(Press-News.org) Self-driving cars occasionally crash because their visual systems can’t always process static or slow-moving objects in 3D space. In that regard, they’re like the monocular vision of many insects, whose compound eyes provide great motion-tracking and a wide field of view but poor depth perception.
Except for the praying mantis.
A praying mantis’ field of view also overlaps between its left and right eyes, creating binocular vision with depth perception in 3D space.
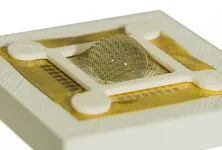
Combining this insight with some nifty optoelectrical engineering and innovative “edge” computing — processing data in or near the sensors that capture it — researchers at the University of Virginia School of Engineering and Applied Science have developed artificial compound eyes that overcome vexing limitations in the way machines currently collect and process real-world visual data. These limitations include accuracy issues, data processing lag times and the need for substantial computational power.
“After studying how praying mantis eyes work, we realized a biomimetic system that replicates their biological capabilities required developing new technologies,” said Byungjoon Bae, a Ph.D. candidate in the Charles L. Brown Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering.
About Those Biomimetic Peepers
The team’s meticulously designed “eyes” mimic nature by integrating microlenses and multiple photodiodes, which produce an electrical current when exposed to light. The team used flexible semiconductor materials to emulate the convex shapes and faceted positions within mantis eyes.
“Making the sensor in hemispherical geometry while maintaining its functionality is a state-of-the-art achievement, providing a wide field of view and superior depth perception,” Bae said.
“The system delivers precise spatial awareness in real time, which is essential for applications that interact with dynamic surroundings.”
Such uses include low-power vehicles and drones, self-driving vehicles, robotic assembly, surveillance and security systems, and smart home devices.
Bae, whose adviser is Kyusang Lee, an associate professor in the department with a secondary appointment in materials science and engineering, is first author of the team’s recent paper in Science Robotics.
Among the team’s important findings on the lab’s prototype system was a potential reduction in power consumption by more than 400 times compared to traditional visual systems.
Benefits of Computing on the Edge
Rather than using cloud computing, Lee’s system can process visual information in real time, nearly eliminating the time and resource costs of data transfer and external computation, while minimizing energy usage.
“The technological breakthrough of this work lies in the integration of flexible semiconductor materials, conformal devices that preserve the exact angles within the device, an in-sensor memory component, and unique post-processing algorithms,” Bae said.
The key is that the sensor array continuously monitors changes in the scene, identifying which pixels have changed and encoding this information into smaller data sets for processing.
The approach mirrors how insects perceive the world through visual cues, differentiating pixels between scenes to understand motion and spatial data. For example, like other insects — and humans, too — the praying mantis can process visual data rapidly by using the phenomenon of motion parallax, in which nearer objects appear to move faster than distant objects. Only one eye is needed to achieve the effect, but motion parallax alone isn’t sufficient for accurate depth perception.
Praying mantis eyes are special because, like us, they use stereopsis — seeing with both eyes to perceive depth — in addition to their hemispherical compound eye geometries and motion parallax to understand their surroundings.
“The seamless fusion of these advanced materials and algorithms enables real-time, efficient and accurate 3D spatiotemporal perception,” said Lee, a prolific early-career researcher in thin-film semiconductors and smart sensors.
“Our team’s work represents a significant scientific insight that could inspire other engineers and scientists by demonstrating a clever, biomimetic solution to complex visual processing challenges,” he said.
Publication
Stereoscopic artificial compound eyes for spatiotemporal perception in three-dimensional space, appeared in the May 15 edition of Science Robotics. UVA electrical and computing engineering graduate students Doeon Lee, Minseong Park, Yujia Mu, Yongmin Baek, Inbo Sim and Cong Shen also contributed to the research.
This work was supported by National Science Foundation and U.S. Air Force Office of Scientific Research.
END
It’s got praying mantis eyes
UVA researchers sharpen machine vision by mimicking nature and taking advanced computing to the edge
2024-07-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Stroke recovery: It’s in the genes
2024-07-24
New research led by UCLA Health has found that specific genes may be related to the trajectory of recovery for stroke survivors, providing doctors insights useful for developing targeted therapies.
Published in the journal Stroke this month, the findings were part of an exploratory study that sought to find if candidate genes could predict a higher likelihood of stroke outcomes related to depression, post-traumatic stress disorder and cognitive decline.
Dr. Steven C. Cramer, MD, the study’s lead author and a professor of neurology at UCLA, said while there are some ...
Foam fluidics showcase Rice lab’s creative approach to circuit design
2024-07-24
HOUSTON – (July 24, 2024) – When picturing next-generation wearables and robotics, the foam filling in your couch cushions is likely not the first thing that comes to mind.
