent in states with less restrictive firearm legislation, showed a correlation with higher suicide mortalities.
There were no significant reductions in suicide death rates in states with laws setting minimum ages for possession or purchase of firearms.
There were no notable distinctions between states with and without firearm laws for homicide mortality rates.
“It was surprising to me that no laws appear to be impacting the rates of homicide in children, not even safe access,” Haines said. “It’s sad and shocking.”
The researchers said the dearth of studies about the impact of gun access in the United States has been an impediment to finding workable solutions, noting that the U.S. accounts for over 90% of pediatric firearm deaths worldwide. Additionally, firearm violence has markedly increased by more than 15% over the past 4 years.
“This is a very early study, and we need to continue to use this kind of research to advance better policies,” Agarwal said. “What we have in place now has limited impact, particularly with regard to homicides.”
In addition to Agarwal and Haines, study authors include Laura Gorenshtein, Kavneet Kaur, Braylee Grisel, Bradley Kawano, Harold Leraas, Jennifer Freeman, Todd Tripoli, and Joseph Fernandez-Moure.
Duke’s trauma division funded the study.
###
END
About The Study: Substance use treatment facilities reported significant gaps in provision of effective treatments for opioid use disorder (OUD). More than one-third of facilities did not offer medications for OUD (MOUD) and less than half offered multiple MOUD types, limiting MOUD treatment options for patients and clinicians.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Tae Woo Park, M.D., M.Sc., email parkt4@upmc.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.11913)
Editor’s ...
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study of U.S. children, nicotine absorption was much lower in children who were exposed to secondhand vapor versus secondhand smoke, but higher than in those exposed to neither. These findings suggest that switching from smoking to vaping indoors may substantially reduce, but not eliminate, children’s secondhand exposure to nicotine and other noxious substances.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Harry Tattan-Birch, Ph.D., email h.tattan-birch@ucl.ac.uk.
To ...
About The Study: This comparative effectiveness research study demonstrated that self-fit over-the-counter hearing aids can offer comparable long-term benefits to audiologist-fit hearing aids for individuals with mild to moderate hearing loss.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Karina C. De Sousa, Ph.D., email karina.swanepoel@up.ac.za.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2024.1825)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
Children exposed to vaping indoors absorb less than one seventh the amount of nicotine as children who are exposed to indoor smoking, but more than those exposed to neither, according to a new study led by UCL researchers.
The study, published in JAMA Network Open and funded by Cancer Research UK, looked at blood tests and survey data for 1,777 children aged three to 11 in the United States.
The researchers said that second-hand exposure to harmful substances in e-cigarettes would likely be much lower still, as e-cigarettes deliver similar levels of nicotine to tobacco but contain only a fraction of the toxicants and ...
– By William Ferguson
When it comes to figuring out why electric aircraft batteries lose power over time, one typically wouldn’t think to turn to a decades-old approach biologists use to study the structure and function of components in living organisms. However, it turns out that omics, a field that helped scientists unravel the secrets of the human genome, could also soon play a key role in making carbon-free air travel a reality.
In a new study in the journal Joule, a team of researchers led ...
Images
A battery component innovation could help keep power delivery high when electric aircraft land with low charge, according to a study led by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory with expertise from the University of Michigan.
The research provides a solution to a problem identified in 2018 in a study led by Venkat Viswanathan, a professor of aerospace engineering at U-M and a coauthor of the new work published in Joule.
"Both takeoff and landing require high power, and landing is more challenging because you’re not fully charged," Viswanathan said. "To get high power you ...
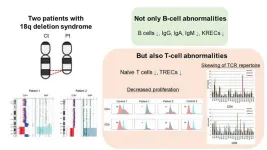
Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) researchers have discovered that patients with 18q deletion syndrome can experience both cellular and humoral immunodeficiency
Tokyo, Japan – Chromosome 18q deletion (18q del) syndromeis a rare genetic condition disorder, affecting approximately 1 in 40,000 to 55,000 individuals, caused by the deletion of genetic material on the long arm of chromosome 18. This genetic anomaly disrupts normal growth and development, and critically, can impair the immune system's functionality. Patients with 18q del syndrome often exhibit humoral immunodeficiency or a common ...
On June 30, 2024, SciOpen 2.0 was officially launched. Developed by Tsinghua University Press, SciOpen initially made its debut in June 2022 as an international digital publishing platform for STM journals. After two years of global operation and continuous iterative upgrades, SciOpen 2.0 has fully embraced the best practices of mainstream publishing models. SciOpen has completed a comprehensive upgrade of its interactive system design and has integrated advanced large-model AI reading capabilities, marking a significant leap forward in its functionality.
These updates steer SciOpen towards ...
(Toronto, July 11, 2024) JMIR Publications invites submissions to a new theme issue titled “Artificial Intelligence in Oncology” in its premier open access journal JMIR Bioinformatics and Biotechnology indexed in PubMed Central and PubMed, SCOPUS, Sherpa/Romeo, DOAJ and EBSCO/EBSCO Essentials.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to revolutionize oncology by enhancing diagnostic accuracy, personalizing treatment plans, predicting patient outcomes, and accelerating drug discovery. Researchers, clinicians, and industry experts are invited ...
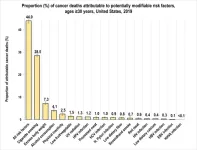
A new study led by researchers at the American Cancer Society (ACS) finds four in 10 cancer cases and about one-half of all cancer deaths in adults 30 years old and older in the United States (or 713,340 cancer cases and 262,120 cancer deaths in 2019) could be attributed to modifiable risk factors, including cigarette smoking, excess body weight, alcohol consumption, physical inactivity, diet, and infections. Cigarette smoking was by far the leading risk factor, contributing to nearly 20% of all cancer cases and 30% of all cancer deaths. The findings are ...