(Press-News.org) Guides typically assist tourists with directions, but the experience could be greatly enhanced if they offered personalized services tailored to individual interests. Recently, researchers have transformed guide RNAs, which direct enzymes, into a smart RNA capable of controlling networks in response to various signals. This innovative research is gaining significant attention in the academic community.
A research team consisting of Professor Jongmin Kim and PhD candidates Hansol Kang and Dongwon Park from the Department of Life Sciences at POSTECH has developed a multi-signal processing guide RNA. This guide RNA can be programmed to logically regulate gene expression. Their findings were recently published in Nucleic Acids Research, an international journal of molecular biology and biochemistry.
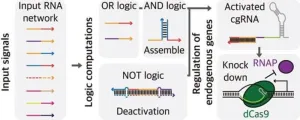
The CRISPR/Cas system, often referred to as "gene scissors," is a technology capable of editing gene sequences to add or delete biological functions. Central to this technology, which is used in several fields such as treating genetic diseases and genetically engineering crops, is a guide RNA that directs the enzyme to edit the gene sequence at a specific location. While advances in RNA engineering have spurred research into guide RNAs that respond to biological signals, achieving precise control of networks of genes to respond to multiple signals has remained challenging.
In this study, the team combined the CRISPR/Cas system with biocomputing to overcome these limitations. Biocomputing is a technology that connects biological components like electronic circuits to program cellular and organismal activities. The researchers implemented a guide RNA gene circuit capable of decision-making based on inputs, similar to a Boolean logic gate, which is one of the fundamental representations of input-output relationships in digitized signal operations.
The team successfully controlled essential genes involved in E. coli metabolism and cell division, demonstrating the capability to combine multiple logic gates for processing various signals and complex inputs. They used this circuit to control cell morphology and metabolic flows at the appropriate level.
This study is significant because it integrates existing systems and technologies to precisely control gene networks, enabling the processing, integration, and response to diverse signals within an organism. This goes beyond the role of guide RNAs in merely directing enzymes to specific locations.
Professor Jongmin Kim of POSTECH stated, “The research could enable the precise design of gene therapies based on biological signals within complex genetic circuits involved in disease.” He added, "RNA molecular engineering allows for the simplicity of software-based structure design which will significantly advance the development of personalized treatments for cancer, genetic disorders, metabolic diseases, and more."
The research was conducted with grants from the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea, and support from the LINC Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea and the Ministry of Education, a program of Korea Basic Science Institute and LINC 3.0 sponsored by the Ministry of Education, the Korea Health Technology R&D Program of the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), the Program for Fostering and Supporting Food Tech R&D Centers of North Gyeongsang Province and Pohang, and IBS POSTECH.
END
Could smart guide RNAs usher in an era of personalized medicine?
2024-07-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Recent progress on VOC pollution control via the catalytic method
2024-07-23
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs), with toxicity and irritability, could cause atmospheric environmental problems such as haze and photochemical smog, seriously threatening the ecological environment and human health. The primary source of VOCs is human production, such as the petrochemical industry, pharmaceutical industry, footwear industry, electronic manufacturing, and cooking fumes. Catalytic oxidation technology can highly effectively remove organic pollutants without secondary pollution, and it is receiving increasing attention in VOC pollution control. In real-world operating conditions, the ...
Stabilizing perovskite solar cells in hot and humid conditions
2024-07-23
HONG KONG (21 July 2024) --- The progress of solar energy technology took a step forward recently with the development of a groundbreaking living passivator at City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK) that can substantially enhance the stability and efficiency of perovskite solar cells.
This newly developed passivator is a type of corrosion inhibitor that appreciably changes the potential of a metal. The CityUHK technology leverages dynamic covalent bonds that activate on exposure to moisture and heat, enabling it to evolve new passivators in response to environmental factors.
This innovative approach allows for real-time repair and maintenance of perovskite solar cells. ...
Trajectory of type 1 diabetes risk shifts after age 10 years between at-risk males and females
2024-07-23
New research presented at this year’s Annual Meeting of the European Association for Study of Diabetes (Madrid, Spain, 9-13 September) shows that the risk of developing type 1 diabetes (T1D) decreases markedly in girls after age 10 years, while the risk in boys stays the same.
