(Press-News.org) RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- A National Institutes of Health grant received by Vijayalakshmi (Viji) Santhakumar, a professor of molecular, cell and systems biology at the University of California, Riverside, has been selected for the prestigious Javits Neuroscience Investigator Award, the first time for the campus.
The five-year, $3.5 million grant from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, or NINDS, of the National Institutes of Health is a collaborative study with Edward Zagha, an associate professor of psychology at UCR. The award will support research into how brain circuits contribute to episodic memory formation and how disruption in these circuits in diseases like epilepsy can contribute to memory and cognitive deficits.
“The knowledge gained from this research project can have broader implications in our understanding of how altered circuit functions can contribute to memory disorders in aging and Alzheimer's disease,” Santhakumar said.
Specifically, her lab will develop fundamental knowledge on how the dentate gyrus, a major processing hub in the brain for integrating information from various senses to form memories of an event, functions at a circuit level and orchestrates broader network activity and behaviors.
“Our goal is to identify how these processes are compromised in brain insults like trauma and epilepsy and identify circuit adaptations that could help restore memory functions in aging, Alzheimer's disease, and epilepsy,” Santhakumar said.
The Javits Neuroscience Investigator Award is given to investigators who have a distinguished record of substantial contributions in a field of neurological science and who are expected to be highly productive over the next seven years. The award originated in 1984 after the U.S. Congress asked that special awards be made for research in the neurosciences in honor of the late Senator Jacob K. Javits of New York, a strong advocate for support of research in a wide variety of disorders of the brain and nervous system.
In the fourth year of the grant, Santhakumar can request a three-year renewal. Over the course of the seven years, the award is expected to support three postdoctoral fellows and two graduate students at UCR, she said.
Santhakumar came to UCR in 2018 from Rutgers University in New Jersey to expand her research vision of developing a multi-level understanding of brain circuit function in health and disease. Since joining the UCR faculty, she has secured extramural grants for a total of over $13 million as a principal investigator, co-investigator, or mentor.
She is on the editorial boards of several journals, including the Journal of Neuroscience, eNeuro, Journal of Neuroinflammation, and Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience, and serves on the board of the American Epilepsy Society. Her many awards and honors include being elected to co-chair the 2024 Gordon Research Conference of Epilepsy and Neuronal Synchronization, Magnificent Mentor Award from the UCR Biomedical Sciences Graduate Program, and an Epilepsy Foundation Young Investigator Award.
The University of California, Riverside is a doctoral research university, a living laboratory for groundbreaking exploration of issues critical to Inland Southern California, the state and communities around the world. Reflecting California's diverse culture, UCR's enrollment is more than 26,000 students. The campus opened a medical school in 2013 and has reached the heart of the Coachella Valley by way of the UCR Palm Desert Center. The campus has an annual impact of more than $2.7 billion on the U.S. economy. To learn more, visit www.ucr.edu.
END
Prestigious NIH award will advance brain research at UCR
Viji Santhakumar is the first recipient on campus of the Javits Neuroscience Investigator Award
2024-07-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Purdue researchers trap atoms, forcing them to serve as photonic transistors
2024-07-29
Researchers at Purdue University have trapped alkali atoms (cesium) on an integrated photonic circuit, which behaves like a transistor for photons (the smallest energy unit of light) similar to electronic transistors. These trapped atoms demonstrate the potential to build a quantum network based on cold-atom integrated nanophotonic circuits. The team, led by Chen-Lung Hung, associate professor of physics and astronomy at the Purdue University College of Science, published their discovery in the American Physical Society’s Physical Review X.
“We developed a technique to use lasers ...
Analogies for modeling belief dynamics
2024-07-29
Researchers who study belief dynamics often use analogies to understand and model the complex cognitive–social systems that underly why we believe the things we do and how those beliefs can change over time. Ideas can be transmitted like a virus, for instance, “infecting” a population as they spread from person to person. We might be drawn — like magnets — to others with a similar worldview. A society’s beliefs can shift slowly before reaching a tipping point that thrusts society into a new phase.
In a new paper in Trends in Cognitive Sciences, SFI Professor Mirta Galesic and ...
Many juvenile ‘lifers’ freed
2024-07-29
In 1953, 15-year-old Joe Ligon and four other Pennsylvania teens went on an alcohol-fueled tear that resulted in the stabbing deaths of two people and injuries to six more.
The teens were tried as a group, and all received life without parole.
After a series of U.S. Supreme Court decisions in 2012 and 2016 found that mandatory life sentences for juveniles was unconstitutional, Ligon’s case went to federal court. After 67 long years in prison, the case was decided in his favor in 2020.
