(Press-News.org) Surveys conducted in England in 1999, 2004, and 2017 have revealed that children with a psychiatric disorder in 2017 experienced more severe difficulties and greater impacts on functioning at school, home, and in their daily lives, compared with children with a disorder in earlier decades. The findings come from a study published in the Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry.
The study used data from interviews and questionnaires completed by parents, children (if they were aged ≥ 11 years), and teachers across all 3 surveys.
The increased difficulties found in the study were specific to self- and parent-reports and were not found when assessing teacher reports.
Ethnic minority status, living in rented accommodations, and being in the lowest income quintile had weaker associations with psychiatric disorders in 2017 compared with 1999.
“Our study reveals a really concerning trend: children of today are experiencing a much greater burden of problems compared with previous generations,” said corresponding author Jessica Armitage, PhD, of Cardiff University, in the UK. “It is crucial that research investigates why this might be, so that we can understand the type and levels of support needed to prevent further negative trends.”
URL upon publication: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jcpp.14040
Additional Information
NOTE: The information contained in this release is protected by copyright. Please include journal attribution in all coverage. For more information or to obtain a PDF of any study, please contact: Sara Henning-Stout, newsroom@wiley.com.
About the Journal
The Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry is widely recognised to be the leading international journal covering both child and adolescent psychology and psychiatry. With a large and expanding global readership, its coverage includes studies on pediatric epidemiology, diagnosis, psychotherapeutic and psychopharmacological treatments, behaviour, cognition, neuroscience, neurobiology, and genetic aspects of childhood disorders.
About Wiley
Wiley is a knowledge company and a global leader in research, publishing, and knowledge solutions. Dedicated to the creation and application of knowledge, Wiley serves the world’s researchers, learners, innovators, and leaders, helping them achieve their goals and solve the world's most important challenges. For more than two centuries, Wiley has been delivering on its timeless mission to unlock human potential. Visit us at Wiley.com. Follow us on Facebook, X, LinkedIn and Instagram.
END
Have the burdens of childhood mental health conditions changed over time in England?
2024-07-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How to eliminate racial disparities in colon cancer
2024-07-24
A new paper in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, published by Oxford University Press, finds that eliminating the race disparity in colon cancer testing in the United States would reduce colon cancer, and colon cancer death rates, dramatically among Black people.
Colorectal cancer rates and deaths from the disease have decreased over time, but racial disparities remain and are significant. Compared to White Americans, Black Americans experience higher rates of colorectal cancer incidence and lower survival rates. Black adults are approximately 23% more likely to receive a colorectal cancer diagnosis than White adults. They are also about 31% more likely to ...
Cook like a Neanderthal: Scientists try to replicate ancient butchering methods to learn how Neanderthals ate birds
2024-07-24
It's hard to know what Neanderthals ate: food preparation, especially when it comes to smaller items like birds, can leave few archaeological traces. But understanding their diets is critical to understanding these incredibly adaptable hominins, who thrived for hundreds of thousands of years in wildly varied environments. To learn what food preparation could look like in the archaeological record, scientists tried cooking like Neanderthals.
“Using a flint flake for butchering required significant precision and effort, which we had not fully valued before this experiment,” said Dr Mariana Nabais of the Institut ...
New study finds alarming rise in persistent ‘forever chemicals’ in pesticides
2024-07-24
WASHINGTON — A peer-reviewed study published today in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives has found that per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), known as “forever chemicals,” are increasingly being added to U.S. pesticide products, contaminating waterways and posing potential threats to human health.
The study, Forever Pesticides: A Growing Source of PFAS Contamination in the Environment, is the first-ever comprehensive review of the many ways PFAS are introduced into U.S. pesticide products. Pesticides containing PFAS are used throughout the country on staple ...
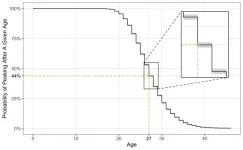
At what age do Olympic athletes peak?
