(Press-News.org)
There are significant differences in how much people are exposed to air pollution, according to a new study co-authored by MIT scholars that takes daily mobility into account.
The study, based in the Bronx, New York, does not just estimate air pollution exposure based on where people live or work, but uses mobile data to examine where people go during a typical day, building a more thorough assessment of the environment’s impact on them.
The research finds exposure to particulate matter 2.5 microns or bigger rises by about 2.4 percent when daily travel patterns are taken into account.
“One of the main strengths of the study is that we try to improve the information we use, on the air quality side and also from the fine-grained estimation of people’s mobility,” says Paolo Santi, a principal research scientist at Senseable City Lab, part of MIT’s Department of Urban Studies and Planning (DUSP), and a co-author of a new paper detailing the study’s results. “That allows us to build trajectories of people’s movement. So, it was the first time we were able to combine these data to come up with a new measure of exposure.”
After all, people’s daily pollution exposure may be a complex combination of either living near, working near, or traveling by sources of particulate matter.
“People move around the city for jobs and education and more, and studying that is where we get this better information about exposure,” says An Wang of the Hong Kong Polytechnic University, another co-author of the study.
The paper, “Big mobility data reveals hyperlocal air pollution exposure disparities,” will be published in Nature Cities.
The authors are Iacopo Testi of the Senseable City Lab; An Wang of Hong Kong Polytechnic University; Sanjana Paul, a graduate student in DUSP; Simone Mora, of the Senseable City Lab; Erica Walker, an associate professor at the Brown University School of Public Health; Marguerite Nyhan, a senior lecturer/associate professor at the National University of Ireland, University College Cork; Fábio Duarte of the Senseable City Lab; Santi; and Carlo Ratti, director of the Senseable City Lab.
To conduct the study, the researchers collected air pollution by mounting solar-power environmental sensors, including optical particle counters, temperature and humidity sensors, and GPS, on New York City’s civic services vehicles in operation in the Bronx.
“This strategy shows that cities can use their existing fleet as environmental sensors,” says Mora.
To measure how people moving through the Bronx are exposed to pollution in different times, the researchers used anonymized phone records of 500,000 different individuals and 500 million daily location records in New York.
The ground-level pollution data showed that the southeastern portion of the Bronx, where expressways and industries meet most intensively, has the most particulate matter.
The mobility data also revealed disparities in exposure when evaluated in terms of demographics, with income disparities present but disparities by ethnicity larger. For instance, some largely Hispanic communities have among the highest exposure levels. But the data also showed large differences in exposure levels within Hispanic communities.
Pollution exposure has significant implications from a health perspective, as Duarte notes. For instances, the Bronx has the worst air quality of any New York City borough, and, in turn, cases of asthma in the Bronx are 2.5 times higher in than any other borough.
“You see the consequences of exposure to pollution in the hospitalization of adults in the Bronx,” Duarte says.
As the researchers acknowledge, because the study was conducted in the fall of 2021, when the global Covid-19 pandemic was still affecting business and commuting, there may be slightly different mobility patterns in the Bronx today. Still, they believe their methods can give rise to additional future studies of the pollution exposure.
Ratti notes that mobile data, including pollution sensors on vehicles, can be used as “a huge monitoring system. It’s not expensive, we have the infrastructure in terms of cars and buses, and just putting sensors on them, you can have better air quality monitoring.”
And Wang notes that granular studies such as this one can be extended into studies that add in additional kinds of air-quality hazards, in addition to PM 2.5 particles.
“This actually opens the door for new analysis for many kinds of toxicity studies combined with exposure,” he says.
The study was supported by the MIT Senseable City Lab Consortium.
###
Written by Peter Dizikes, MIT News
END
A research team led by UC San Diego has, for the first time, shown that a wearable, non-invasive device can measure activity in human cervical nerves in clinical settings.
The device records what the team calls Autonomic Neurography (ANG), neural activity from the human vagus and carotid sinus nerves as well as other autonomic nerves found in the skin and muscle of the neck. The vagus nerve is a “superhighway” of the involuntary nervous system, with tendrils extending from the base of the skull through the torso and abdomen to influence digestion, heart rate and the immune system. The vagus nerve ...
