(Press-News.org) Most influenza viruses enter human or animal cells through specific pathways on the cells’ surface. Researchers at the University of Zurich have now discovered that certain human flu viruses and avian flu viruses can also use a second entry pathway, a protein complex of the immune system, to infect cells. This ability helps the viruses infect different species – and potentially jump between animals and humans.
The majority of type A influenza viruses circulating in birds and pigs aren’t normally a health risk for humans. However, the viruses may pose a threat if there is an outbreak like the one currently in dairy cattle in the US or during seasonal epidemics. In rare cases, a virus can jump from animals to humans – with potentially devastating consequences such as a global pandemic.
Additional receptor offers alternative entry pathway
Most influenza viruses enter host cells by using their envelope proteins, which stand up from the surface like spikes. The so-called hemagglutinin binds to sialic acid, a chemical group on the surface of human cells and the cells of various animal species. An international research team led by Professor Silke Stertz from the Institute of Medical Virology at the University of Zurich (UZH) has now shown that flu viruses also have a second method to infect host cells. “Human influenza A viruses of subtype H2N2 and related H2N2 avian influenza viruses can enter cells through a second receptor. They use an alternative entry pathway,” says Stertz.
The researchers found that hemagglutinin also binds to MHC class II protein complexes. These complexes on the surface of certain immune and respiratory cells are responsible for differentiating between the body’s own cells and foreign cells. “We found that MHC class II complexes in humans, pigs, ducks, swans and chickens allow viruses to enter cells, but not those in bats,” says Stertz.
Transmission from animals to humans likely
This dual ability to infect cells was observed in lab-grown cell lines and human airway cultures. How well the viral receptor fits onto the cell surface structures plays a crucial part in determining which host species and tissues are infected and ultimately how severe the infection will be. Receptor specificity also influences whether a virus is able to infect different animal species or even humans (zoonosis). “Our finding shows that influenza viruses can adapt to use different entry pathways. This might influence their ability to infect different species and potentially jump between animals and humans,” emphasizes the UZH virologist.
The risk that avian, swine and other animal influenza viruses could trigger a flu pandemic in humans may thus be greater than previously assumed. The ability to use MHC class II proteins for cell entry could have been one of the reasons why H2N2 influenza viruses emerged as a pandemic virus in Asia back in 1957. This is another good reason to step up global influenza surveillance in both animals and humans.
END
Influenza viruses can use two ways to infect cells
2024-07-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Engineering resilience: Advanced FEM enhances earthquake impact assessment
2024-07-17
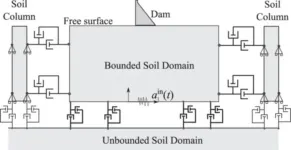
In a significant advancement for geotechnical engineering, a refined space-time finite element method (v-ST/FEM) has been introduced to tackle the complex dynamics of soil-structure interaction during seismic events. This new approach allows for more accurate simulations of the response of earth structures to earthquake vibrations, marking a crucial step in improving infrastructure resilience against natural disasters.
Designing structures like dams, tunnels, and embankments to withstand transient loads from sources such as earthquakes, high-speed trains, and explosions requires robust dynamic soil-structure interaction (SSI) analysis. Traditional methods often fall short in handling ...
The Vps21 signaling pathway regulates white-opaque switching and mating in Candida albicans
2024-07-17
This study was led by Dr. Guanghua Huang (School of Life Sciences, Fudan University). The team discovered that the conserved Vps21 signaling pathway plays critical roles in the regulation of white-opaque switching and mating in Candida albicans, a major human fungal pathogen.
Candida albicans is able to cause cutaneous diseases as well as life-threatening systemic infections in humans. It has multiple cellular morphologies and can undergo transitions among different morphologies to adapt to environmental changes. White-opaque transitions represent a typical morphological phenotypic switching system ...
Autoantibodies behind lifelong risk of viral infections
2024-07-17
A new study shows that about two percent of the population develop autoantibodies against type 1 interferons, mostly later in life. This makes individuals more susceptible to viral diseases like COVID-19. The study, conducted by UZH researchers together with a USZ team, is based on an analysis of a large collection of historical blood samples.