2024-07-24
There’s a lot that goes into an Olympic athlete’s quest for gold – years of training and rigour – but also, an athlete’s age. A team of University of Waterloo students used statistics to figure out when an Olympic track-and-field athletes’ peak performance will be.
Track-and-field encompasses running, jumping, throwing, and combined event disciplines. Most athletes’ career performance progressions can typically be visualized as a bell curve, in which they train over several years to reach their best performance, or “peak,” at a ...
Link found between kneecap shape and debilitating joint disease
2024-07-24
The shape of a person’s kneecap could be an indicator of whether they’re more at risk of developing osteoarthritis, according to a new study from The Australian National University (ANU).
According to lead author of the study, Associate Professor Laura Wilson, women who develop knee osteoarthritis often experience more severe symptoms than men, but the reason for this is not well understood. Osteoarthritis, the most common form of arthritis, is a debilitating joint disease that causes pain, stiffness and swelling.
The research team set out to investigate whether kneecap shape might be a contributing factor.
“We wanted to focus on ...
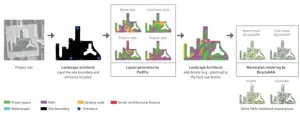
Generative AI tools like Pix2Pix–BicycleGAN are revolutionizing landscape design by enhancing masterplan generation and rendering
2024-07-24
In recent years, the rapid development and enhancement of image generation technologies and mapping tools driven by generative artificial intelligence (AI) have significantly impacted the traditional landscape design industry. Thus, it is pressing for landscape architects to delineate the relationship between image generation and landscape design and explore potential opportunities of practice and research. Research on masterplan generation primarily focuses on “image-to-image” generative adversarial network (GAN). The application of these tools has developed from the generation of architectural floor ...
Expanding APAC presence, Insilico Medicine seals strategic collaboration on AI-driven mash therapy development with Korean Biotech Therasid Bioscience
2024-07-24
Insilico Medicine(“Insilico”), a clinical-stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven drug discovery company, recently announces that the company has entered a strategic collaboration with Therasid Bioscience, an innovative biotechnology company founded in South Korea, to utilize advanced AI technology to co-develop novel therapies for the treatment of metabolic dysfunction associated steatohepatitis (MASH).
MASH, previously known as Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), is a severe form of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), characterized by liver inflammation and damage caused by a buildup of fat. Potentially progressing ...
When it comes to butterflies, people prefer pretty ones. That’s a problem for scientists.
2024-07-24
Research shows humans often perceive attractive people as more intelligent, healthier, better leaders and more trustworthy. It turns out this bias extends to the insect world.
A new study by scientists at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences reveals that data reported on a popular community science platform is biased. On iNaturalist, butterflies with captivating markings, easily identifiable features or those that are familiar species are reported more frequently than obscure species with no distinct qualities.
Why it matters: Online ...
UBC Okanagan study raises concerns about partner violence in queer relationships
2024-07-24
When people think of a concussion or a traumatic brain injury caused by intimate partner violence (IPV), they might picture people in a heterosexual relationship, or a man hurting a woman.
But a UBC Okanagan researcher points out that IPV, and its repercussions, is an issue in all relationships. Doctoral student Tori Stranges recently published a paper examining the prevalence and damage done by violence in Two-Spirit, Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Trans, Queer (or Questioning), Intersex and Asexual (2SLGBTQIA+) relationships.
“It’s very common for people to think that violence doesn’t ...
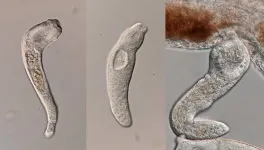
Human-infecting parasite produces sterile soldiers like ants and termites
2024-07-24
New research from scientists at UC San Diego’s Scripps Institution of Oceanography finds a tiny freshwater parasite known to cause health problems in humans defends its colonies with a class of soldiers that cannot reproduce.
The discovery, published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences and funded by the National Institutes of Health, vaults this species of parasitic flatworm into the ranks of complex animal societies such as ants, bees and termites, which also have distinct classes of workers and soldiers that have given up reproduction to serve their colony.
When it gets into humans, usually via the consumption of raw or undercooked fish, this species ...