(Press-News.org) Our ability to recognize music might not diminish with age, with older concert attendees identifying themes in music as well as younger participants
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0305969
Article Title: Age and familiarity effects on musical memory
Author Countries: Canada, UK
Funding: The author(s) disclosed receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: this work was supported by BRZ’s Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada grant. The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Our ability to recognize music might not diminish with age, with older concert attendees identifying themes in music as well as younger participants
2024-07-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The COVID-19 pandemic slowed progress towards health-related Sustainable Development Goals and increased inequalities
2024-07-24
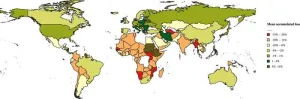
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly widened existing economic and health disparities between wealthy and low-income countries and slowed progress toward health-related Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), according to a new study published July 24, 2024, in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Wanessa Miranda of Federal University of Minas Gerais, Brazil, and colleagues.
The global SDGs were established in 2015 as a wide and integrated agenda with themes ranging from eradicating poverty and promoting well-being to addressing socioeconomic ...
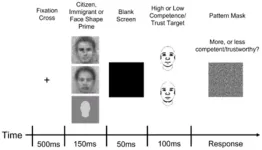
Even people who harbor positive sentiments toward immigrants imagine immigrants' faces as less trustworthy and less competent than US citizens' faces
2024-07-24
Even people who harbor positive sentiments toward immigrants imagine immigrants' faces as less trustworthy and less competent than US citizens' faces
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0306872
Article Title: Intergroup evaluative bias in facial representations of immigrants and citizens in the United States
Author Countries: USA
Funding: This work was facilitated by the National Science Foundation Division of Behavioral and Cognitive Sciences, grant #1764097 awarded to ART and grant #2215236 awarded to ...
Southern Ocean absorbing more CO2 than previously thought, study finds
2024-07-24
New research led by the University of East Anglia (UEA) and Plymouth Marine Laboratory (PML) has found that the Southern Ocean absorbs more carbon dioxide (CO2) than previously thought.
Using direct measurements of CO2 exchange, or fluxes, between the air and sea, the scientists found the ocean around Antarctica absorbs 25% more CO2 than previous indirect estimates based on shipboard data have suggested.
The Southern Ocean plays a major role in absorbing CO2 emitted by human activities, a process vital for controlling the Earth's climate. However, there are big uncertainties ...
Saharan dust regulates hurricane rainfall
2024-07-24
Giant plumes of Sahara Desert dust that gust across the Atlantic can suppress hurricane formation over the ocean and affect weather in North America.
But thick dust plumes can also lead to heavier rainfall – and potentially more destruction – from landfalling storms, according to a July 24 study in Science Advances. The research shows a previously unknown relationship between hurricane rainfall and Saharan dust plumes.
“Surprisingly, the leading factor controlling hurricane precipitation is not, as traditionally thought, sea surface temperature or humidity in the atmosphere. Instead, it’s Sahara dust,” said the corresponding ...
Fighting leukemia by targeting its stem cells
2024-07-24
Acute myeloid leukaemia is one of the deadliest cancers. Leukaemic stem cells responsible for the disease are highly resistant to treatment. A team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), University Hospital of Geneva (HUG), and Inserm has made a breakthrough by identifying some of the genetic and energetic characteristics of these stem cells, notably a specific iron utilisation process. This process could be blocked, leading to the death or weakening of these stem cells without affecting healthy cells. These results, published in Science Translational Medicine, pave the way for new therapeutic strategies.
Acute ...
NASA’s Webb images cold exoplanet 12 light-years away
2024-07-24
An international team of astronomers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has directly imaged an exoplanet roughly 12 light-years from Earth. The planet, Epsilon Indi Ab, is one of the coldest exoplanets observed to date.
The planet is several times the mass of Jupiter and orbits the K-type star Epsilon Indi A (Eps Ind A), which is around the age of our Sun, but slightly cooler. The team observed Epsilon Indi Ab using the coronagraph on Webb’s MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument). Only a few tens of exoplanets have been directly imaged previously by space- and ground-based observatories.
“Our prior observations of this system have been more indirect measurements ...
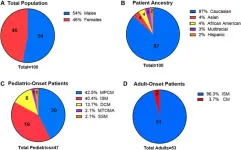
Prevalence and impact of the KIT M541L variant in patients with mastocytosis
2024-07-24
“This study uniquely examines the prevalence and impact of the KIT M541L variant in both adult and pediatric patients with mastocytosis further stratified by disease variant.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 24, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on July 22, 2024, entitled, “Prevalence and impact of the KIT M541L variant in patients with mastocytosis.”
Activating mutations in KIT, particularly D816V, have been associated with mastocytosis. Additionally, expression of heterozygous KIT M541L has been primarily ...
Experts outline considerations to deploy AI in radiology
2024-07-24
Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools can play a key role in medical imaging if radiologists trust in their design, deploy them with adequate training and establish clear guidelines regarding clinical accountability, according to a recently published Special Report in Radiology: Artificial Intelligence, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
RSNA and the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) Society have led a series of joint panels and seminars focused on the present impact and future directions of AI in radiology. These conversations ...
Johns Hopkins Medicine’s Center for Inherited Disease Research renews 7-year award for up to $98 million
2024-07-24
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
With renewed funding of up to $98.8 million for seven years, Johns Hopkins Medicine scientists will continue to be a worldwide resource for discovering the genes and their variations that contribute to human disease.
Leaders of the Johns Hopkins Center for Inherited Disease Research, established in 1996, received the fourth consecutive renewal for up to $98,880,900 in funds from a consortium of 10 institutes at the National Institutes of Health. The seven-year award is divided between ...
Preventing brain damage in preterm babies
2024-07-24
SAN FRANCISCO—Mark Petersen, MD, has seen firsthand the devastating effects of brain bleeds in premature babies. It’s an exceedingly common condition that affects up to 20 percent of infants born before 28 weeks of gestation, bringing an increased risk for developmental delays and autism.
“As a neonatologist and neuroscientist, it’s frustrating that we don’t have any treatments to counteract the harmful effects of bleeding in the developing brain, even though we know it often leads to lasting problems,” says Petersen, director ...