(Press-News.org) An international team of astronomers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has directly imaged an exoplanet roughly 12 light-years from Earth. The planet, Epsilon Indi Ab, is one of the coldest exoplanets observed to date.
The planet is several times the mass of Jupiter and orbits the K-type star Epsilon Indi A (Eps Ind A), which is around the age of our Sun, but slightly cooler. The team observed Epsilon Indi Ab using the coronagraph on Webb’s MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument). Only a few tens of exoplanets have been directly imaged previously by space- and ground-based observatories.
“Our prior observations of this system have been more indirect measurements of the star, which actually allowed us to see ahead of time that there was likely a giant planet in this system tugging on the star,” said team member Caroline Morley of the University of Texas at Austin. “That's why our team chose this system to observe first with Webb.”
“This discovery is exciting because the planet is quite similar to Jupiter — it is a little warmer and is more massive, but is more similar to Jupiter than any other planet that has been imaged so far,” added lead author Elisabeth Matthews of the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy in Germany.
Previously imaged exoplanets tend to be the youngest, hottest exoplanets that are still radiating much of the energy from when they first formed. As planets cool and contract over their lifetime, they become significantly fainter and therefore harder to image.
A Solar System Analog
“Cold planets are very faint, and most of their emission is in the mid-infrared,” explained Matthews. “Webb is ideally suited to conduct mid-infrared imaging, which is extremely hard to do from the ground. We also needed good spatial resolution to separate the planet and the star in our images, and the large Webb mirror is extremely helpful in this aspect.”
Epsilon Indi Ab is one of the coldest exoplanets to be directly detected, with an estimated temperature of 35 degrees Fahrenheit (2 degrees Celsius) — colder than any other imaged planet beyond our solar system, and colder than all but one free-floating brown dwarf. The planet is only around 180 degrees Fahrenheit (100 degrees Celsius) warmer than gas giants in our solar system. This provides a rare opportunity for astronomers to study the atmospheric composition of true solar system analogs.
“Astronomers have been imagining planets in this system for decades; fictional planets orbiting Epsilon Indi have been the sites of Star Trek episodes, novels, and video games like Halo,” added Morley. “It's exciting to actually see a planet there ourselves, and begin to measure its properties.”
Not Quite As Predicted
Epsilon Indi Ab is the twelfth closest exoplanet to Earth known to date and the closest planet more massive than Jupiter. The science team chose to study Eps Ind A because the system showed hints of a possible planetary body using a technique called radial velocity, which measures the back-and-forth wobbles of the host star along our line of sight.
“While we expected to image a planet in this system, because there were radial velocity indications of its presence, the planet we found isn’t what we had predicted,” shared Matthews. “It’s about twice as massive, a little farther from its star, and has a different orbit than we expected. The cause of this discrepancy remains an open question. The atmosphere of the planet also appears to be a little different than the model predictions. So far we only have a few photometric measurements of the atmosphere, meaning that it is hard to draw conclusions, but the planet is fainter than expected at shorter wavelengths.”
The team believes this may mean there is significant methane, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide in the planet’s atmosphere that are absorbing the shorter wavelengths of light. It might also suggest a very cloudy atmosphere.
The direct imaging of exoplanets is particularly valuable for characterization. Scientists can directly collect light from the observed planet and compare its brightness at different wavelengths. So far, the science team has only detected Epsilon Indi Ab at a few wavelengths, but they hope to revisit the planet with Webb to conduct both photometric and spectroscopic observations in the future. They also hope to detect other similar planets with Webb to find possible trends about their atmospheres and how these objects form.
NASA's upcoming Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will use a coronagraph to demonstrate direct imaging technology by photographing Jupiter-like worlds orbiting Sun-like stars – something that has never been done before. These results will pave the way for future missions to study worlds that are even more Earth-like.
These results were taken with Webb’s Cycle 1 General Observer program 2243 and have been published in the journal Nature.
The James Webb Space Telescope is the world’s premier space science observatory. Webb is solving mysteries in our solar system, looking beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probing the mysterious structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Webb is an international program led by NASA with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency) and CSA (Canadian Space Agency).
Downloads
Right click any image to save it or open a larger version in a new tab/window via the browser's popup menu.
View/Download all image products at all resolutions for this article from the Space Telescope Science Institute.
View/Download the research results published in the journal Nature.
END
NASA’s Webb images cold exoplanet 12 light-years away
An international team of astronomers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has directly imaged an exoplanet roughly 12 light-years from Earth. The planet, Epsilon Indi Ab, is one of the coldest exoplanets observed to date.
2024-07-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
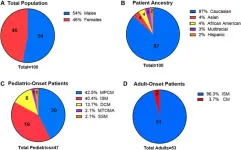
Prevalence and impact of the KIT M541L variant in patients with mastocytosis
2024-07-24
“This study uniquely examines the prevalence and impact of the KIT M541L variant in both adult and pediatric patients with mastocytosis further stratified by disease variant.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 24, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on July 22, 2024, entitled, “Prevalence and impact of the KIT M541L variant in patients with mastocytosis.”
