In clinical trial, fecal matter transplant helped half of patients with gastrointestinal cancers overcome resistance to immunotherapy treatment
2024-07-25
(Press-News.org) Findings from a small, proof-of-concept clinical trial have suggested that fecal microbiota transplants (FMTs) can boost the effectiveness of immunotherapy in a range of gastrointestinal cancers. In the study, published July 25 in the journal Cell Host & Microbe, six of 13 patients who had previously shown resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors benefited from receiving FMTs from donors who had previously responded to treatment. The investigators also identified specific strains of bacteria associated with better or worse responses to FMT and immune checkpoint drugs.
“This research highlights the complex interplay between beneficial and detrimental bacteria within the gut microbiota in determining treatment outcomes,” says co-corresponding author Hansoo Park of Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology, in Gwangju, South Korea. “While the connection between gut microbiota and immune response to cancer therapy has been a growing area of interest, our study provides concrete evidence and new avenues for improving treatment outcomes in a broader range of cancers.”
Immune checkpoint inhibitors have revolutionized cancer treatment, but many patients never respond or develop resistance after an initial response. The researchers decided to study FMT in patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors because emerging evidence suggests that the gut microbiota plays a crucial role in modulating the immune system and can significantly impact the efficacy of these therapies. Previous small clinical trials had reported that FMTs could overcome resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors in some melanoma patients, but the potential for FMTs to overcome resistance in other advanced solid cancers had not been explored. This study is the first to show the potential benefits of this treatment in clinical settings beyond melanoma.
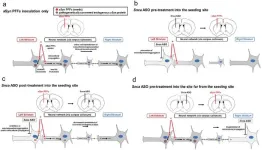
The trial included patients with metastatic solid-tumor cancers who were resistant to the anti-PD-1 drug nivolumab. Four had gastric cancer, five had esophageal cancer, and four had hepatocellular carcinoma. The six FMT donors, who also had gastric cancer, esophageal cancer, or hepatocellular carcinoma, had had a complete or partial response for at least 6 months after treatment with nivolumab or pembrolizumab. The FMTs were given via colonoscopy after the recipients had received antibiotics to tamp down their own microbiotas.
“One of the most surprising results was from a hepatocellular carcinoma patient who initially showed no response to the first FMT and continued to experience cancer progression. However, after switching the donor for the second FMT, the patient exhibited remarkable tumor shrinkage,” says co-corresponding author Sook Ryun Park, of Asan Medical Center at the University of Ulsan College of Medicine in Seoul, South Korea. “Both donors were long-lasting, good responders to anti-PD-1 inhibitors, but because we did not yet know the causative bacteria responsible for the FMT response, we could not predict whether the treatment would be effective.”
The investigators then took a closer look at which bacteria were most likely to affect whether patients benefited from FMT combined with checkpoint inhibitors. In doing so, they identified a novel bacterial strain that helped to improve FMT efficacy, Prevotella merdae Immunoactis. They also identified two strains that had a detrimental impact on FMT efficacy, Lactobacillus salivarius and Bacteroides plebeius.
They plan to continue studying these and other strains with the goal of developing better ways to boost immunotherapy effectiveness by altering the gut microbiota. “By examining the complex interactions within the microbiome, we hope to identify optimal microbial communities that can be used to enhance cancer treatment outcomes,” says Hansoo Park. “This comprehensive approach will help us understand how the microbial ecosystem as a whole contributes to therapeutic success.”
The researchers acknowledge the challenges of adopting FMT as part of standard treatment on a broad scale, including the lack of standardized protocols and regulatory guidelines, the potential risks of transmitting pathogens, and logistical issues surrounding large-scale manufacturing and distribution of FMT products. “Developing efficient and cost-effective methods for production and distribution is necessary for widespread adoption,” says Sook Ryun Park. “Addressing these challenges through comprehensive research and careful planning will be essential for integrating FMT into the standard of care for cancer treatment.”
###
This study was supported by grants from the Asan Institute for Life Sciences, Asan Medical Center, National Cancer Centre, Korea; GIST Research Institute, funded by the GIST; Bio and Medical Technology Development Program from Ministry of Science; and ICT, Korean Government.
Cell Host & Microbe, Kim et al. “Fecal microbiota transplantation improves anti-PD-1 inhibitor efficacy in refractory unresectable or metastatic solid cancers refractory to anti-PD-1 inhibitor.” https://cell.com/cell-host-microbe/fulltext/S1931-3128(24)00228-2
Cell Host & Microbe (@cellhostmicrobe), published by Cell Press, is a monthly journal that publishes novel findings and translational studies related to microbes (which include bacteria, fungi, parasites, and viruses). The unifying theme is the integrated study of microbes in conjunction and communication with each other, their host, and the cellular environment they inhabit. Visit http://www.cell.com/cell-host-microbe. To receive Cell Press media alerts, contact press@cell.com.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-07-25
Newly announced research by Royal Ontario Museum (ROM) examining greenhouse gas emissions from the drying lake bed of Great Salt Lake, Utah, calculates that 4.1 million tons of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases were released in 2020. This research suggests that drying lake beds are an overlooked but potentially significant source of greenhouse gases, which may further increase due to climate change. These results were announced in the paper, “A desiccating saline lake bed is a significant source of anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions,” published in the journal One Earth.
