(Press-News.org) The Gerontological Society of America (GSA) — the nation’s largest interdisciplinary organization devoted to the field of aging — has chosen Jiska Cohen-Mansfield, PhD, FGSA, of Tel Aviv University as the 2024 recipient of the Robert W. Kleemeier Award.
This distinguished honor is given annually to a GSA member in recognition for outstanding research in the field of gerontology. It was established in 1965 in memory of Robert W. Kleemeier, PhD, a former president of the Society whose contributions to the quality of life through research in aging were exemplary.
The award presentation will take place at GSA’s 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting, which will be held from November 13 to 16 in Seattle, Washington. This conference is organized to foster interdisciplinary collaboration among researchers, educators, and practitioners who specialize in the study of the aging process.
At Tel Aviv University, Cohen-Mansfield is a professor in the Department of Health Promotion, which she founded in 2005 within the School of Public Health, and co-director of the Minerva Center for Interdisciplinary Studies of the End of Life, which she established in 2011.
She previously served as a professor at Georgetown University Medical School and The George Washington University Medical School. In 1984, she founded the Research Institute on Aging at the Hebrew Home of Greater Washington, the largest nursing home in Maryland.
Cohen-Mansfield has authored over 350 peer-reviewed papers, 45 book chapters and 17 psychological assessments along with editing 10 books and monographs. Her research has been cited more than 41,000 times.
The impact of her work is at the heart of the person-centered care movement, which is integral to the philosophy of caring for individuals in long-term care. She introduced the Cohen-Mansfield Agitation Inventory and Agitation Mapping Instrument. This work was transformational within long term care. Her model divided behaviors into aggressive/nonaggressive and verbal/vocal—physical. She developed tools to measure agitation through informants, observation, and technology. In total she created 17 different assessment instruments linked to this and other critical issues in gerontology.
Cohen-Mansfield is one of the leading researchers in non-pharmacological interventions. She has been a major contributor to the restraint reduction and elimination programs in long-term care and the de-emphasis on using medications to reduce agitated behaviors. She developed interventions for loneliness and to enhance quality of life at the end of life. A review of her work in the community indicated that her research had major impacts on areas such as physical activity, loneliness, end of life care, pain, and non-pharmacological interventions.
Cohen-Mansfield is a GSA fellow, which represents the highest category of membership within the Society, as well as a fellow of the American Psychological Association. She has received many additional honors, including the Busse Research Award, the Barry Reisberg Award for Alzheimer's Research, the Pfizer Quality Improvement Award, the Psychologists in Long-Term Care Outstanding Contribution Award, the Powell Lawton Distinguished Contribution Award in Applied Gerontology, the International Psychogeriatric Association 2015 Award for Distinguished Service to the Field of Psychogeriatrics.
She studied psychology and statistics at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem and earned her master's degree in statistics from Hebrew University as well as another master's degree and a PhD degree in clinical psychology from the State University of New York at Stony Brook. Later she earned an MBA from The George Washington University.
###
The Gerontological Society of America (GSA) is the nation's oldest and largest interdisciplinary organization devoted to research, education, and practice in the field of aging. The principal mission of the Society — and its 5,500+ members — is to advance the study of aging and disseminate information among scientists, decision makers, and the general public. GSA’s structure includes a nonpartisan public policy institute, the National Academy on an Aging Society, and GSA is also home to the National Center to Reframe Aging and the National Coordinating Center for the Resource Centers for Minority Aging Research.
END
The Gerontological Society of America (GSA) — the nation’s largest interdisciplinary organization devoted to the field of aging — has chosen Lisa L. Barnes, PhD, FGSA, of Rush University Medical Center as the 2024 recipient of the James Jackson Outstanding Mentorship Award.
This distinguished honor is given annually and recognizes individuals who have exemplified outstanding commitment and dedication to mentoring minority researchers in the field of aging. It was renamed in 2021 in memory of James Jackson, PhD, FGSA, a pioneering psychologist ...
