(Press-News.org) Philadelphia, July 18, 2024 – Accumulating evidence on the effect of the time of eating in relation to our circadian rhythm and metabolism shows that when we eat may influence our overall health and well-being. A special issue of the Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics (JAND) on chrononutrition, published by Elsevier, examines the effects of various fasting regimens and covers safety considerations and practical guidance.
The field of chrononutrition is gaining traction as it explores the relationship between temporal eating patterns, circadian rhythms, and metabolism for optimal health.
Guest Editor Krista Varady, PhD, Department of Kinesiology and Nutrition, University of Illinois Chicago, specializes in studying the efficacy of intermittent fasting for weight loss, weight management, and lowering the risk of metabolic diseases in obese adults. With more than 15 years of research experience, she is recognized as one of the top researchers in this field.
Dr. Varady says, "Intermittent fasting has emerged as one of the most popular diets for weight loss in recent years. The diet can be defined, in basic terms, as periods of eating, alternated with periods of not eating. This special issue examines the effects of various fasting regimens, such as time-restricted eating, alternate day fasting, and the 5:2 diet, on body weight, cardiometabolic disease risk, and sleep and exercise performance in human subjects. Pertinent safety considerations and practical guidance on applying the diets are also covered."
Editor-in-Chief of JAND, Linda G. Snetselaar, PhD, RDN, FAND, LD, a professor in the Department of Epidemiology at the University of Iowa, adds, "The findings presented in this special issue have important clinical implications. I believe the timing of eating will become increasingly important as we address dietary interventions related to chronic disease risk factors."
The special issue includes the novel study "Randomized Controlled Feasibility Trial of Late 8-Hour Time-Restricted Eating for Adolescents With Type 2 Diabetes," in which researchers examine the feasibility of eating within an 8-hour window as an interventional strategy for weight loss and glucose management among adolescents diagnosed with obesity and new-onset type 2 diabetes, compared with a prolonged eating window.
Lead investigator Alaina P. Vidmar, MD, Children’s Hospital Los Angeles and Keck School of Medicine of USC, explains, "The prevalence of type 2 diabetes in adolescents is steadily increasing, specifically among historically marginalized communities. Many adolescents prefer to go to bed later and sleep in later, so an early eating window may not align with developmental and social schedules that often shift their food consumption to later in the day. We trialed a late eating window for our cohort and found that late time-restricted eating is safe and acceptable for this subset of adolescents as it can result in clinically meaningful weight loss, reduction in alanine transaminase, and significant caloric reduction; it did not negatively impact sleep, eating behaviors, or physical activity."
Another paper, "Indices of Sleep Health Are Associated With Timing and Duration of Eating in Young Adults," details findings from a cross-sectional study among 52 young adults without chronic diseases or conditions on whether timing and/or duration of eating behaviors throughout the day affect sleep health.
Lead investigator Jess A. Gwin, PhD, Military Nutrition Division, U.S. Army Research Institute of Environmental Medicine, says, "Breakfast skipping and nighttime eating are among typical eating behaviors observed in young adults in the United States. Our study found that the timing of eating was associated with sleep-wake onset and sleep efficiency. This highlights the need for additional studies to understand whether manipulating the timing of eating occasions to better align with sleep-wake cycles could improve sleep health."
Interventions tailored to individuals’ preferences and circumstances may benefit time-restricted eating adherence, according to the article "Time-Restricted Eating in Community-Dwelling Adults: Correlates of Adherence and Discontinuation in a Cross-Sectional Online Survey Study.” Leader of the research team Sydney G. O’Connor, PhD, Office of Behavioral and Social Sciences Research, National Institutes of Health, notes, "Dietary adherence is the strongest predictor of successful weight loss and maintenance; therefore, identifying dietary strategies that facilitate adherence is a priority in the field of behavioral weight management. We looked at motivators such as weight maintenance, health (not weight), improved sleep, disease prevention, and drivers such as the ability to work from home and the impact of COVID-19."
Dr. Varady concludes, "Many people stop adhering to standard diets that restrict calories because they become frustrated with having to regularly monitor food intake day in and day out. Intermittent fasting protocols can bypass this requirement by allowing participants to simply ‘watch the clock’ instead of monitoring calories, while still producing weight loss. Furthermore, intermittent fasting does not require the purchase of expensive food products and allows individuals to continue consuming familiar foods, making it a highly accessible diet, especially for lower resource patient groups. Although fasting regimens are no more effective than other diet interventions for weight management, these protocols offer individuals an alternative, straightforward approach to addressing obesity by omitting the need for calorie counting. While weight loss is important, having a diet with a wide variety of nutrient dense foods such as fruits, vegetables and legumes is paramount in maintaining a replete nutritional status. These foods can be both inexpensive and culturally appropriate."
