(Press-News.org)
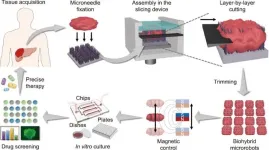
In a pioneering development for the biomedical field, a research team led by Yuanjin Zhao from Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, China, has published a research article in Engineering. The article, titled “Controllable Histotomy Based on Hierarchical Magnetic Microneedle Array Robots,” introduces a novel technique for tissue slicing and cultivation that could revolutionize the way primary tissues are handled in clinical settings.
The in vitro cultivation of patient-derived tissues is crucial for accurate diagnosis, precision medication, individualized therapy, and tissue engineering. However, current tissue slicing and cultivation techniques often fall short of clinical requirements. The research team’s innovative approach addresses these challenges by introducing a controllable histotomy strategy that utilizes hierarchical magnetic microneedle array robots.
This strategy involves a three-dimensionally printed, mortise-tenon-structured slicing device, coupled with a magnetic-particle-loaded and pagoda-shaped microneedle array scaffold. The multilayered structure of the microneedles allows for the effective fixation of tissue specimens, avoiding tissue slipping during the slicing process. Moreover, the encapsulated magnetic microneedle fragments enable the tissue pieces to act as magnetically responsive biohybrid microrobots, facilitating their separation, transportation, and dynamic culture through magnetic fields.
The team demonstrated the technique’s efficacy by tailoring primary pancreatic cancer tissues into tiny pieces and culturing them in multilayered microfluidic chips for high-throughput drug screening. The results indicate the promising future of this technique in clinical settings, offering a significant step forward in the precision medicine landscape.
“The development of this controllable histotomy technique marks a significant advancement in the field of tissue engineering and drug screening,” said Jiaming Wu, the editor of Engineering. “By leveraging the capabilities of magnetic microneedle array robots, researchers have been able to create a more efficient and precise method for tissue manipulation and analysis.”
The research article also discusses the potential for further improvements to the technique, such as automating the horizontal sectioning and production of tissue cubes, and scaling up the microtomy device for higher throughput. Additionally, the team envisions the application of this technology beyond cancer research, to other types of patient-derived primary tissues, and its potential for long-term tissue cultivation and observation.
The innovative work by Yuanjin Zhao’s team not only pushes the boundaries of current tissue analysis techniques but also opens up new possibilities for personalized medicine and the development of more effective treatments. As the technology matures, it is expected to play a pivotal role in the advancement of biomedical research and clinical applications.
The paper “Controllable Histotomy Based on Hierarchical Magnetic Microneedle Array Robots,” authored by Xiaoxuan Zhang, Hanxu Chen, Taiyu Song, Jinglin Wang, Yuanjin Zhao. Full text of the open access paper: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2024.05.004. For more information about the Engineering, follow us on X (https://twitter.com/EngineeringJrnl) & like us on Facebook (https://www.facebook.com/EngineeringJrnl).
END
Gallium nitride (GaN) semiconductors can now be grown without ammonia, a toxic chemical that needs a sophisticated detoxifying system before it can be released into the atmosphere. The new technique is not only more environmentally friendly but also allows for the efficient and high-quality growth of crystals at a lower cost. Scientists can make semiconductors more efficiently with a reduced need for raw materials and power. Researchers from Nagoya University in Japan led the study, which was published in Scientific Reports.
GaN is a compound made up of gallium (Ga) and nitrogen ...
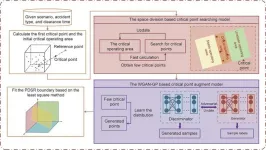
Fast and accurate transient stability analysis is crucial to power system operation. With high penetration level of wind power resources, practical dynamic security region (PDSR) with hyper plane expression has outstanding advantages in situational awareness and series of optimization problems. The precondition of obtaining accurate PDSR boundary is to locate sufficient points around the boundary (critical points). Therefore, a research team led by Yanli Liu from Tianjin University, China, has developed a space division and Wasserstein generative adversarial network with gradient penalty (WGAN-GP) based fast generation method of PDSR boundary. The study, published in Engineering.
The ...
A new report from the University of California San Diego School of Global Policy and Strategy reveals significant changes in support for labor unions among U.S. workers.
The report, published by the Economics Policy Institute, delves into the evolving attitudes toward unions and identifies three major shifts are occurring in U.S. workers: a recent, marked decline in opposition to labor unions, a rise of workers who are interested in—but unsure about—unions and an emerging generation gap in attitudes toward unionization between younger and older workers.
“While we compared levels of support for workplace unionization ...
Ensuring older hospital patients receive specialised medication management could reduce their stay in hospital and potentially lower their risk of death, according to new research conducted by Flinders University in collaboration with Flinders Medical Centre.
One in ten older people experience ‘adverse drug reactions’ (ADRs) to medications whilst in hospital, the research published in The Journal of the American Medical Directors Association (JAMDA) found.
“As the population is getting older, patients have more chronic medical ...
New Orleans, LA - July 30, 2024 – Ochsner Health announces an enterprise-wide agreement with DeepScribe to implement its ambient AI clinical documentation technology across its 46 hospitals and 370 health and urgent care centers. DeepScribe ambient AI turns each patient conversation into a complete, accurate note with real-time insights for clinicians, empowering them to be fully present with the patient while helping health systems achieve quality and value-based goals.
Ochsner clinicians participating during the pilot phase have already seen a positive effect on the patient experience, with 96 percent of their patients stating they are likely to recommend ...
New evidence has emerged about the long-term effects of the COVID-19 pandemic in Los Angeles County, as shown by a recent study in the journal PLOS ONE. Scientists at USC and the Los Angeles County Department of Public Health (DPH) found that existing disparities in mental health between white and non-white residents worsened.
The study used two surveys conducted in 2018 and in spring 2021 to measure the risk for major depression among adults, alongside data about death rates. The researchers considered monthly averages between March 2020 (when the ...
“Sometimes the crazy ideas lead to watershed improvements.”
That was a key takeaway from new research conducted by Utah State University, published in the American Society of Civil Engineer’s Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management. Using Google Sheets during video calls, 26 Colorado River Basin managers and experts took on water user roles to discuss consuming, banking and trading Colorado River water.
As Western states face aridity and reservoir levels depleting, more ...
The first Cuban-American to be inducted into the Academy of Sciences in Cuba is a retired Cal Poly biology professor and renowned microbiologist.
In May 2024, Professor Emeritus Raul J. Cano was awarded membership in the Academy’s headquarters in the National Capitol building in Havana.
Cano, who previously received national attention for his work with amber dating back millions of years, has been heavily involved in research and clinical projects in Cuba over the past five years.
Cano partnered with Clinical Hospital Hermanos Ameijeiras in Havana for clinical research in probiotics. ...
WASHINGTON (July 30, 2024) — A study led by Georgetown University neuroscientists reveals that the part of the brain that receives and processes visual information in sighted people develops a unique connectivity pattern in people born blind. They say this pattern in the primary visual cortex is unique to each person — akin to a fingerprint.
The findings, described July 30, 2024, in PNAS, have profound implications for understanding brain development and could help launch personalized rehabilitation and sight restoration strategies.
For decades, scientists have known that the visual ...
FAYETTEVILLE, Ark. — Ryan Dickson, an assistant professor of horticulture for the Arkansas Agricultural Experiment Station, has been developing research since 2018 on growing blackberries indoors and recently secured a nearly $750,000 grant to further that work over the next four years.
The experiment station is the research arm of the University of Arkansas System Division of Agriculture and is home to the largest public-sector breeding program for fresh-market blackberries in the United States. ...