The Science
Polyphenols are a diverse group of organic compounds produced by plants. These compounds are often toxic to microorganisms. In peatlands, scientists thought that microorganisms avoided this toxicity by degrading polyphenols using an enzyme that requires oxygen. However, when there is little or no oxygen, like after flooding due to climate induced thawing, the enzyme is inactive, and polyphenols accumulate. This inhibits microbes’ carbon cycling. In this study, scientists mined data for thousands of microbial genomes recovered from Stordalen Mire, an Arctic peatland in Sweden. They discovered that these microorganisms used alternative polyphenol-active ...
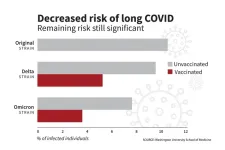
The risk of developing long COVID has decreased significantly over the course of the COVID-19 pandemic, according to an analysis of data led by Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
Researchers attributed about 70% of the risk reduction to vaccination against COVID-19 and 30% to changes over time, including the SARS-CoV-2 virus’s evolving characteristics and improved detection and management of COVID-19.
The research is published July 17 in The New England Journal of Medicine.
“The research on declining rates ...
The University of Freiburg is establishing a new tenure track professorship in Earth and Planetary Geodynamics at the Faculty of Environment and Natural Resources, made possible by a 1.71 million euro grant from the Volkswagen Foundation. The new tenure track professorship is part of a comprehensive strategic initiative for combining Earth system sciences with planetary sciences at the University that also includes the establishment of a new Earth System Simulation Lab (EaSySim) and the introduction of an Earth Sciences ...
A research team at the Texas A&M School of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences (VMBS) has received a $5 million grant from the United States Department of Defense’s Defense Threat Reduction Agency to support the detection and prevention of brucellosis in Armenia.
Brucellosis, which is caused by several bacterial species of Brucella, is a zoonotic disease that can spread to humans from dogs and major livestock species, including cattle, pigs, sheep, and goats. It can have a major impact on a country’s public health and agricultural economy.
The team of Texas A&M researchers, led by VMBS Associate Professor Dr. Angela Arenas, will ...
MINNEAPOLIS – For people with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (MS), a new study has found that the drug ofatumumab is more effective than teriflunomide at helping people across racial and ethnic groups reach a period of no disease activity. The study is published in the July 17, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. Ofatumumab, a monoclonal antibody, is a newer drug for treating MS. Teriflunomide, an immunomodulatory agent, has been available for over a decade.
MS is a disease in ...
MINNEAPOLIS – Insurance coverage, ethnicity and location may all play a role in a person’s ability to receive care after a stroke, according to a study published in the July 17, 2024, online issue of Neurology® Clinical Practice, an official journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
“Receiving the right care after a stroke is crucial to recovery and minimizing disability,” said study author Shumei Man, MD, PhD, of the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio and a member of the American Academy of Neurology. “Unfortunately, decisions about care may be influenced by factors such as race, insurance, and geographic location. Our study ...
A majority of people in Afghanistan support human rights for Afghan women, and men are especially likely to support women’s rights when primed to think about their eldest daughters, according to a study published July 17, 2024, in the open-access journal PLOS ONE, by Kristina Becvar and colleagues from the University of Massachusetts at Amherst.
Human rights groups have been concerned for the rights of Afghan women in particular since the Taliban took control of Kabul in 2021. Since then, Afghan ...
Scientists at the University of Sydney and Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine have made a remarkable discovery: a commonly used blood thinner, heparin, can be repurposed as an inexpensive antidote for cobra venom.
Cobras kill thousands of people a year worldwide and perhaps a hundred thousand more are seriously maimed by necrosis – the death of body tissue and cells – caused by the venom, which can lead to amputation.
Current antivenom treatment is expensive and does not effectively ...
Have you ever wondered how insects are able to go so far beyond their home and still find their way? The answer to this question is not only relevant to biology but also to making the AI for tiny, autonomous robots. TU Delft drone-researchers felt inspired by biological findings on how ants visually recognize their environment and combine it with counting their steps in order to get safely back home. They have used these insights to create an insect-inspired autonomous navigation strategy for tiny, lightweight robots. The strategy allows such robots to come back home after long trajectories, while requiring extremely little computation and memory (0.65 kiloByte per ...