END
When you eat may impact your overall health, nutrition experts say
A special issue of the Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics on chrononutrition demystifies the science behind the efficacy of fasting regimes
2024-07-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researcher receives NASA funding to study ozone pollution
2024-07-18
NORMAN, OKLA. – University of Oklahoma professor Chenghao Wang has received three years of funding through the National Aeronautics and Space Administration Early Career Investigator Program in Earth Science. Wang, an assistant professor in both the OU School of Meteorology and the Department of Geography and Environmental Sustainability, will study compound heat and ozone pollution episodes in urban environments.
Heat waves and air pollution are two increasingly occurring challenges that disproportionately impact urban areas. When multiple stressor events happen simultaneously, these compound events can have more significant impacts than isolated events. ...
New ECDC Director Pamela Rendi-Wagner emphasises importance of restoring and reinforcing public trust in science after pandemic, in editorial for Eurosurveillance
2024-07-18
In an editorial for the scientific journal Eurosurveillance, the incoming ECDC Director Dr Pamela Rendi Wagner outlined her vision for the European Union’s public health agency, highlighting the mounting challenges to public health after the COVID-19 pandemic, including war in Europe, climate change, and increasing social inequalities. She also emphasised the importance of reinforcing and restoring public trust in science.
Current challenges in public health
“War, flooding and the effects of ...
In China, property rights take wrong turn
2024-07-18
In China, Property Rights Take Wrong Turn
Protecting them fueled an economic boom; eroding them risks long-term damage
AUSTIN, Texas — China’s economy, long an engine of world growth, has been sputtering lately. During the second quarter of 2024, it grew at an annual rate of 4.7% — down from an average 7% a year during the past decade. For the next two years, the International Monetary Fund forecasts more of the same.
Analysts have blamed China’s slowdown on short-term factors, such as debt-ridden real estate and a delayed recovery from the COVID-19 ...
Solar farms with stormwater controls mitigate runoff, erosion, study finds
2024-07-18
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — As the number of major utility-scale ground solar panel installations grows, concerns about their impacts on natural hydrologic processes also have grown. However, a new study by Penn State researchers suggests that excess runoff or increased erosion can be easily mitigated — if these “solar farms” are properly built.
Solar panels are impervious to water, and vast arrays of them, it was feared, could increase the volume and velocity of stormwater runoff similar ...
Drexel team identifies drug-like molecules that show early success in targeting breast cancer brain metastases
2024-07-18
Researchers from Drexel’s College of Medicine have identified new drugs that show early success in shrinking breast cancer tumors that have metastasized in the brain. The discovery marks the first time that targeting a key metabolic enzyme in cancer cells in the brain has shrunk tumors in a mouse model. The findings, which could develop into more effective therapies for breast cancer brain metastases, were recently published in the journal Frontiers in Pharmacology.
Brain tumor growth depends on converting an energy source for the brain known as acetate, to acetyl-CoA — a molecule involved in biochemical reactions in carbohydrates, ...
Archivist explores Troy's invisible workers
2024-07-18
While poring over nearly century-old photos documenting the University of Cincinnati’s historic excavation at Troy, archivist Jeff Kramer was struck by just how many people worked behind the scenes for years to contribute to its success.
The archivist and research associate in UC’s Department of Classics created a digital archive of pictures and documents from UC archaeologist Carl Blegen’s influential 1930s project that identified nine periods of reconstruction and evidence of a great battle and fiery devastation that some historians said was suggestive of the ransacking of Troy.
But ...
Stretchable electronics might make their way onto the market thanks to roll-to-roll process
2024-07-18
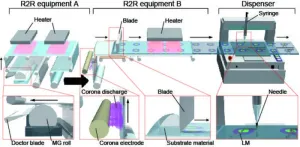
Electronics have evolved over the years to supersede simply enhancing day-to-day life to becoming almost seamlessly integrated with daily life. People have become accustomed to wearable electronics, but what about stretchable ones? There is a growing demand for this type of technology, but the current methods are not easily scalable for mass production to make these devices available to the public. However, mass development may be possible using the roll-to-roll (R2R) process, which prints various layers on a flexible rolled substrate, cutting out the manual nature of the process. By rolling this type of electronic out into the market, the possibility for stretchable electronics and even ...
