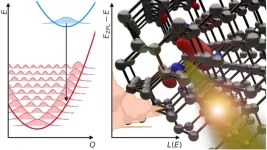
(Press-News.org) (Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Computers benefit greatly from being connected to the internet, so we might ask: What good is a quantum computer without a quantum internet?
The secret to our modern internet is the ability for data to remain intact while traveling over long distances, and the best way to achieve that is by using photons. Photons are single units (“quanta”) of light. Unlike other quantum particles, photons interact very weakly with their environment. That stability also makes them extremely appealing for carrying quantum information over long distances, a process that requires maintaining a delicate state of entanglement for an extended period of time. Such photons can be generated in a variety of ways. One possible method involves using atomic-scale imperfections (quantum defects) in crystals to generate single photons in a well-defined quantum state.
Decades of optimization have resulted in fiber-optic cables that can transmit photons with extremely low loss. However, this low-loss transmission works only for light in a narrow range of wavelengths, known as the “telecom wavelength band.” Identifying quantum defects that produce photons at these wavelengths has proven difficult, but funding from the U.S. Department of Energy and the National Science Foundation (NSF) has enabled researchers in the UC Santa Barbara College of Engineering to understand why that is. They describe their findings in “Rational Design of Efficient Defect-Based Quantum Emitters,” published in the journal APL Photonics.
“Atoms are constantly vibrating, and those vibrations can drain energy from a light emitter,” says UCSB materials professor Chris Van de Walle. “As a result, rather than emitting a photon, a defect might instead cause the atoms to vibrate, reducing the light-emission efficiency.” Van de Walle’s group developed theoretical models to capture the role of atomic vibrations in the photon-emission process and studied the role of various defect properties in determining the degree of efficiency.
Their work explains why the efficiency of single-photon emission drastically decreases when the emission wavelength increases beyond the wavelengths of visible light (violet to red) to the infrared wavelengths in the telecom band. The model also allows the researchers to identify techniques for engineering emitters that are brighter and more efficient.
“Choosing the host material carefully, and conducting atomic-level engineering of the vibrational properties are two promising ways to overcome low efficiency,” said Mark Turiansky, a postdoctoral researcher in the Van de Walle lab, a fellow at the NSF UC Santa Barbara Quantum Foundry, and the lead researcher on the project.
Another solution involves coupling to a photonic cavity, an approach that benefited from the expertise of two other Quantum Foundry affiliates: computer engineering professor Galan Moody and Kamyar Parto, a graduate student in the Moody lab.
The team hopes that their model and the insights it provides will prove useful in designing novel quantum emitters that will power the quantum networks of the future.
END
Bright prospects for engineering quantum light
When — and why — does a photon emitter not emit? Research at UC Santa Barbara illuminates the issue.
2024-07-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New high-resolution 3D maps show how the brain’s blood vessels changes with age
2024-07-30
HERSHEY, Pa. — Healthy blood vessels matter for more than just heart health. Vascular well-being is critical for brain health and potentially in addressing age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disorders, like Alzheimer’s disease, according to new study led by Penn State researchers. The findings point to an understudied but possible key role the brain’s vascular network — or energy infrastructure — plays in the onset of neurodegenerative disease.
They published their work today (July 30) in Nature Communications.
Using advanced imaging techniques, the team developed maps of a mouse brain that illustrate ...
Genes or environment? A new model for understanding disease risk factors
2024-07-30
HERSHEY, Pa. — Every disease is shaped by a genetic component as well as environmental factors like air pollution, climate and socioeconomic status. However, the extent to which genetics or environment plays a role in disease risk — and how much can be attributed to each — isn’t well understood. As such, the actions individuals can take to reduce their risk for disease aren’t often clear.
A team led by Penn State College of Medicine researchers found a way to tease apart genetic and ...
Study reveals impact of concern about misinformation on Americans’ media consumption habits
2024-07-30
Most Americans are aware of fake news and misinformation. In a new study, researchers from the University of Pennsylvania sought to uncover whether the threat of misinformation drives Americans to seek out news sources that reflect their own political beliefs.
The study, published in the Harvard Kennedy School Misinformation Review, found that Democrats, older individuals, and those with higher education levels are more concerned about misinformation in general and that, compared to Republicans, ...
USF students will swab first responder vehicles through a CDC-funded infection control initiative
2024-07-30
TAMPA, Fla. (July 30, 2024) – University of South Florida students are leading infection control training for fire and emergency medical services personnel as part of a groundbreaking initiative supported by a multi-million-dollar cooperative agreement with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
This fall, student research and project assistants will begin swabbing first responder vehicles, ambulances, fire trucks and equipment to identify pathogen exposure risks and enhance training.
“By working on this aspect ...
