(Press-News.org) NEW ORLEANS – The Ochsner-Xavier Institute for Health Equity and Research, or OXIHER, has published its first strategic plan, outlining strategic priorities and achievements since the institute began in 2020.
The strategic plan is available here.
A partnership between Ochsner Health and Xavier University of Louisiana, OXIHER examines health disparities at the community level while educating healthcare providers on creating and nurturing a culture of equity, and training more students for advanced careers in healthcare.
The new plan details OXIHER’s substantial progress in its first three years in addressing the leading health inequities experienced by Louisiana residents. To date,
More than 34,000 community members have been reached through more than 100 outreach events supported by OXIHER
36% of newly enrolled patients in Ochsner clinical trials represent racial and ethnic minority groups
$3 million in legislative funding has been received for Xavier Ochsner College of Medicine
66% of Ochsner Health nurse scholars come from diverse backgrounds, along with 93% of community health worker trainees
OXIHER’s partnership with Ochsner’s digital medicine hypertension program helped reduce racial disparities in blood pressure control among Medicaid-insured patients from a high of 16% down to 1% after 18 months of follow-up
The report also details OXIHER’s five areas of focus to address the social factors that contribute to health disparities:
Community engagement
Outcomes research
Population health strategies
Workforce development and educational initiatives
Health advocacy
“We believe that clinical expertise, data, knowledge and action will lead to improved health for the people in the communities we serve,” says Eboni Price-Haywood, MD, OXIHER medical director.
For more information about the institute’s mission and how communities can join the effort, visit OXIHER online.
###
About Ochsner Health
Ochsner Health is the leading nonprofit healthcare provider in the Gulf South, delivering expert care at its 46 hospitals and more than 370 health and urgent care centers. For 12 consecutive years, U.S. News & World Report has recognized Ochsner as the No. 1 hospital in Louisiana. Additionally, Ochsner Children’s has been recognized as the No. 1 hospital for kids in Louisiana for three consecutive years. Ochsner inspires healthier lives and stronger communities through a combination of standard-setting expertise, quality and connection not found anywhere else in the region. In 2023, Ochsner Health cared for more than 1.5 million people from every state in the nation and 65 countries. Ochsner’s workforce includes more than 38,000 dedicated team members and over 4,700 employed and affiliated physicians. To learn more about how Ochsner empowers people to get well and stay well, visit https://www.ochsner.org/.
END
The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory has been awarded funding from DOE’s Office of Technology Transitions for four new projects that will help with commercialization of innovative clean-energy technology for a sustainable future.
Argonne scientists will work to turn their innovative ideas into next-generation technology necessary to build cleaner, more resilient energy systems. These projects build on Argonne’s decades-long role at the forefront of the quest to decarbonize ...
Researchers from North Carolina State University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have designed a protocol for harnessing the power of quantum sensors. The protocol could give sensor designers the ability to fine-tune quantum systems to sense signals of interest, creating sensors that are vastly more sensitive than traditional sensors.
“Quantum sensing shows promise for more powerful sensing capability that can approach the fundamental limit set by the law of quantum mechanics, but the challenge lies in being able to direct ...
Thanks to an accidental discovery, researchers at the University of British Columbia have created a new super-black material that absorbs almost all light, opening potential applications in fine jewelry, solar cells and precision optical devices.
Professor Philip Evans and PhD student Kenny Cheng were experimenting with high-energy plasma to make wood more water-repellent. However, when they applied the technique to the cut ends of wood cells, the surfaces turned extremely black.
Measurements by Texas A&M University’s ...
NASA will deliver a patch kit for NICER (Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer), an X-ray telescope on the International Space Station, on the agency’s Northrop Grumman 21st commercial resupply mission. Astronauts will conduct a spacewalk to complete the repair.
Located near the space station’s starboard solar array, NICER was damaged in May 2023. The mission team delivered the patch kit to NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in May 2024 so it could be prepped and packed for the upcoming resupply mission.
“It’s ...
Lung diseases kill millions of people around the world each year. Treatment options are limited, and animal models for studying these illnesses and experimental medications are inadequate. Now, researchers describe in ACS Applied Bio Materials their success in creating a mucus-based bioink for 3D printing lung tissue. This advance could one day help study and treat chronic lung conditions.
While some people with lung diseases receive transplants, donor organs remain in short supply. As an alternative, medications and other treatments can be used to manage symptoms, but no cure is available for disorders such as chronic obstructive ...
The tech community is more strongly divided in how they feel about artificial intelligence (AI) than the general public according to a study of Reddit discourse following the launch of ChatGPT.
Researchers from the University of Rochester led by Jiebo Luo, a professor of computer science and the Albert Arendt Hopeman Professor of Engineering, used ChatGPT and natural language processing techniques to analyze the themes and sentiments of 33,912 comments in 388 unique subreddits in the roughly six months following the generative AI tool’s launch in November 2022. The findings appear in Telematics and Informatics.
Reddit is an online social ...
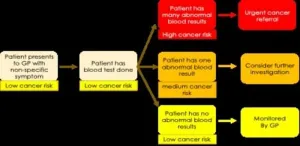
Incorporating information from common blood tests can enhance cancer risk assessment in patients with abdominal symptoms, according to a study publishing July 30th in the open-access journal PLOS Medicine by Meena Rafiq from University College London, UK, and colleagues.
Early cancer detection is key to successful treatment. However, many undiagnosed cancer patients present to their primary care provider with non-specific symptoms that can be a result of several other benign causes, making it difficult ...
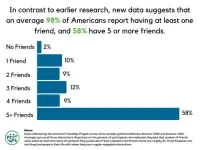
American adults may typically have more friends than indicated by other recent surveys, with fewer Americans having no friends at all – though many would like closer friendships. Natalie Pennington of Colorado State University, US, and colleagues present these preliminary findings from the ongoing “American Friendship Project” in a study published July 30, 2024, in the open-access journal PLOS ONE.
Having more and higher quality friendships is linked with greater happiness and life satisfaction. However, research suggests that ...
The results of routine blood tests could be used to speed up cancer diagnosis among people with stomach pain or bloating, suggests a new study led by UCL researchers.
Most people who report these symptoms to their GP are referred for blood tests. However, it is not known how well these blood tests, used to explore a range of possible causes of ill health, can predict cancer risk.
The new study, published in PLOS Medicine, looked at data from more than 400,000 people aged 30 or older in the UK who had visited a GP due to stomach ...
Which packaging type for a 12-ounce, single-serve container of orange juice would you choose as the most sustainable option:
Aluminum/canned, made with recycled material;
Carton, described as biodegradable/compostable;
Glass, 100% recyclable; or
Plastic, described as biodegradable/compostable?
If you were like the U.S. consumers surveyed by food scientists in a University of Massachusetts Amherst study, you’d prefer glass and believe it was the most sustainable choice. And you all would be mistaken.
“Glass was ...