From roots to leaves: The nitrogen connection to photosynthetic efficiency
2024-07-18
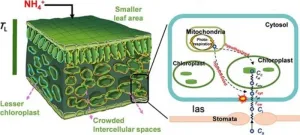
Delving into the nuances of plant nutrition, researchers have discovered that the form of nitrogen intake profoundly affects the efficiency of photosynthesis in plants. This pivotal finding sheds light on how plants process and utilize nitrogen, offering critical insights for enhancing crop productivity and optimizing nitrogen use in agriculture.
Photosynthesis efficiency in plants is influenced by the type of nitrogen absorbed. Ammonium (NH4+) and nitrate (NO3-) are the primary nitrogen sources, each affecting plant physiology differently. Variations in leaf anatomy, such as cell wall thickness and chloroplast number, play a crucial role in ...
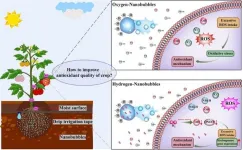
Bubbling with benefits: Hydrogen nanobubbles boost tomato antioxidants
2024-07-18
A pioneering study has unlocked the potential of hydrogen nanobubbles to significantly augment the antioxidant content in tomatoes. This innovative irrigation technique not only fortifies the fruit with higher concentrations of health-boosting compounds but also opens new avenues for enhancing the nutritional value of agricultural produce. The research provides a blueprint for leveraging hydrogen's unique properties to combat oxidative stress and promote a healthier diet.
Tomatoes are a key source ...
Engineering: Tool predicts rogue waves up to 5 minutes in advance
2024-07-18
A new tool that can be used to predict the emergence of unusually large and unpredictable waves at sea — known as rogue waves — up to five minutes into the future is presented in a study published in Scientific Reports. The authors suggest that the tool could be used to issue advance warnings to ships and offshore platforms to enable those working on them to seek shelter, perform emergency shutdowns, or manoeuvre to minimise the impacts of approaching rogue waves.
The tool developed by Thomas Breunung and Balakumar Balachandran consists of a neural network that has been trained ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
DGIST identifies “magic blueprint” for converting carbon dioxide into resources through atom-level catalyst design
COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy may help prevent preeclampsia
Menopausal hormone therapy not linked to increased risk of death
Chronic shortage of family doctors in England, reveals BMJ analysis
Booster jabs reduce the risks of COVID-19 deaths, study finds
Screening increases survival rate for stage IV breast cancer by 60%
ACC announces inaugural fellow for the Thad and Gerry Waites Rural Cardiovascular Research Fellowship
University of Oklahoma researchers develop durable hybrid materials for faster radiation detection
Medicaid disenrollment spikes at age 19, study finds
Turning agricultural waste into advanced materials: Review highlights how torrefaction could power a sustainable carbon future
New study warns emerging pollutants in livestock and aquaculture waste may threaten ecosystems and public health
Integrated rice–aquatic farming systems may hold the key to smarter nitrogen use and lower agricultural emissions
Hope for global banana farming in genetic discovery
Mirror image pheromones help beetles swipe right
Prenatal lead exposure related to worse cognitive function in adults
Research alert: Understanding substance use across the full spectrum of sexual identity
Pekingese, Shih Tzu and Staffordshire Bull Terrier among twelve dog breeds at risk of serious breathing condition
Selected dog breeds with most breathing trouble identified in new study
Interplay of class and gender may influence social judgments differently between cultures
Pollen counts can be predicted by machine learning models using meteorological data with more than 80% accuracy even a week ahead, for both grass and birch tree pollen, which could be key in effective
Rewriting our understanding of early hominin dispersal to Eurasia
Rising simultaneous wildfire risk compromises international firefighting efforts
Honey bee "dance floors" can be accurately located with a new method, mapping where in the hive forager bees perform waggle dances to signal the location of pollen and nectar for their nestmates
Exercise and nutritional drinks can reduce the need for care in dementia
Michelson Medical Research Foundation awards $750,000 to rising immunology leaders
SfN announces Early Career Policy Ambassadors Class of 2026
Spiritual practices strongly associated with reduced risk for hazardous alcohol and drug use
Novel vaccine protects against C. diff disease and recurrence
An “electrical” circadian clock balances growth between shoots and roots
Largest study of rare skin cancer in Mexican patients shows its more complex than previously thought
[Press-News.org] When you eat may impact your overall health, nutrition experts sayA special issue of the Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics on chrononutrition demystifies the science behind the efficacy of fasting regimes