How epigenetics influence memory formation
2024-07-25
(Press-News.org)
When we form a new memory, the brain undergoes physical and functional changes known collectively as a “memory trace”. A memory trace represents the specific patterns of activity and structural modifications of neurons that occur when a memory is formed and later recalled.
But how does the brain “decide” which neurons will be involved in a memory trace? Studies have suggested that the inherent excitability of neurons plays a role, but the currently accepted view of learning has neglected to look inside the command center of the neuron itself, its nucleus. In the nucleus, there seems to be another dimension altogether that has gone unexplored: epigenetics.
Inside every cell of a given living organism, the genetic material encoded by the DNA is the same, yet the various cells types that make up the body, like skin cells, kidney cells, or nerve cells each express a different set of genes. Epigenetics is the mechanism of how cells control such gene activity without changing the DNA sequence.
Now, scientists at EPFL led by neuroscientist Johannes Gräff have explored whether epigenetics might affect the likelihood of neurons to be selected for memory formation. Their research on mice, now published in Science, shows that the epigenetic state of a neuron is key to its role in memory encoding. “We are shedding light on the earliest step of memory formation from a DNA-centric level”, says Gräff.
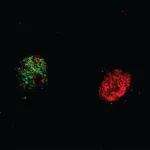
Gräff and his team wondered if epigenetic factors could influence the “mnemonic” function of a neuron. A neuron can be epigenetically open when the DNA inside its nucleus is unraveled or relaxed; and closed when the DNA is compact and tight.
They found that it is the open ones that are more likely to be recruited into the “memory trace”, the sparse set of neurons in the brain that shows electrical activity when learning something new. Indeed, the neurons that were in a more open chromatin state were also the ones demonstrating higher electrical activity.
The EPFL scientists then used a virus to deliver epigenetic enzymes to artificially induce openness of the neurons. They found that the corresponding mice learnt much better. When the scientists used the opposite approach to close the neurons’ DNA, the mice’s ability to learn was cancelled.
The findings open up new ways to understand learning that encompass the neuron’s nucleus, and may even lead one day to medication for improving learning. As Gräff explains: “They move away from the dominant neuroscientific view on learning and memory that focuses on the importance of synaptic plasticity, and newly place emphasis on what happens inside the nucleus of a neuron, on its DNA. This is especially important, as many cognitive disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease and post-traumatic stress disorder are characterized by epigenetic mechanisms gone wrong.”
Other contributors
EPFL Laboratory of Behavioural Genetics
EPFL Bioinformatics Competence Center
Reference
Giulia Santoni, Simone Astori, Marion Leleu, Liliane Glauser, Simon A. Zamora, Myriam Schioppa, Isabella Tarulli, Carmen Sandi, Johannes Gräff. Chromatin plasticity predetermines neuronal eligibility for memory trace formation. Science 26 July 2024. DOI: 10.1126/science.adg9982
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-07-25
University of Sydney researchers are proposing a new way to curb industrial emissions, by tapping into the “atomic intelligence” of liquid metals to deliver greener and more sustainable chemical reactions.
Despite global efforts towards renewable energy and electrification, chemical production accounts for approximately 10-15 percent of total greenhouse gas emissions. More than 10 percent of the world’s total energy is used in chemical factories, with these numbers rising.
This is due to the large amounts of energy required to cause ...
2024-07-25
Rainfall fluctuates more vigorously. Why? Scientists say it's because of us.
Many people around the world have noticed that rainfall is becoming increasingly erratic. Intense downpours are occurring more frequently, while dry periods seem to last longer and become more severe. These changes have raised concerns and prompted scientists to investigate the links between climate change and these unpredictable rainfall patterns.
A new study provides the first systematic observational evidence that human-induced climate change is making rainfall patterns more volatile globally.
Published in the journal Science on July 26, a joint study by the Institute of Atmospheric Physics ...
