(Press-News.org) About The Study: In this cross-sectional study, the expression of several stress-related genes in prostate tumors was higher among men residing in disadvantaged neighborhoods. This study is one of the first to suggest associations of neighborhood disadvantage with prostate tumor RNA expression. Additional research is needed in larger studies to replicate findings and further investigate interrelationships of neighborhood factors, tumor biology, and aggressive prostate cancer to inform interventions to reduce disparities.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Kathryn Hughes Barry, Ph.D., M.P.H., email kbarry@som.umaryland.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.21903)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.21903?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=071224
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Neighborhood disadvantage and prostate tumor RNA expression of stress-related genes
JAMA Network Open
2024-07-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Screen media use and mental health of children and adolescents
2024-07-12
About The Study: This secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial found that a short-term reduction in leisure-time screen media use within families positively affected psychological symptoms of children and adolescents, particularly by mitigating internalizing behavioral issues and enhancing prosocial behavior. More research is needed to confirm whether these effects are sustainable in the long term.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jesper Schmidt-Persson, Ph.D., email jesp@kp.dk.
To ...
Mediterranean diet and cardiometabolic biomarkers in children and adolescents
2024-07-12
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that Mediterranean diet-based interventions may be useful tools to optimize cardiometabolic health among children and adolescents.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jose Francisco Lopez-Gil, Ph.D., email josefranciscolopezgil@gmail.com.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.21976)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
A chemical claw machine bends and stretches when exposed to vapors
2024-07-12
Scientists at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) in Saudi Arabia have developed a tiny “claw machine” that is able to pick up and drop a marble-sized ball in response to exposure to chemical vapors.
The findings, published July 12 in the journal Chem, point to a technique that can enable soft actuators—the parts of a machine that make it move—to perform multiple tasks without the need for additional costly materials. While existing soft actuators can be “one-trick ponies” restricted to one type of movement, this novel composite film contorts itself ...
Living in disadvantaged neighborhoods influences stress-related genes, which may contribute to aggressive prostate cancer in African American men
2024-07-12
BALTIMORE, MD, July 12, 2024 — Those living in disadvantaged neighborhoods have significantly higher activity of stress-related genes, new research suggests, which could contribute to higher rates of aggressive prostate cancer in African American men. The study, which was co-led by the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) and Virginia Commonwealth University (VCU), was published today in JAMA Network Open.
African American men have a higher incidence of prostate cancer and are more than twice as likely to die from the disease than White men in the U.S. They are often diagnosed with an ...
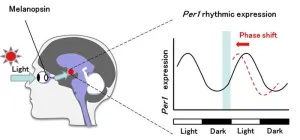
Melanopsin DNA aptamers can regulate input signals of mammalian circadian rhythms by altering the phase of the molecular clock
2024-07-12
Overview:
DNA aptamers of melanopsin that regulate the clock hands of biological rhythms were developed by the Toyohashi University of Technology and the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) group.
DNA aptamers can specifically bind to biomolecules to modify their function, potentially making them ideal oligonucleotide therapeutics. We screened the DNA aptamer melanopsin (OPN4), a blue light photopigment in the retina that plays a key role in the use of light signals to reset the phase of circadian rhythms in the central clock.
First, 15 DNA aptamers of melanopsin (Melapts) were identified following eight rounds of Cell-SELEX ...
Challenges and prospects for post-conflict peacebuilding in urban settings
2024-07-12
Wars and conflicts leave devastating destruction in their wake. With so many conflicts now taking place in urban environments, scientists are studying how post-conflict peacebuilding happens in these urban settings. Dahlia Simangan, an associate professor at The IDEC Institute, Hiroshima University, has analyzed the case of Marawi, a city in the Philippines, to better understand the urban environment’s influence on post-siege reconstruction and peacebuilding. This study contributes to a more comprehensive understanding of peacebuilding by integrating conventional peacebuilding components and urban characteristics.
The findings are published ...
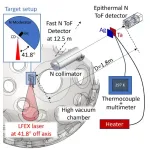
Neutrons give a hot new way to measure the temperature of electronic components
2024-07-12
Osaka, Japan – From LEDs to batteries, our lives are full of electronics, and there is a constant push to make them more efficient and reliable. But as components become increasingly sophisticated, getting reliable temperature measurements of specific elements inside an object can be a challenge.
This is problematic because measuring a device’s temperature is vital for monitoring its performance or designing the materials from which it’s manufactured. Now, in a new study led by Osaka ...
High and low tide cause low and high methane fluxes
2024-07-12
High and low tide cause low and high methane fluxes
Methane, a strong greenhouse gas that naturally escapes from the bottom of the North Sea, is affected by the pressure of high or low tide. Methane emissions from the seafloor can be just easily three times as much or as little, depending on the tide. This is shown by NIOZ oceanographer Tim de Groot, in a publication in Nature Communications Earth and Environment. "Our research shows that you can never rely on one measurement when you want to know how much methane escapes from the seafloor," De Groot emphasizes.
Swamp ...
A better way to make RNA drugs
2024-07-12
While the COVID-19 vaccines introduced many people to RNA-based medicines, RNA oligonucleotides have already been on the market for years to treat diseases like Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and amyloidosis. RNA therapies offer many advantages over traditional small molecule drugs, including their ability to address almost any genetic component within cells and to guide gene editing tools like CRISPR to their targets.
However, the promise of RNA is currently limited by the fact that rapidly growing global demand is outpacing the industry’s ability to manufacture it. The standard method of chemically ...
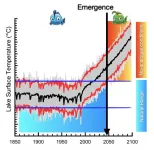
Unprecedented warming threatens earth’s lakes and their ecosystems
2024-07-12
Lakes, with their rich biodiversity and important ecological services, face a concerning trend: rapidly increasing temperatures. A recent study published in Nature Geoscience by an international team of limnologists and climate modelers reveals that if current anthropogenic warming continues until the end of this century, lakes worldwide will likely experience pervasive and unprecedented surface and subsurface warming, far outside the range of what they have encountered before.
The study uses lake temperature ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
[Press-News.org] Neighborhood disadvantage and prostate tumor RNA expression of stress-related genesJAMA Network Open