The vast majority of American voters think alike on what they find important in life, but both Republicans and Democrats fail to recognise their shared views and values, according to new research from the Universities of Bath and Essex.
This finding is revealed today in the academic journal Social Psychological and Personality Science less than a month after the US Republican presidential nominee Donald Trump survived an assassination attempt when a gunman shot at him during a campaign rally.
“There’s a general perception ...
A new generation of specialty optical fibres has been developed by physicists at the University of Bath in the UK to cope with the challenges of data transfer expected to arise in the future age of quantum computing.
Quantum technologies promise to provide unparalleled computational power, allowing us to solve complex logical problems, develop new medicines and provide unbreakable cryptographic techniques for secure communications. However, the cable networks used today to transmit information across the globe are likely to be sub-optimal for quantum communications, due to the solid cores of their optical fibres.
Unlike regular optical ...
Past studies have suggested that taking cholesterol-lowering statin drugs may lower individuals’ risk of developing liver cancer. In a new study of non-statin cholesterol-lowering medications, one type was linked to lower risks of liver cancer. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Cholesterol absorption inhibitors, bile acid sequestrants, fibrates, niacin, and omega-3 fatty acids are types of non-statin cholesterol-lowering medications prescribed to manage cholesterol and lipid levels. The different classes ...
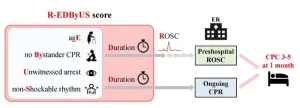
When it comes to treating cardiac arrest, acting quickly can mean the difference between life and death.
Researchers from Osaka Metropolitan University have developed a new scoring model, using only prehospital resuscitation data, that accurately predicts neurological outcomes of patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA). This model potentially allows healthcare providers to make quick and accurate decisions upon the patient’s arrival at the hospital, ultimately improving patient care and resource allocation.
Their findings were published in Resuscitation on May 31.
Cardiac arrest can lead to death within minutes. OHCA is not uncommon and often results ...
In Canada, rates of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP) have increased, but the good news is there has been a decline in some related health conditions, according to new research published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231547.
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy include chronic hypertension (high blood pressure), gestational hypertension, and preeclampsia or eclampsia. These disorders affect 5%–10% of pregnancies worldwide, and cause more than 50 000 maternal deaths and 500 000 deaths in fetuses and infants ...
Free genetic testing, offered partially or fully subsidized by industry, may have trade-offs, and health systems in Canada must carefully weigh potential clinical, ethical, and legal considerations to protect patient data, authors argue in a CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) commentary https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231588.
“Near- and long-term expansion in no-cost testing and industry partnership in genetics, with patient data as the commodity, is likely,” writes Kirsten ...
Eating a vegan diet for eight weeks is associated with reductions in biological age estimations based on levels of DNA methylation — a type of chemical modification of DNA (known as an epigenetic modification) that alters gene expression but not DNA itself. Previous research has reported that increased DNA methylation levels are associated with ageing. The findings, which are based on a small randomised controlled trial of 21 pairs of adult identical twins, are published in BMC Medicine.
Varun Dwaraka, Christopher ...
Researchers in Australia have found that when women are given accurate information about a test that indicates the number of eggs in their ovaries, they have less interest in taking the test compared to women who viewed information available online.
The researchers initiated the study, which is published today (Monday) in Human Reproduction [1], one of the world’s leading reproductive medicine journals, because of the large amount of misleading and incorrect information promoted to women about the anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH) test on websites, including fertility clinic websites, and via social media.
AMH ...
A decarbonised steel industry that includes carbon dioxide removal techniques in its net zero arsenal could use lower-grade iron ore, according to a new study.
Steel accounts for 5-8% of carbon dioxide emissions globally. Its total emissions have risen over the past decade, largely due to increased demand.
The International Energy Agency has stated that, without innovation, the scope to limit emissions is ‘limited’. Therefore, the commercialisation of new zero-emission production processes is critical.
Innovative ...