Furthermore, risk of T1D is significantly higher boys with a single autoantibody than their female counterparts, suggesting the sex could be linked with autoantibody development, indicating the importance of incorporating sex in the assessment ...
Long-term sulfonylurea use linked to higher risk of low blood sugar unawareness in type 2 diabetes patients
2024-07-22
Background and Goal: Sulfonylureas are a class of oral medications used to manage blood glucose levels in patients with type 2 diabetes. These drugs increase insulin production regardless of blood sugar levels. For this reason, the drugs can cause blood sugar to drop too low, leading to hypoglycemia. The goal of this study was to compare how prevalent impaired awareness of hypoglycemia was when patients with type 2 diabetes were treated with either insulin or sulfonylureas for both long and short-term periods.
Study Approach: Researchers collected data from a group of 898 participants with type 2 diabetes enrolled in pharmacies, clinics, ...
Health care providers weigh in on their experiences developing an AI tool to understand primary care patients’ social determinants of health
2024-07-22
Background and Goal: Social determinants of health are the conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age. These conditions include income, education, and access to health care. Knowledge of these factors is essential for primary care clinicians to deliver fair and complete care, plan programs and distribute resources effectively. However, this information is rarely captured consistently in clinical settings. This study identified how an Artificial Intelligence (AI) social determinants of health tool can be designed using a collaborative design strategy with input from primary care team members.
Study Approach: ...
Pandemic’s impact on primary care: Significant drop in visits and uneven telehealth use across patient groups
2024-07-22
Background and Goal: The COVID-19 pandemic likely worsened disparities in access to primary care. The goal of this study was to quantify the nationwide decline in primary care visits and the increase in telehealth utilization and explore whether certain groups of patients were disproportionately impacted.
Study Approach: Researchers used primary care electronic health record data from the American Family Cohort— to examine the percentage change in total visit volume, change in in-person visit volume, and telehealth ...
Transforming clinical practice initiative linked to reduced emergency department visits
2024-07-22
Background and Goal: The Transforming Clinical Practice Initiative was a four-year nationwide program aimed at improving outpatient health care quality. The initiative, funded by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, also prepared practices for payment systems based on care quality rather than service quantity and included a Change Package to guide practice transformations. This research brief examines whether these transformations were associated with reductions in emergency department visits among both primary and specialty care practices.
Study Approach: Researchers analyzed data from 3,773 practices in the Transforming Clinical Practice ...
Dutch version of the person-centered primary care measure survey demonstrates sufficient validity and sufficient reliability for use in Dutch primary care practices
2024-07-22
Person-centered care focuses on treating patients as individuals with unique needs and involving them actively in their care decisions. The Person-Centered Primary Care Measure (PCPCM) is a recently developed, patient-reported survey able to assess person-centeredness. The PCPCM has demonstrated strong validity and reliability. The goal of this study was to translate the original PCPCM survey into Dutch, adapt the survey for people with low literacy, and evaluate its structure, consistency, and accuracy.
Study Approach: The survey was translated into Dutch and then back to English to ensure accuracy. The Dutch version was then tested to make sure it worked well for Dutch-speaking ...
Sexual and gender minority adults avoid necessary care due to identity discordance with clinicians and experiences of discrimination
2024-07-22
Background and Goal: Identity discordance between patients and clinicians is associated with worse self-rated patient experience and less receipt of necessary care. Most prior studies have focused on racial discordance. However, whether these phenomena also apply to sexual and gender minority adults is currently unknown. This study evaluated how prevalent avoidance due to patient-clinician identity discordance is and its potential association with health care discrimination among sexual and gender minority ...
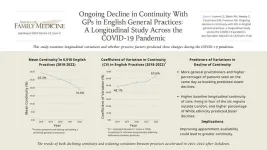
Pandemic lockdown exacerbated ongoing declines in continuity of care within English general practices
2024-07-22
Background and Goal: Longitudinal continuity of care is the repeated contact between an individual and the same general practitioner (GP). This type of continuity of care is widely regarded as a cornerstone of primary care. Higher levels of longitudinal continuity of care are associated with better health outcomes, greater patient satisfaction, and more cost-effective use of health care resources. This study aimed to describe more recent variations between practices in the slopes of longitudinal continuity of care levels across the COVID-19 pandemic. The study also set out to determine if practice-related ...