2024-07-25
In this Special Issue of Science, four Reviews and a Policy Forum explore the intersections of science, health, and policy related to the air we breathe, tackling topics including how air pollution is monitored, what impacts it has on human health, how those impacts are felt most by populations with fewer resources, and what changes we can make to the built environment to secure clean air.
In one Review, Wei Huang and colleagues discuss the new air quality guidelines from the World Health Organization (WHO) and related challenges ...
2024-07-25
Anthropogenic climate warming has led to increased precipitation variability over much of the globe, according to a new study, which points to several hotspots for this trend. This effect is particularly prominent over Europe, Australia, and eastern North America, say the study’s authors, and is largely driven by increasing atmospheric moistening and decadal-scale changes in atmospheric circulation. As the climate warms, the atmosphere becomes more capable of holding moisture, leading to greater fluctuations between extreme precipitation events and wider swings between wet and dry episodes. Such amplified ...
2024-07-25
Specific neurons in the brain’s zona incerta (ZI) play a crucial role in the early social interactions of an infant and its mother, building their bond and reducing stress, according to a new study in mice. Activation of the same neurons in adult mice increased anxiety- and fear-like responses, the study showed. In humans, as in other mammals, infants have an inborn tendency to form an attachment bond with their mothers or caregivers – a bond that plays a crucial role in the infant’s development. This bond helps newborns feel secure and serves as a safety net from which to explore their surroundings, learn, and develop crucial skills and behaviors. However, the neural mechanisms ...
2024-07-25
Machine learning models can reliably inform clinicians about the disability progression of multiple sclerosis, according to a new study published this week in the open-access journal PLOS Digital Health by Edward De Brouwer of KU Leuven, Belgium, and colleagues.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic progressive autoimmune disease that leads to severe disability over time through a complex pattern of progression, recovery, and relapse. Its global prevalence has increased by more than 30% over the last decade. ...
2024-07-25
Novel human lung organoids can form lifelike models for tuberculosis infection, and might be used to test efficacy of anti-TB drugs.
####
Article URL: http://journals.plos.org/plospathogens/article?id=10.1371/journal. ppat.1012295
Article Title: Advances in an In Vitro Tuberculosis Infection Model Using Human Lung Organoids for Host-Directed Therapies
Author Countries: Republic of Korea
Funding: This research was supported by the Korea National Institutes of Health (NIH) (No. 2021-ER2001-00) awarded to E.M.K., the Korea Institute of Toxicology, Republic of Korea (No. 1711195891) awarded to E.M.K., the Korea Environment Industry & Technology ...
2024-07-25
Researchers at QuTech developed somersaulting spin qubits for universal quantum logic. This achievement may enable efficient control of large semiconductor qubit arrays. The research group published their demonstration of hopping spins in Nature Communications and their work on somersaulting spins in Science.
In 1998, Loss and DiVincenzo published the seminal work ‘quantum computation with quantum dots’. In their original work, hopping of spins was proposed as a basis for qubit logic, but an experimental implementation has remained lacking. After more than 20 years, experiments have caught up with theory. Researchers ...
2024-07-25
Professor Morawska, director of THRIVE, from QUT’s School of School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences said the rapid global spread of Covid-19 had soon made it clear the world was unprepared to respond appropriately.
“In the early days of the pandemic the World Health Organisation and many national health authorities claimed the virus was ‘not in the air’ but rather present in large quantities on surfaces. This led to a misconception about how the virus was transmitted,” ...
2024-07-25
Crave that cup of coffee in the morning? Globally, consumers drink more than 2.2 billion cups daily. Someone grows all that joe: More than 100 million farmers worldwide produce coffee.
Coffee beans consumed across the globe come from two species: Coffea arabica and Coffea canephora, also known as Robusta (or Conilon) coffee. Historically, coffee drinkers prefer Arabica beans for their specific flavor and aroma, said Felipe Ferrao, a University of Florida research assistant scientist in horticultural sciences.
But by 2050, about 80% of Arabica production is predicted to decrease because of climate change. So, Ferrao and colleagues from France (RD2 Vision) and Brazil (Incaper ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] How epigenetics influence memory formation