(Press-News.org) Background and Goal: Social determinants of health are the conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age. These conditions include income, education, and access to health care. Knowledge of these factors is essential for primary care clinicians to deliver fair and complete care, plan programs and distribute resources effectively. However, this information is rarely captured consistently in clinical settings. This study identified how an Artificial Intelligence (AI) social determinants of health tool can be designed using a collaborative design strategy with input from primary care team members.
Study Approach: Semi-structured, 50-minute workshops were conducted with the St. Michael’s Hospital Academic family health team in Toronto, Ontario, Canada from May to June 2023. Participants were asked for their feedback on a proposed AI-based tool that derives patient social determinants of health from electronic health record (EHR) data.
Main Results:
15 participants of the health team participated across 4 workshops.
Participants reported that most patient information was not available or difficult to find in their EHR.
Participants recommended starting with 1-2 social determinants (such as income and housing). They also emphasized the need for adequate resources, staff, and training materials.
Many challenges were reported, including how to discuss the use of AI with patients and confirm their social needs identified by the AI tool.
Why It Matters: The integration of AI into health care is rapidly advancing, presenting both opportunities and challenges. This study provides valuable insights from end users on the meaningful design and implementation of an AI-based tool for social data in primary care. The AI-based tool can potentially improve patient care and reduce clinician burnout.
Developing an AI Tool to Derive Social Determinants of Health for Primary Care Patients: Qualitative Findings From a Codesign Workshop
Stephanie Garies, PhD, et al
Department of Family & Community Medicine, St. Michael’s Hospital, Unity Health Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
PRE-EMBARGO LINK (Link expires at 5 p.m. July 22nd, 2024)
PERMANENT LINK
END
Health care providers weigh in on their experiences developing an AI tool to understand primary care patients’ social determinants of health
2024-07-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Pandemic’s impact on primary care: Significant drop in visits and uneven telehealth use across patient groups
2024-07-22
Background and Goal: The COVID-19 pandemic likely worsened disparities in access to primary care. The goal of this study was to quantify the nationwide decline in primary care visits and the increase in telehealth utilization and explore whether certain groups of patients were disproportionately impacted.
Study Approach: Researchers used primary care electronic health record data from the American Family Cohort— to examine the percentage change in total visit volume, change in in-person visit volume, and telehealth ...
Transforming clinical practice initiative linked to reduced emergency department visits
2024-07-22
Background and Goal: The Transforming Clinical Practice Initiative was a four-year nationwide program aimed at improving outpatient health care quality. The initiative, funded by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, also prepared practices for payment systems based on care quality rather than service quantity and included a Change Package to guide practice transformations. This research brief examines whether these transformations were associated with reductions in emergency department visits among both primary and specialty care practices.
Study Approach: Researchers analyzed data from 3,773 practices in the Transforming Clinical Practice ...
Dutch version of the person-centered primary care measure survey demonstrates sufficient validity and sufficient reliability for use in Dutch primary care practices
2024-07-22
Person-centered care focuses on treating patients as individuals with unique needs and involving them actively in their care decisions. The Person-Centered Primary Care Measure (PCPCM) is a recently developed, patient-reported survey able to assess person-centeredness. The PCPCM has demonstrated strong validity and reliability. The goal of this study was to translate the original PCPCM survey into Dutch, adapt the survey for people with low literacy, and evaluate its structure, consistency, and accuracy.
Study Approach: The survey was translated into Dutch and then back to English to ensure accuracy. The Dutch version was then tested to make sure it worked well for Dutch-speaking ...
Sexual and gender minority adults avoid necessary care due to identity discordance with clinicians and experiences of discrimination
2024-07-22
Background and Goal: Identity discordance between patients and clinicians is associated with worse self-rated patient experience and less receipt of necessary care. Most prior studies have focused on racial discordance. However, whether these phenomena also apply to sexual and gender minority adults is currently unknown. This study evaluated how prevalent avoidance due to patient-clinician identity discordance is and its potential association with health care discrimination among sexual and gender minority ...
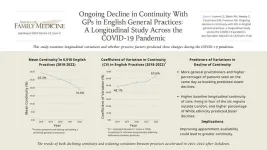
Pandemic lockdown exacerbated ongoing declines in continuity of care within English general practices
2024-07-22
Background and Goal: Longitudinal continuity of care is the repeated contact between an individual and the same general practitioner (GP). This type of continuity of care is widely regarded as a cornerstone of primary care. Higher levels of longitudinal continuity of care are associated with better health outcomes, greater patient satisfaction, and more cost-effective use of health care resources. This study aimed to describe more recent variations between practices in the slopes of longitudinal continuity of care levels across the COVID-19 pandemic. The study also set out to determine if practice-related ...
July/August Annals of Family Medicine Tip Sheet
2024-07-22
Original Research
Structural Racism and Inconsistent Hospital Policies Result in Health Care Professionals Disproportionately Testing Black Newborns for Prenatal Drug Exposure
Background and Goal: Black birthing parents and their newborns disproportionately experience newborn drug testing for prenatal substance exposure by health care professionals. This practice contributes to Child Protective Services reporting, family separation, and termination of parental rights. This qualitative study, conducted at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, MI, explored knowledge, attitudes, and experiences ...
Teens benefit from a new primary care virtual driving assessment model
2024-07-22
Integrating driving support into a primary care setting can address a leading cause of family stress as well as teen adolescent morbidity and mortality. Motor vehicle crashes are a leading cause of death for adolescents, and a leading cause of crashes is driver error. To address this, researchers at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania implemented a 15-minute self-administered virtual driving assessment test in 19 primary care practices. 3,037 adolescents 15 years and older completed the virtual driving ...
Implementing diabetic retinopathy screening using in-clinic retinal photographs and automated software analysis increases screening rates for diabetic retinopathy among low-income minority patients
2024-07-22
One-third of diabetic adults in the U.S. do not receive annual eye exams. Additionally, lack of pupillary dilation before exams is associated with ungradable, or insufficient exams. In September 2022, the OhioHealth Grant Medical Center Family Medicine practice implemented on-site diabetic retinopathy screening using digital fundus photography and automated retinal imaging without dilation. The practice later introduced eye dilation for specific patients.
By identifying patients needing screening before appointments and using electronic health record reminders, the clinic increased the rate of interpretable exams from 20% in November 2022 to 35% in May 2023. That same month, the ...
Structural racism and inconsistent hospital policies result in health care professionals disproportionately testing black newborns for prenatal drug exposure
2024-07-22
Background and Goal: Black birthing parents and their newborns disproportionately experience newborn drug testing for prenatal substance exposure by health care professionals. This practice contributes to Child Protective Services reporting, family separation, and termination of parental rights. This qualitative study, conducted at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, MI, explored knowledge, attitudes, and experiences of health care professionals and Child Protective Services professionals regarding the influence of structural ...
Study examines the impact of social connections and professional networks of NAPCRG members in driving scientific success
2024-07-22
Background and Goal: This study marks the 50th anniversary of the North American Primary Care Research Group (NAPCRG)—the premiere primary care research organization, particularly in family medicine—by examining social connections among members.
Study Approach: Researchers used social network analysis to characterize individual members and the relational structure among NAPCRG community members.
The study invited 5,905 current and past NAPCRG members and participants. The survey, based on the validated Program to Analyze, Record, and Track Networks to Enhance Relationships ...