(Press-News.org) SAN ANTONIO — July 31, 2024 —Southwest Research Institute will provide engineering and equipment support for advanced cryptologic technology for shipboard and airborne platforms as part of a $35.7 million contract with the U.S. Navy. The five-year contract will deliver services from June 2024 through June 2029, with the option for the U.S. Navy to add $14 million and extend the contract through 2031.
SwRI develops electronic warfare (EW) technology to detect, intercept and disrupt a range of signals on the electromagnetic spectrum, supporting efforts to thwart adversaries. As part of EW systems, cryptologic technology identifies and responds to encrypted or coded radio frequency signals.
“We develop technology critical to warfighter success,” said SwRI Senior Program Manager Robert C. Torres, who is leading this effort. “Our cryptologic equipment enhances battlespace awareness through intelligent signal surveillance of the electromagnetic environment.”
The comprehensive contract includes support services for associated equipment from installation, calibration, integration and training to life-cycle logistics support, spare parts management, maintenance, repair and technology updates.
“The Defense and Intelligence Division at SwRI has a long history of leading communications and signals intelligence programs for Department of Defense forces,” said Torres. “We are continuously designing and upgrading this technology and developing next-generation equipment to support the armed forces of the U.S. and our allies.”
For more than 70 years, SwRI has developed advanced signals intelligence technology, supporting maritime, airborne and land-based operations. SwRI has deployed field-proven cryptologic equipment for use in more than 300 applications worldwide, including systems for the U.S., the Five Eyes Alliance — Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom and the United States — and other allied intelligence communities.
To learn more, visit https://www.swri.org/industries/signals-intelligence-solutions.
END
SwRI awarded $35.7 million to support cryptologic systems for U.S. Navy
Electronic warfare technology intercepts signals of interest during naval missions
2024-07-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
With biodiversity under threat, scientists suggest the need for a new biorepository—on the moon
2024-07-31
With numerous species facing extinction, an international team of researchers has proposed an innovative solution to protect the planet's biodiversity: a lunar biorepository. This concept, detailed in a recent article in the journal BioScience, is aimed at creating a passive, long-lasting storage facility for cryopreserved samples of Earth's most at-risk animal species.
Led by Dr. Mary Hagedorn of the Smithsonian's National Zoo and Conservation Biology Institute, the team envisions taking advantage of the Moon's naturally cold temperatures, particularly in permanently shadowed regions near the poles, where temperatures remain consistently below –196 degrees ...
Strong El Nino makes European winters easier to forecast
2024-07-31
Heavy rain and flooding in Brazil in November could tell forecasters whether December, January and February in Britain will be cold and dry or mild and wet.
This is because forecasting European winter weather patterns months in advance is made simpler during years of strong El Niño or La Niña events in the tropical Pacific Ocean, a new study has found.
A strong El Nino or La Nina in the Pacific Ocean can bring big changes in temperatures, wind patterns and rainfall patterns to South America. When ...
MD Anderson and collaborators to launch project studying T cells on International Space Station
2024-07-31
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and collaborators are initiating a research project that will send T cells to the International Space Station (ISS) to study the effects of prolonged microgravity on cell differentiation, activation, memory and exhaustion. These results will be further analyzed on Earth to uncover signaling pathways and identify potential immune targets that can improve treatment strategies for patients with cancer and other diseases.
To accomplish this work, MD Anderson researchers ...
Chameleon testbed secures $12 million in funding for phase 4: Expanding frontiers in computer science research
2024-07-31
Chameleon, led by Senior Scientist Kate Keahey from Argonne National Laboratory, has been a cornerstone of CS research and education for nearly a decade. The platform has served over 10,000 users, contributing to more than 700 research publications. Chameleon has now secured an additional $12 million in funding from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) to roll out its next four-year phase. With this new funding, Chameleon will continue to innovate and support its growing community, enabling groundbreaking discoveries in CS systems research.
ABOUT CHAMELEON: A PLATFORM FOR INNOVATION
Chameleon is a large-scale, deeply reconfigurable experimental ...
For bigger muscles push close to failure, for strength, maybe not
2024-07-31
When performing resistance training such as lifting weights, there’s a lot of interest in how close you push yourself to failure – the point where you can’t do another rep – and how it affects your results.
While research has looked at this concept in different ways, to date, no meta-analysis has explored the pattern (i.e., linear or non-linear) of how the distance from failure (measured by repetitions in reserve) affects changes in muscle strength and size.
As such, it’s ...
Improving Alzheimer’s disease imaging — with fluorescent sensors
2024-07-31
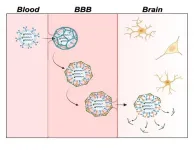
Neurotransmitter levels in the brain can indicate brain health and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. However, the protective blood-brain barrier (BBB) makes delivering fluorescent sensors that can detect these small molecules to the brain difficult. Now, researchers in ACS Central Science demonstrate a way of packaging these sensors for easy passage across the BBB in mice, allowing for improved brain imaging. With further development, the technology could help advance Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis and treatment.
It is common for neurotransmitter levels ...
Most blood thinner dosing problems happen after initial prescription
2024-07-31
Millions of Americans take anticoagulants, commonly known as blood thinners. These medications work to prevent blood clots that cause heart attack and stroke.
More than two-thirds of those people take a type of blood thinner called a direct oral anticoagulant. DOACs, such as rivaroxaban (brand name Xarelto) and apixaban (brand name Eliquis), are under- or over-prescribed in up to one in eight patents.
These prescribing issues can have life threatening consequences, and they most often occur after a provider writes the initial prescription, according to a study led by Michigan Medicine.
“Direct oral anticoagulants may be viewed ...
AI boosts the power of EEGs, enabling neurologists to quickly, precisely pinpoint signs of dementia
2024-07-31
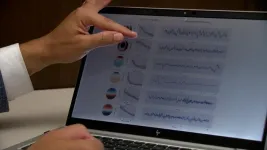
ROCHESTER, Minn. — Mayo Clinic scientists are using artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to analyze electroencephalogram (EEG) tests more quickly and precisely, enabling neurologists to find early signs of dementia among data that typically go unexamined.
The century-old EEG, during which a dozen or more electrodes are stuck to the scalp to monitor brain activity, is often used to detect epilepsy. Its results are interpreted by neurologists and other experts trained to spot patterns among the test's squiggly waves.
In new research published in Brain Communications, scientists at the Mayo Clinic Neurology AI Program (NAIP) demonstrate ...
AI predicts male infertility risk with blood test, no semen needed
2024-07-31
According to a World Health Organization (WHO) study (2017), about half of all infertility is due to men. Semen analysis is considered essential for diagnosis of male infertility, but is not readily available at medical institutions other than those specializing in infertility treatment, and there is a high threshold for receiving it.
In this study, a group led by Associate Professor Hideyuki Kobayashi of the Department of Urology, Toho University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan developed an AI model that can predict the risk ...
Researchers pioneer new approach to enhance all-solid-state lithium batteries
2024-07-31
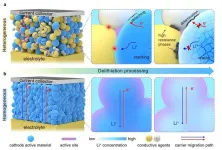
Researchers at the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, along with collaborators from leading international institutions, have introduced an innovative cathode homogenization strategy for all-solid-state lithium batteries (ASLBs).
This new approach, detailed in their recent publication in Nature Energy on July 31, significantly improves the cycle life and energy density of ASLBs, representing an important advancement in energy storage technology.
Current ASLBs face challenges due to heterogeneous composite cathodes, which require ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
[Press-News.org] SwRI awarded $35.7 million to support cryptologic systems for U.S. NavyElectronic warfare technology intercepts signals of interest during naval missions