(Press-News.org) About The Study: In this randomized study, individuals who received a cash benefit had significantly fewer emergency department visits, including those related to behavioral health and substance use, fewer admissions to the hospital from the emergency department, and increased use of outpatient subspecialty care. Study results suggest that policies that seek to alleviate poverty by providing income support may have important benefits for health and access to care.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Sumit D. Agarwal, M.D., M.P.H., Ph.D., email sagarwal14@bwh.harvard.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.13004)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/10.1001/jama.2024.13004?guestAccessKey=3eda559a-ddf8-4c8d-963b-9b42a2e2396f&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=072224
END
Effect of cash benefits on health care utilization and health
JAMA
2024-07-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mendelian randomization analysis for intestinal disease: Achievement and future
2024-07-22
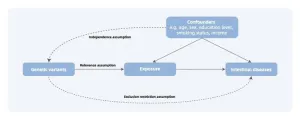
Traditional epidemiological studies have identified numerous potential risk factors, but observational studies have struggled to establish causal links due to confounding factors and reverse causation. Theoretically avoiding confounding and reverse causation, Mendelian randomization (MR) infers causality, offering novel research perspectives and methods for investigating risk factors of intestinal diseases (Figure 1).
MR research on intestinal disease
Based on MR methodology, researchers have identified lifestyle factors, circulating nutrients, and obesity as being associated with the risk of ...
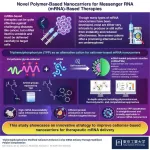
Improving the design of mRNA-loaded nanocarriers for targeted therapies
2024-07-22
Among the vastly different ways of tackling a disease, controlling the genetic expression of cells is undoubtedly one of the most powerful. Over the past few decades, scientists have come up with dozens of innovative strategies that involve using messenger RNA (mRNA) to ‘force’ cells to build specific proteins. These mRNA-based therapies have recently gained prominence as vaccines against infectious diseases like COVID-19. Additionally, they hold significant potential for treating cancer and genetic disorders.
Since mRNA itself is ...
Chimpanzees gesture back and forth quickly like in human conversations
2024-07-22
When people are having a conversation, they rapidly take turns speaking and sometimes even interrupt. Now, researchers who have collected the largest ever dataset of chimpanzee “conversations” have found that they communicate back and forth using gestures following the same rapid-fire pattern. The findings are reported on July 22 in the journal Current Biology.
“While human languages are incredibly diverse, a hallmark we all share is that our conversations are structured with fast-paced turns of just 200 milliseconds on average,” ...
Deep-ocean floor produces its own oxygen
2024-07-22
An international team of researchers, including a Northwestern University chemist, has discovered that metallic minerals on the deep-ocean floor produce oxygen — 13,000 feet below the surface.
The surprising discovery challenges long-held assumptions that only photosynthetic organisms, such as plants and algae, generate Earth’s oxygen. But the new finding shows there might be another way. It appears oxygen also can be produced at the seafloor — where no light can penetrate — to support the oxygen-breathing (aerobic) sea life living in complete darkness.
The ...
Prenatal cannabis use and maternal pregnancy outcomes
2024-07-22
About The Study: The results of this cohort study suggest that prenatal cannabis use was associated with several adverse maternal health outcomes during pregnancy. Continued research is needed to understand whether characteristics of prenatal cannabis use (e.g., dose, mode, and timing) moderate these associations.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Kelly C. Young-Wolff, Ph.D., M.P.H., email kelly.c.young-wolff@kp.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
Prevalence of epilepsy in people of sexual and gender minoritized groups
2024-07-22
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that sexual and gender minority adults in the U.S. have a disproportionate prevalence of epilepsy. The reasons for this disparity are likely complex and may be associated with biological and psychosocial determinants of health unique to this population; as such, these individuals are in need of protected access to medical care.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Emily L. Johnson, M.D., M.P.H., email ejohns92@jhmi.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2024.2243)
Editor’s ...
Overground gait training with a wearable robot in children with cerebral palsy
2024-07-22
About The Study: In this randomized clinical trial, overground robot-assisted gait training using a wearable robot significantly improved gross motor function and gait pattern. This new torque-assisted wearable exoskeletal robot, based on assist-as-needed control, may complement standard rehabilitation by providing adequate assistance and therapeutic support to children with cerebral palsy.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Min-Keun Song, M.D., Ph.D., email drsongmk@chonnam.ac.kr.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our ...
Sexual and gender minorities are twice as likely to report active epilepsy
2024-07-22
What:
Sexual and gender minorities (SGM)—individuals who identify as gay, lesbian, bisexual, queer, transgender, non-binary, or gender-diverse—are twice as likely to report active epilepsy compared to non-SGM individuals, based on a National Institutes of Health (NIH) analysis of data from the population-based National Health Information Survey. “Active epilepsy” means a person has been diagnosed with epilepsy and has had more than one seizure in the past year or is currently taking anti-seizure medication.
This study suggests that epilepsy could be added to the growing ...
SARS-CoV-2 pandemic increases maternal deaths from non-respiratory causes, study finds
2024-07-22
During the peak of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, there was an increase in maternal mortality in Chile. This is confirmed by a natural population experiment based on data from the Department of Health Statistics and Information (DEIS) of the Chilean Ministry of Health. The research was published in PLOS Global Public Health.
In a collaborative study, led by Professor Elard Koch, senior epidemiologist and founder of MELISA Institute (Chile), and conducted with a team of researchers from the Universidad Católica Sedes Sapientiae (Peru), the Pontificia Universidad ...
New precision medicine guidelines to improve patient care
2024-07-22
A University of Virginia School of Medicine scientist and other top experts from around the world have developed the first comprehensive guidelines for reporting cutting-edge “precision medicine” research in a bid to improve patient care and health equity for people everywhere.
Precision medicine aims to tailor treatments to individual patients to get the best possible outcomes. It does this by considering many different factors specific to the patient, such as the patient’s genetics, environment, lifestyle and more. But until now there have been no standardized guidelines for reporting precision ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Effect of cash benefits on health care utilization and healthJAMA