(Press-News.org) Scientist Dr. Aparna Bhaduri, assistant professor of medicine and biological chemistry, and neurosurgeon Dr. Kunal Patel, assistant professor of neurosurgery, both part of the UCLA Health Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center, have received the 2024 Neurobiology of Brain Disorders Award from the McKnight Endowment Fund for Neuroscience, which supports innovative research by U.S. scientists who are studying neurological and psychiatric diseases.
The award, $300,000 over the next three years, supports their efforts in gaining a deeper understanding of the microenvironment's role in shaping human glioblastoma, an aggressive type of brain cancer that is fast growing and difficult to treat.
One of the critical challenges in treating this cancer is the limited understanding of how it develops and spreads. Traditional mouse models and studies of tumors removed from the brain provide limited insights into the tumor's growth dynamics within the brain. To help combat this issue, the team will employ novel techniques to create organoid systems from stem cell lines that closely resemble the human brain environment. These organoids will then be implanted with tumor samples collected by Patel from surgical patients.
Bhaduri and her lab will use these models to explore the lineage relationships of the glioblastoma cell types and their evolution as the tumor progresses. By examining the roles of different cells within the core, periphery, and various parts of the tumor, the team hopes to reveal critical insights into the tumor's development and its interaction with its environment.
“We are incredibly grateful for this grant, which will allow us to delve deeper into the complex interactions between glioblastoma and its surrounding environment,” said Bhaduri, who is also a member of the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research at UCLA. “By understanding these dynamics, we hope to identify new strategies to disrupt tumor growth and improve patient outcomes.”
END
Researchers receive McKnight award to study the evolution of deadly brain cancer
2024-07-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Heather Dyer selected as the 2024 ESA Regional Policy Award Winner
2024-07-26
The Ecological Society of America (ESA) will present its 17th annual Regional Policy Award to Heather Dyer, Chief Executive Officer of the San Bernardino Valley Municipal Water District, Sunday, Aug. 4, 5:00 p.m. PDT, during the ESA Annual Meeting Opening Plenary. The ESA annual award recognizes an elected or appointed local policymaker whose record reflects the use of ecological science to inform policy decisions.
“ESA is honored to recognize Dyer,” said ESA President Shahid Naeem. “It’s rare for a biologist with ecosystems expertise to transition from technical science work to executive ...
New study disputes Hunga Tonga volcano’s role in 2023-24 global warm-up
2024-07-26
New research from a collaborative team featuring Texas A&M University atmospheric scientist Dr. Andrew Dessler is exploring the climate impact of the 2022 Hunga Tonga volcano eruption and challenging existing assumptions about its effects in the process.
The remarkable two-day event, which occurred in mid-January 2022, injected vast amounts of volcanic aerosols and water vapor into the atmosphere. Historically, large volcanic eruptions like Tambora in 1815 and Mt. Pinatubo in 1991 have led to significant cooling effects on the global climate by blocking sunlight with their aerosols. ...
Climate is most important factor in where mammals choose to live, study finds
2024-07-26
While human activity has had a massive effect on the natural world, a new study from North Carolina State University finds that climate is still the most influential factor in determining where mammals can thrive. The work sheds light on how climate change will affect wildlife populations.
Roland Kays, lead author of a paper on the work, said the study’s goal was to compare the importance of climate versus human factors in where mammals chose to live. To do so, researchers collected data on 25 mammal species from 6,645 locations across the United States. The study is one of the largest camera trap data analyses ever done. The data came ...
New study highlights global disparities in activity limitations and assistive device use
2024-07-26
A new study of over 175,000 people in 25 countries revealed that individuals in low- and middle-income countries face greater challenges with daily activities and are less likely to use assistive devices compared to those in high-income countries. These findings raise concerns about the global burden of disability, particularly in low-income countries.
Despite decreases in death and cardiovascular disease rates and increases in life expectancy worldwide, people in low- and middle-income countries still ...
Study finds targeting inflammation may not help reduce liver fibrosis in MAFLD
2024-07-26
Researchers at UCLA Health uncovered new information about the role inflammation plays in mitigating liver fibrosis, which is associated with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), one of the most common diseases in the world affecting up to 40 percent of U.S. adults. While inflammation in the liver has long been considered a prerequisite to developing liver fibrosis, the scarring and thickening of tissue that can impair the liver’s ability to function, this new research suggests ...
Meet Insilico in Singapore: Alex Zhavoronkov PhD shares insights into various aspects of AI-powered drug discovery
2024-07-26
From July 30-31, Alex Zhavoronkov, PhD, founder and co-CEO of clinical stage artificial intelligence (AI)-driven drug discovery company Insilico Medicine will be attending SCRI Clinical Trials Symposium 2024 at Raffles City Convention Centre, and Brainstorm AI 2024: The New Race for AI at The Ritz-Carlton, Millenia Singapore, sharing strategic insights with global leaders across the technology and healthcare industries.
On 2:00 p.m, July 31, Alex Zhavoronkov PhD will be speaking at the session named “Methodologies and Considerations for ...
Insilico Medicine introduces Science42: DORA, the intelligent writing assistant for accelerated research
2024-07-26
Writing research papers is critical for disseminating scientific findings, but it does come with efficiency burdens, particularly for early-career researchers and non-native English speakers. A survey published in Nature in 2018 indicated that approximately 37% of respondents reported that they spend more than 20 hours a week on writing and revising scientific papers.
Recent progress in Natural Language Processing (NLP) technology, particularly with the rise of Generative Pre-trained Transformers (GPT) and other Large Language Models (LLMs), has equipped researchers with a powerful set of tools for processing extensive amounts of literature ...
A deep dive into polyimides for high-frequency wireless telecommunications
2024-07-26
As 5G technologies continue to evolve, scientists and engineers are already exploring new ways to turn things up a notch for 6G. One of the biggest challenges to address in both 5G and 6G is the many detrimental effects that operating at extremely high frequencies has on wireless communications. At frequencies nearing the terahertz range, problems such as signal attenuation and interference are more prominent, and maintaining signal integrity becomes much harder.
Some of these issues can be greatly mitigated by using insulating materials with exceptional dielectric properties. Glass- and ceramic-based insulating materials ...
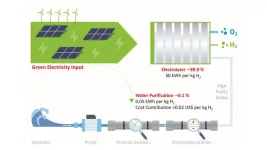
Green hydrogen from direct seawater electrolysis- experts warn against hype
2024-07-26
At first glance, the plan sounds compelling: invent and develop future electrolysers capable of producing hydrogen directly from unpurified seawater. But a closer look reveals that such direct seawater electrolysers would require years of high-end research. And what is more: DSE electrolyzers are not even necessary - a simple desalination process is sufficient to prepare seawater for conventional electrolyzers. In a commentary in Joule, international experts compare the costs and benefits of the different approaches and come to a clear recommendation.
Fresh water is a limited ...
Thousands of birds and fish threatened by mining for clean energy transition
2024-07-26
New research has found that 4,642 species of vertebrate are threatened by mineral extraction around the world through mining and quarrying, and drilling for oil and gas.
Mining activity coincides with the world's most valuable biodiversity hotspots, which contain a hyper-diversity of species and unique habitats found nowhere else on Earth.
The biggest risk to species comes from mining for materials fundamental to our transition to clean energy, such as lithium and cobalt – both essential components of solar ...