“Human-caused ...
2024-07-25
About The Study: Hospitals in communities with the greatest level of socioeconomic disadvantage had the lowest likelihood of becoming stroke certified while hospitals in the most advantaged communities had the highest likelihood in this cohort study. These findings suggest that there is a need to support hospitals in disadvantaged communities to obtain stroke certification as a way to reduce stroke disparities.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Renee Y. Hsia, M.D., M.Sc., email renee.hsia@ucsf.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link ...
2024-07-25
About The Study: This cohort study indicates that the risk of dying of breast cancer increases substantially after experiencing a contralateral breast cancer. Women with breast cancer treated with bilateral mastectomy had a greatly diminished risk of contralateral breast cancer; however, they experienced similar mortality rates as patients treated with lumpectomy or unilateral mastectomy.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Steven A. Narod, M.D., email steven.narod@wchospital.ca.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2024.2212)
Editor’s ...
2024-07-25
TMDU researchers demonstrate proof of concept of antisense nucleic acid therapy to prevent the spread of α-synuclein pathologies in synucleinopathies.
Tokyo, Japan – Parkinson’s disease (PD), as well as many other neurodegenerative disorders, has shown a link between the abnormal aggregation of a protein called α-synuclein (aSyn) and neuronal death. These aggregates, known as Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites depending on their subcellular localization, can spread by continuously causing normal endogenous aSyn to misfold. The complex nature of this aggregation process poses significant challenges ...
2024-07-25
Designing the spatial arrangement of underground powerhouses involves numerous complex parameters and boundaries, requiring frequent reference to various cases and specifications. Traditional methods struggle to efficiently retrieve this information, leading to suboptimal designs and extended project timelines. Due to these challenges, there is a pressing need for a more intelligent and efficient approach to streamline the design process, enhance accuracy, and improve project management in hydropower engineering.
Researchers from Tianjin University, in collaboration with PowerChina Kunming Engineering Corporation Limited and other ...
2024-07-25
Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) are highly regarded for their exceptional performance and straightforward fabrication. However, traditional hole transport layers (HTLs) like Poly (triarylamine) (PTAA), Nickel Oxide (NiOx), and poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-poly (styrenesulfonate) (PEDOT) have inherent limitations that impede efficiency and stability. These materials often suffer from issues such as hydrophobicity, high reactivity, and acidity, which negatively affect the overall performance of PSCs. Due to these challenges, there is a pressing ...
2024-07-25
To achieve carbon neutrality, advancements in energy conversion and storage technologies are essential. Current aqueous energy devices suffer from performance limitations due to the trade-off between permeability and selectivity in permselective membranes. This trade-off hampers the efficiency of energy conversion and storage systems, necessitating the development of membranes that can balance these properties effectively. Due to these challenges, further research is required to explore innovative membrane structures that can enhance the performance of energy conversion and storage devices.
A research team from Tsinghua University has published a study (DOI: 10.26599/EMD.2024.9370041) ...
2024-07-25
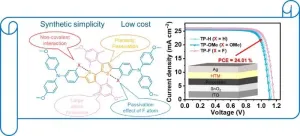
Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) are celebrated for their exceptional photovoltaic performance and affordability. However, the high cost of charge transport materials remains a major obstacle to their commercialization. Conventional materials like 2,2',7,7'-Tetrakis[N,N-di(4-methoxyphenyl)amino]-9,9'-spirobifluorene (Spiro-OMeTAD), are expensive and complex to produce. Therefore, developing low-cost, efficient alternatives is essential to make PSCs more economically viable. Addressing these issues is crucial for advancing solar technology and achieving broader adoption. Hence, this study focuses ...
2024-07-25
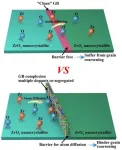
To date, ceramic scientists have devised various strategies to impede grain coarsening. The utilization of nano-sized precursor powder can not only facilitate the densification process, but also yields bulk ceramics with reduced grain sizes compared with micron-sized precursor powder. Rapid sintering by passes the low-temperature surface diffusion stage and directly enters the high-temperature sintering stage through rapid heating, rendering it an effective way to inhibit grain coarsening. However, these aforementioned strategies fail to prevent coarsening during the application of nano-ceramics in medium- ...
2024-07-25
The development of innovative medicines is an expensive, time-consuming and risky business. On average, it usually takes at least a decade and billions of dollars to bring a new drug from project initiation to approval. Identifying effective targets and conducting biological analysis is the first step in the process and remains a top priority in drug development.
To facilitate for maximum data privacy and data security, Insilico Medicine ("Insilico"), developed a hardware platform, PandaOmics Box, that does not require Internet access and allows for on-premise biological analytics, target identification, biomarker ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] In clinical trial, fecal matter transplant helped half of patients with gastrointestinal cancers overcome resistance to immunotherapy treatment