Virus infections trigger the cells of the immune system to release type 1 interferons. These proteins act as early messengers that warn uninfected cells and tissues that a virus is spreading. This allows ...
Heritable chronic cholestatic liver diseases
2024-07-17
Chronic cholestasis, defined as the impairment of bile acid formation and/or flow persisting for more than six months, encompasses a broad spectrum of hepatobiliary disorders, both heritable and acquired. This review focuses on heritable causes of chronic cholestasis, which, although less common, present significant clinical challenges. Heritable chronic cholestatic liver diseases are typically diagnosed in childhood, but many cases present and persist into adulthood. This review aims to highlight the genetics, clinical pathophysiology, presentation, ...
What fat cats on a diet may tell us about obesity in humans
2024-07-17
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Pet cats may be excellent animal models for the study of obesity origins and treatment in humans, a new study of feline gut microbes suggests – and both species would likely get healthier in the research process, scientists say.
Veterinary researchers analyzed fecal samples from fat cats as the animals lost and maintained weight over the course of four dietary changes, including strict calorie reduction. The team found that food-related changes to the cats’ gut microbiome – the assortment ...
Designing safer opioids
2024-07-17
Opioid medications offer people relief from debilitating pain, but these drugs come with dangers: the risk for addiction, miserable withdrawal symptoms and the potential for fatal overdose. In a study in ACS Central Science, researchers have identified a strategy to design safer opioids. They showed that an experimental opioid, which binds to an unconventional spot in the receptor, suppresses pain in animal models with fewer side effects — most notably those linked to fatal overdoses.
Opioid medications tap into the body’s natural system for mitigating pain by activating pain-suppressing ...
Completely stretchy lithium-ion battery for flexible electronics
2024-07-17
When you think of a battery, you probably don’t think stretchy. But batteries will need this shape-shifting quality to be incorporated into flexible electronics, which are gaining traction for wearable health monitors. Now, researchers in ACS Energy Letters report a lithium-ion battery with entirely stretchable components, including an electrolyte layer that can expand by 5000%, and it retains its charge storage capacity after nearly 70 charge/discharge cycles.
Electronics that bend and stretch need batteries with similar properties. Most researchers who have ...
New opportunity to improve diagnosis, care for people with cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome
2024-07-17
DALLAS, July 17, 2024 — About 1 in 3 U.S. adults have at least three risk factors for cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) syndrome, a health disorder related to the strong connections among cardiovascular disease, kidney disease and metabolic disease (such as Type 2 diabetes and obesity).[1] Yet there is no single clinical practice guideline to treat people with CKM syndrome, and gaps exist in preventing, screening, managing and comprehensively treating these diseases.
To address this complex health threat, the American Heart Association, ...
Stress-related cell damage linked to negative mental and physical health effects among caregivers
2024-07-17
It’s no secret that the caregivers of spouses with memory impairment face enormous amounts of stress. Researchers at Rice University have found that this intense pressure can be felt at the cellular level and is linked to negative physical and mental health effects, including dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.
The study titled “Mitochondrial health, physical functioning, and daily affect: Bioenergetic mechanisms of dementia caregiver well-being,” is published online ...
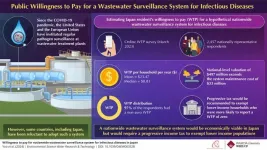
Understanding willingness to pay for nationwide wastewater surveillance in Japan
2024-07-17
Globally, the COVID-19 pandemic and the increased likelihood of other such outbreaks in the future warrant the strengthening of epidemic surveillance systems. Among these, continuous wastewater surveillance at wastewater treatment plants is considered more advantageous for understanding the community-level disease dynamics, as compared to clinical surveillance. This is because such a continuous system captures the epidemic status of a larger population without any selection bias and provides higher testing capacity even during an outbreak. Moreover, such a system is relatively inexpensive. ...