Activating mutations in KIT, particularly D816V, have been associated with mastocytosis. Additionally, expression of heterozygous KIT M541L has been primarily ...
Experts outline considerations to deploy AI in radiology
2024-07-24
Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools can play a key role in medical imaging if radiologists trust in their design, deploy them with adequate training and establish clear guidelines regarding clinical accountability, according to a recently published Special Report in Radiology: Artificial Intelligence, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
RSNA and the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) Society have led a series of joint panels and seminars focused on the present impact and future directions of AI in radiology. These conversations ...
Johns Hopkins Medicine’s Center for Inherited Disease Research renews 7-year award for up to $98 million
2024-07-24
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
With renewed funding of up to $98.8 million for seven years, Johns Hopkins Medicine scientists will continue to be a worldwide resource for discovering the genes and their variations that contribute to human disease.
Leaders of the Johns Hopkins Center for Inherited Disease Research, established in 1996, received the fourth consecutive renewal for up to $98,880,900 in funds from a consortium of 10 institutes at the National Institutes of Health. The seven-year award is divided between ...
Preventing brain damage in preterm babies
2024-07-24
SAN FRANCISCO—Mark Petersen, MD, has seen firsthand the devastating effects of brain bleeds in premature babies. It’s an exceedingly common condition that affects up to 20 percent of infants born before 28 weeks of gestation, bringing an increased risk for developmental delays and autism.
“As a neonatologist and neuroscientist, it’s frustrating that we don’t have any treatments to counteract the harmful effects of bleeding in the developing brain, even though we know it often leads to lasting problems,” says Petersen, director ...
JNM maintains strong metrics in 2023 Journal Citation Reports
2024-07-24
Reston, VA—The Journal of Nuclear Medicine (JNM)—the flagship publication of the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging—has maintained its status as one of the top medical imaging journals worldwide, according to new data just released in Clarivate's 2023 Journal Citation Reports. With an impact factor of 9.1, JNM saw increases in its five-year impact factor, journal citation indicator, and article influence score, among other categories.
“This is an exciting time for nuclear medicine, with ground-breaking advances in molecular imaging, theranostics, artificial intelligence, and other areas,” said Johannes Czernin, MD, ...
New study determines incidence of and risk factors for hepatitis C virus reinfection among men with HIV, offers new insight on transmission
2024-07-24
Paper Title: Hepatitis C Virus Reinfection Among Men Who Have Sex With Men With HIV in New York City
Journal: Clinical Infectious Diseases, July 2024
Authors: Daniel S. Fierer, MD, Professor of Medicine (Infectious Diseases) at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, and other coauthors.
Bottom Line: This study provides new perspectives on transmission of hepatitis C virus (HCV), a virus that infects the liver and can be transmitted during injection of drugs, among men who have sex with men (MSM).
How: The researchers performed a prospective cohort study in New York City of MSM with HIV who had cleared ...
Dark matter flies ahead of normal matter in mega galaxy cluster collision
2024-07-24
Astronomers have untangled a messy collision between two massive clusters of galaxies in which the clusters' vast clouds of dark matter have decoupled from the so-called normal matter. The two clusters each contain thousands of galaxies and are located billions of light-years away from Earth. As they plowed through each other, the dark matter—an invisible substance that feels the force of gravity but emits no light—sped ahead of the normal matter. The new observations are the first to directly probe the decoupling of the dark and normal matter velocities.
Galaxy ...
Lyda Hill Philanthropies funds innovative wildfire solutions in Colorado
2024-07-24
Lyda Hill Philanthropies has donated $290,000 to Cary Institute of Ecosystem Studies for the Western Fire & Forest Resilience Collaborative. The two-year grant will help to engage a research team within the Collaborative that is focused on wildfire-related challenges and solutions in Colorado, where Lyda Hill has deep family ties.
Led by Winslow Hansen at Cary Institute and launched with seed funding from the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, the Western Fire & Forest Resilience Collaborative joins together multidisciplinary ...
Increasing cardiac ketones may help heart failure in mouse study
2024-07-24
Research Highlights:
In mice with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), increasing ketone supply to the heart allowed their hearts to utilize more ketones and produce more energy.
Researchers hope this study may help to improve our understanding of the complex and different root causes of HFpEF from a metabolic perspective and potentially identify targets for development of medications to treat HFpEF.
Note: The study featured in this news release is a research abstract. Abstracts ...
Toward a quantum electron microscope: a compact pulse hollow cone hybrid TEM/SEM by CityUHK to revolutionize electron microscopy
2024-07-24
Electron microscopes have long been indispensable tools in scientific research, offering unparalleled resolution and magnification capabilities. However, current electron microscopy technologies face significant limitations, including high cost, large size, strong radiation damage to samples through interaction with the electron beam, and the need for cryogenic temperatures. A research team from City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK) is working on a new quantum electron microscope (QEM) to eliminate interaction between the electron beam and sample. At this stage, the team is using partial key components of QEM ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] NASA’s Webb images cold exoplanet 12 light-years awayAn international team of astronomers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has directly imaged an exoplanet roughly 12 light-years from Earth. The planet, Epsilon Indi Ab, is one of the coldest exoplanets observed to date.