Grainger Engineers to lead Illinois Quantum and Microelectronics Park, shape the future of quantum computing
2024-07-30
Today, The Grainger College of Engineering at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign joined other partners from around the state in officially announcing its leadership role in the Illinois Quantum and Microelectronics Park. The project – a quantum-focused research and development campus in Chicago – will be managed by a University of Illinois-led organization on behalf of the State of Illinois and Governor J.B. Pritzker.
Advances in quantum information science and engineering, together with next generation microelectronics, promise to transform computing, which underpins much of how our modern society operates. Grainger Engineering Associate Dean for Research ...
Research warns of “systematic weaknesses in jury decisions”
2024-07-30
There are “systemic weaknesses” in the way juries make decisions – and these are likely to be contributing to the conviction of innocent people, failures to convict the guilty, and inequalities, new research warns.
The current legal rules involving procedure and evidence are not consistently designed based on robust evidence about how the juries make decisions, but the system could function better, according to a new book.
Dr Rebecca Helm, from the University of Exeter, outlines how juries are likely to struggle to make effective legal decisions in predictable case types, including cases involving sexual offences in which testimony ...
NYU Tandon School of Engineering and Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur announce seven joint research projects launching their new partnership
2024-07-30
NYU Tandon School of Engineering and Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur (IIT Kanpur) have unveiled their inaugural roster of collaborative research projects, the first such initiatives under the broad partnership that NYU and IIT Kanpur established last year.
The seven projects, jointly led by researchers from each institution, aim to advance innovations across vital scientific fields including cybersecurity, biotechnology, artificial intelligence, robotics, and wireless communications.
NYU and IIT Kanpur announced their initial partnership agreement in September 2023, ...
Study finds genetic variant among people who experience a rare recovery from ALS
2024-07-30
DURHAM, N.C. – Though exceedingly rare, some people diagnosed with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) partially or fully recover from the lethal neurodegenerative disease.
A better understanding of this baffling phenomenon, reported in medical literature for at least 60 years, could point to potential new treatment approaches. To that end, researchers at Duke Health and St. Jude’s Research Hospital launched a study of ALS recovery patients and found certain genetic factors that appear to protect ...
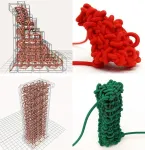
Watch ut IKEA: CMU Researchers eye knitted furniture
2024-07-30
Yuichi Hirose has a dream — a dream that someday everyone will have access to a machine capable of knitting furniture.
This machine wouldn't just knit the furniture's exterior fabric, but would use knitting to fashion solid three-dimensional chairs, tables and other objects. Tired of that love seat? Just unravel it and reuse the yarn to knit yourself an ottoman.
This new fabrication technique — first envisioned by Hirose, a robotics Ph.D. student in Carnegie Mellon University's School of Computer Science — is called solid knitting. The idea captured his imagination more than a decade ago. And now, working with a research team headed by James ...
Enjoy your work? Don’t sell yourself short. Buyers are willing to pay more for products you enjoy producing
2024-07-30
Researchers from Tilburg University, Northwestern University, and Lehigh University published a new Journal of Marketing study that examines how a seller’s enjoyment in making a product influences buyers’ willingness to pay and the price the seller charges.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Production Enjoyment Asymmetrically Impacts Buyers’ Willingness to Pay and Sellers’ Willingness to Charge” and is authored ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
UF research finds a gentler way to treat aggressive gum disease
Strong alcohol policy could reduce cancer in Canada
Air pollution from wildfires linked to higher rate of stroke
Tiny flows, big insights: microfluidics system boosts super-resolution microscopy
Pennington Biomedical researcher publishes editorial in leading American Heart Association journal
New tool reveals the secrets of HIV-infected cells
HMH scientists calculate breathing-brain wave rhythms in deepest sleep
Electron microscopy shows ‘mouse bite’ defects in semiconductors
Ochsner Children's CEO joins Make-A-Wish Board
Research spotlight: Exploring the neural basis of visual imagination
Wildlife imaging shows that AI models aren’t as smart as we think
Prolonged drought linked to instability in key nitrogen-cycling microbes in Connecticut salt marsh
Self-cleaning fuel cells? Researchers reveal steam-powered fix for ‘sulfur poisoning’
Bacteria found in mouth and gut may help protect against severe peanut allergic reactions
Ultra-processed foods in preschool years associated with behavioural difficulties in childhood
A fanged frog long thought to be one species is revealing itself to be several
Weill Cornell Medicine selected for Prostate Cancer Foundation Challenge Award
[Press-News.org] Bright prospects for engineering quantum lightWhen — and why — does a photon emitter not emit? Research at UC Santa Barbara illuminates the issue.