However, Rice University engineers have shown that something as simple as the flow of air through the airy, meshlike structure of open-cell foam can be used to perform digital computation, analog sensing and combined digital-analog control in soft textile-based wearable systems.
“In this work, we integrated material intelligence — the ability of materials to sense and respond to their environment ...
Montana State scientists publish evidence for new groups of methane-producing organisms
2024-07-24
A team of scientists from Montana State University has provided the first experimental evidence that two new groups of microbes thriving in thermal features in Yellowstone National Park produce methane – a discovery that could one day contribute to the development of methods to mitigate climate change and provide insight into potential life elsewhere in our solar system.
The journal Nature this week published the findings from the laboratory of Roland Hatzenpichler, associate professor in MSU’s Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry in the College ...
Daily rhythms depend on receptor density in biological clock
2024-07-24
In humans and other animals, signals from a central circadian clock in the brain generate the seasonal and daily rhythms of life. They help the body to prepare for expected changes in the environment and also optimize when to sleep, eat and do other daily activities.
Scientists at Washington University in St. Louis are working out the particulars of how our internal biological clocks keep time. Their new research, published July 24 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, helps answer longstanding questions about how circadian rhythms are generated and maintained.
In all mammals, the signals for circadian rhythms come from a small part of the brain called the suprachiasmatic ...
New England Journal of Medicine publishes outcomes from practice-changing E1910 trial for patients with BCR::ABL1-negative B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia
2024-07-24
A significant survival improvement for adults with newly diagnosed BCR::ABL1-negative B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia is published today by the New England Journal of Medicine. The practice-changing finding is from the randomized phase 3 study E1910 (NCT02003222), which evaluated blinatumomab immunotherapy in patients who were in remission and tested negative for measurable residual disease (MRD) after an initial round of chemotherapy. At 3 years of follow-up, 85% of the patients who went on to receive additional standard consolidation chemotherapy plus experimental blinatumomab were alive, compared to 68% of those who received chemotherapy only.
Blinatumomab (Blincyto, ...
Older adults want to cut back on medication, but study shows need for caution
2024-07-24
More than 82% of Americans age 50 to 80 take one or more kinds of prescription medication, and 80% of them say they’d be open to stopping one or more of those drugs if their health care provider gave the green light, a new University of Michigan study shows.
But it’s not as simple as that, the researchers say. They call for prescribers and pharmacists to talk with older adults about their personal situation and figure out if any kind of “deprescribing” is right for them.
The study, published in the Journal of General Internal Medicine, uses data from U-M’s National Poll on Healthy Aging, and builds on a poll report issued in April 2023.
It ...
Nationwide flood models poorly capture risks to households and properties
2024-07-24
Irvine, Calif., July 24, 2024 – Government agencies, insurance companies and disaster planners rely on national flood risk models from the private sector that aren’t reliable at smaller levels such as neighborhoods and individual properties, according to researchers at the University of California, Irvine.
In a paper published recently in the American Geophysical Union journal Earth’s Future, experts in UC Irvine’s Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering caution that relatively new, nation-scale flood data provides an inadequate representation of local topography and infrastructure, factors known to control the spread of floods ...
Does your body composition affect your risk of dementia or Parkinson’s?
2024-07-24
MINNEAPOLIS – People with high levels of body fat stored in their belly or arms may be more likely to develop diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s than people with low levels of fat in these areas, according to a study published in the July 24, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study also found that people with a high level of muscle strength were less likely to develop these diseases than people with low muscle strength.
“These neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s affect over 60 million people worldwide, and that number is expected ...
Researchers discover faster, more energy-efficient way to manufacture an industrially important chemical
2024-07-24
Polypropylene is a common type of plastic found in many essential products used today, such as food containers and medical devices. Because polypropylene is so popular, demand is surging for a chemical used to make it. That chemical, propylene, can be produced from propane. Propane is a natural gas commonly used in barbeque grills.
Scientists from the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory and Ames National Laboratory report a faster, more energy-efficient way to manufacture propylene than the process currently used.
Converting propane into propylene ...
AI model identifies certain breast tumor stages likely to progress to invasive cancer
2024-07-24
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a type of preinvasive tumor that sometimes progresses to a highly deadly form of breast cancer. It accounts for about 25 percent of all breast cancer diagnoses.
Because it is difficult for clinicians to determine the type and stage of DCIS, patients with DCIS are often overtreated. To address this, an interdisciplinary team of researchers from MIT and ETH Zurich developed an AI model that can identify the different stages of DCIS from a cheap and easy-to-obtain breast tissue image. Their model shows that both the state and arrangement ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] It’s got praying mantis eyesUVA researchers sharpen machine vision by mimicking nature and taking advanced computing to the edge