Every minute counts: rapid and accurate prediction model for cardiac arrest treatment
New scoring model enhances early prognosis prediction using prehospital resuscitation data only
2024-07-29
(Press-News.org)
When it comes to treating cardiac arrest, acting quickly can mean the difference between life and death.
Researchers from Osaka Metropolitan University have developed a new scoring model, using only prehospital resuscitation data, that accurately predicts neurological outcomes of patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA). This model potentially allows healthcare providers to make quick and accurate decisions upon the patient’s arrival at the hospital, ultimately improving patient care and resource allocation.
Their findings were published in Resuscitation on May 31.
Cardiac arrest can lead to death within minutes. OHCA is not uncommon and often results in low survival rates. In Japan, over 100,000 patients experience OHCA annually, with less than 10% returning to normal life.
Rapid and accurate neurological prediction calculations are critical in OHAC cases. Effective prediction models can save lives, reduce suffering, and cut down on unnecessary costs associated with futile resuscitation efforts.
“Current prognosis prediction models require complex calculations and blood test data, making them impractical for rapid use immediately after patient transport,” said Takenobu Shimada, a medical lecturer at Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Medicine and lead author of the study.
The research team addressed this gap by constructing a scoring model that uses readily available prehospital data to predict unfavorable neurological outcomes. Analyzing data from the All-Japan Utstein Registry, they examined information collected between 2005 and 2019 on prehospital resuscitation and neurological recovery one month post-arrest for 942,891 adults with presumed cardiac-origin OHCA. Adverse outcomes include severe disability, vegetative state, or death.
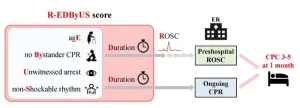
Named the “R-EDByUS score,” the developed model is derived from the initials of its five variables: age, duration to return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) or time to hospital arrival, absence of bystander CPR, whether the arrest was witnessed and, finally, initial heart rhythm (shockable versus non-shockable).
Patients were divided into two groups based on whether they achieved ROSC before hospital arrival or were still undergoing CPR upon arrival. The researchers developed detailed regression-based and simplified models to calculate R-EDByUS scores for each group.
The results demonstrated that the R-EDByUS scores predicted neurological outcomes with high precision, achieving C-statistics values of approximately 0.85 for both groups. C-statistics measure the predictive accuracy of a model, ranging from 0.5 (no predictive power) to 1.0 (perfect accuracy), with higher values indicating superior performance.
“The R-EDByUS score enables high-precision prognosis prediction immediately upon hospital arrival, and its application via smartphone or tablet makes it suitable for everyday clinical use,” Shimada said.
This scoring model is expected to become a valuable tool for healthcare providers, aiding in the prompt assessment and management of patients undergoing resuscitation.
“In emergency care for OHCA, invasive procedures, such as mechanical circulatory support, can be lifesaving but are also highly burdensome,” Shimada said. “Our predictive model helps identify patients who are likely to benefit from intensive care while reducing unnecessary burdens on those with poor predicted outcomes.”
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-07-29
In Canada, rates of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP) have increased, but the good news is there has been a decline in some related health conditions, according to new research published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231547.
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy include chronic hypertension (high blood pressure), gestational hypertension, and preeclampsia or eclampsia. These disorders affect 5%–10% of pregnancies worldwide, and cause more than 50 000 maternal deaths and 500 000 deaths in fetuses and infants ...
2024-07-29
Free genetic testing, offered partially or fully subsidized by industry, may have trade-offs, and health systems in Canada must carefully weigh potential clinical, ethical, and legal considerations to protect patient data, authors argue in a CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) commentary https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231588.
“Near- and long-term expansion in no-cost testing and industry partnership in genetics, with patient data as the commodity, is likely,” writes Kirsten ...