Ligon was granted his freedom in 2021 — at 83 years of age and after ...
UW model shows cortical implants like Elon Musk’s Blindsight unlikely to ‘exceed normal human vision’
2024-07-29
Elon Musk recently declared on X that Blindsight, a cortical implant to restore vision, would have low resolution at first “but may ultimately exceed normal human vision.”
That pronouncement is unrealistic at best, according to new research from the University of Washington.
Ione Fine, lead author and UW professor of psychology, said Musk’s projection for the latest Neuralink project rests on the flawed premise that implanting millions of tiny electrodes into the visual cortex, the region of the brain that processes information received from the eye, will result in high-resolution vision.
For the study, ...
UVA's Data Justice Academy receives new funding from NSF
2024-07-29
The National Science Foundation will provide funding to the University of Virginia’s Data Justice Academy, the agency recently announced, support that will help the summer program continue to serve undergraduate students from groups that are historically underrepresented in data science.
Established in 2021, the Data Justice Academy provides a 10-week residential experience to participants in which they perform mentored research while learning technical skills.
The overriding goal of the Data Justice Academy, which is jointly managed by UVA’s School of Data Science and Equity Center, ...
Orthopedic surgeon-scientist Dr. Frank Henn named Chair of the Department of Orthopaedics
2024-07-29
University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) Dean Mark T. Gladwin, MD, announced today that R. Frank Henn, III, MD, Professor of Orthopaedics, who has served as Interim Chair of the Department since 2022, has been appointed to serve as the new Chair of UMSOM’s Department of Orthopaedics, effective immediately.
Dr. Henn, who joined the Department in 2010, is an academic leader and highly regarded, board-certified orthopaedic surgeon; he has published significant scientific research, and is a leading clinician focusing on the care of the shoulder and knee, with an emphasis in cartilage ...
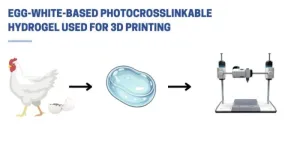
Nature inspires a breakthrough: scientists develop revolutionary egg white-based bioink for advanced tissue engineering
2024-07-29
Los Angeles, California – July 29, 2024 - Terasaki Institute scientists have created a cutting-edge technology inspired by nature by developing a novel bioink derived from egg whites or Egg White methacryloyl (EWMA). Bioinks are mainly used in 3D bioprinting to create artificial tissues. These natural or synthetic materials support living cells, aiding their adhesion, growth, and differentiation. They are essential for developing complex tissue structures for medical research, drug testing, and organ transplantation. This novel EWMA bioink represents a promising addition to this field, offering a unique combination of properties that address many challenges faced in tissue engineering.
The ...
California a botanical and climate change hot spot
2024-07-29
From coastal redwoods and Joshua trees to golden poppies and sagebrush, California is a global botanical hotspot. It’s also a place confronted with extreme heat, wildfires and crumbling coastlines. The state’s natural beauty and history of pioneering conservation efforts make it a test bed for protecting biodiversity in the face of current and future climate change, argues a study led by the University of California, Davis.
Published July 29 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the study, “Climate Change and California’s Terrestrial Biodiversity,” is part of a special ...
Young scientists face career hurdles in interdisciplinary research
2024-07-29
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Scientists agree that solving some of society’s greatest challenges in biomedicine such as food sustainability, aging and disease treatment will need researchers from a variety of scientific fields working together.
But a new study finds that the young scientists who most embrace interdisciplinary research face “career impediments” not seen in their peers who focus their work only within their own disciplines.
The results are troublesome and pose a “grave challenge” to efforts to increase interdisciplinary ...
New progress in research into malignant catarrhal fever in cattle
2024-07-29
A research team led by University of Liège scientists has published a groundbreaking study on malignant catarrhal fever (MCF). This disease is caused by the alcelaphine gammaherpesvirus 1 (AlHV-1), which infects its natural host, the wildebeest. This study sheds light on the mechanisms by which this virus, which is asymptomatic and latent in the wildebeest, causes an oligoclonal expansion of CD8+ T lymphocytes in cattle, leading to the development of MCF.
In 2013, the research team had already demonstrated (1) that malignant catarrhal fever (MCF), which is fatal in cattle, only develops if the AlHV-1 virus can maintain a ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
[Press-News.org] Prestigious NIH award will advance brain research at UCRViji Santhakumar is the first recipient on campus of the Javits Neuroscience Investigator Award