2024-07-29
Eating a vegan diet for eight weeks is associated with reductions in biological age estimations based on levels of DNA methylation — a type of chemical modification of DNA (known as an epigenetic modification) that alters gene expression but not DNA itself. Previous research has reported that increased DNA methylation levels are associated with ageing. The findings, which are based on a small randomised controlled trial of 21 pairs of adult identical twins, are published in BMC Medicine.
Varun Dwaraka, Christopher ...
2024-07-29
Researchers in Australia have found that when women are given accurate information about a test that indicates the number of eggs in their ovaries, they have less interest in taking the test compared to women who viewed information available online.
The researchers initiated the study, which is published today (Monday) in Human Reproduction [1], one of the world’s leading reproductive medicine journals, because of the large amount of misleading and incorrect information promoted to women about the anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH) test on websites, including fertility clinic websites, and via social media.
AMH ...
2024-07-29
A decarbonised steel industry that includes carbon dioxide removal techniques in its net zero arsenal could use lower-grade iron ore, according to a new study.
Steel accounts for 5-8% of carbon dioxide emissions globally. Its total emissions have risen over the past decade, largely due to increased demand.
The International Energy Agency has stated that, without innovation, the scope to limit emissions is ‘limited’. Therefore, the commercialisation of new zero-emission production processes is critical.
Innovative ...
2024-07-28
About The Study: The results of this cohort study suggest that combining plasma p-tau217 and Aβ42/40 levels could be useful for predicting development of Aβ pathology in people with early stages of subthreshold Aβ accumulation. These biomarkers might thus facilitate screening of participants for future primary prevention trials.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Oskar Hansson, M.D, Ph.D. (Oskar.Hansson@med.lu.se) and Shorena Janelidze, Ph.D. (shorena.janelidze@med.lu.se).
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2024.2619)
Editor’s ...
2024-07-28
About The Study: In this cohort study, seed amplification assays (SAA) α-syn+ was consistently associated with nucleus basalis of Meynert (NBM) atrophy already during asymptomatic stages. Further, in memory clinic cognitively impaired populations, SAA α-syn+ was associated with NBM atrophy, which partially mediated α-syn–induced attention/executive impairment.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Laura E.M. Wisse, Ph.D. (laura.wisse@med.lu.se) and Oskar Hansson, M.D., Ph.D. (oskar.hansson@med.lu.se).
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2024.2713)
Editor’s ...
2024-07-28
About The Study: The amyloid probability score 2 (APS2) blood test and percentage of p-tau217 alone had high diagnostic accuracy for identifying Alzheimer disease among individuals with cognitive symptoms in primary and secondary care using predefined cutoff values. Future studies should evaluate how the use of blood tests for these biomarkers influences clinical care.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Sebastian Palmqvist, M.D., Ph.D. (sebastian.palmqvist@med.lu.se) and Oskar Hansson, M.D., Ph.D. (oskar.hansson@med.lu.se).
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.13855)
Editor’s ...
2024-07-28
About The Study: Plasma biomarkers of Alzheimer disease (AD) neuropathology, neuronal injury, and astrogliosis increase with age and are associated with known dementia risk factors. AD-specific biomarkers’ association with dementia starts in midlife whereas late-life measures of AD, neuronal injury, and astrogliosis biomarkers are all associated with dementia.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Priya Palta, Ph.D., M.H.S., email priya_palta@med.unc.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.6619)
Editor’s ...
2024-07-27
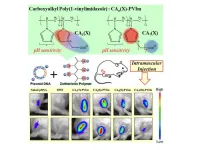
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have created a new drug delivering molecule, a zwitterionic polymer complex that can help get plasmid DNA inside cells when injected into skeletal muscle, a crucial step in the expression of therapeutic RNA and proteins. The new compound effectively bound to plasmid DNA without affecting its structure. Injected into mouse muscles, the team observed widespread gene expression, promising applications to treatments of serious muscle diseases.
Drug delivery systems underpin many of the clinical breakthroughs of our age. For example, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Every minute counts: rapid and accurate prediction model for cardiac arrest treatment
New scoring model enhances early prognosis prediction using prehospital resuscitation data only