(Press-News.org)
Most self-service interactive devices — kiosks, ATMs and other digital interfaces — don't measure up to the accessibility needs of Canadians who report to have a disability, a new study has found.
In partnership with the CSA Group (Canadian Standards Association), University of Waterloo researchers interviewed people with lived experiences of disability and received an overwhelming consensus that most self-serve devices have little to no accessibility features or they have trouble finding them.
More than one-quarter of Canadians aged 15 years and older identify as having a disability, according to the 2022 Canadian Survey on Disability.
"Regardless of one's ability level, it's important that people are able to use these devices correctly with minimal distress and have a consistent experience with access to consistent features," said Gaya Bin Noon, PhD candidate at Waterloo's School of Public Health Sciences and the study's lead author.
Common concerns expressed by participants included the protection of personal information, privacy and security and the consistency and usability of these devices.
Participants also cited that their ability to use a self-service device is undermined if they need to seek assistance from a staff member, in addition to their concerns about revealing personal information.
"Independence is a big one for me," said one participant. "It's really important to be able to accomplish a task on your own independently, especially if it's something confidential."
One solution found in this study was to pair personal devices, or smartphones, to compensate for any accessibility shortcomings in self-service devices. A personal device would minimize the need for alternative accessible technology while maintaining privacy and security.
"Many smartphones already have personalized accessibility features attached, with screen readers and all of the user's personal data already loaded in," Bin Noon said. "They would be guaranteed to have something that they are familiar with and that works."
Another theme in the researchers' interviews with participants was the need to broadly promote accessible features and increase accessibility training for on-site staff. Participants noted that users frequently seek out accessibility information on company or organization websites, making it especially important that online resources clearly state any self-service devices' accessibility features.
Waterloo researchers hope this study can help shape guidelines on optimal safety and usability for manufacturers of self-serve devices.
"We're also trying to raise awareness as to what the gaps are and how it affects people who are just trying to live their lives, like going to the bank, encountering airport border control, ordering sushi or checking in at their doctor's office," Bin Noon said.
The study, Concerns regarding the accessibility of self-service interactive devices for people with disabilities, was recently published in Disability and Rehabilitation: Assistive Technology. Co-authors include Bin Noon, Dr. Plinio Morita, students Luka Ugaya Mazza and Gillian Morgan from Waterloo's School of Public Health Sciences, as well as Stephanie Singh and Dragica Jeremic Nikolic from the CSA Group.
END
A new study led by researchers at Durham University have uncovered an incredibly rare and detailed fossil, named Youti yuanshi, that gives a peek inside one of the earliest ancestors of modern insects, spiders, crabs and centipedes.
This fossil dates back over 520 million years to the Cambrian period, when the major animal groups we know today were first evolving.
This fossil belongs to a group called the euarthropods, which includes modern insects, spiders and crabs. What makes this fossil so special ...
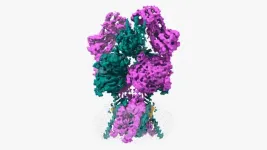
The general anesthetic propofol may hold the keys to developing new treatment strategies for epilepsy and other neurological disorders, according to a study led by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and Sweden’s Linköping University.
In their study, published July 31 in Nature, the researchers determined the high-resolution structural details of how propofol inhibits the activity of HCN1, an ion channel protein found on many types of neurons. Drug developers consider inhibiting HCN1 a promising strategy for treating neurologic disorders including epilepsy and chronic pain. The researchers also found, to their surprise, that when HCN1 contains ...
About The Study: The results of this survey study of U.S. adults suggest that trust in physicians and hospitals decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic. As lower levels of trust were associated with lesser likelihood of pursuing vaccination, restoring trust may represent a public health imperative.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Roy H. Perlis, MD, MSc, email rperlis@mgh.harvard.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.24984)
Editor’s ...
About The Study: In this comparative effectiveness study of state firearm policies, the joint effect estimates of combinations of firearm laws were calculated, showing that restrictive firearm policies were associated with substantial reductions in firearm mortality. Although policymakers would benefit from knowing the effects of individual policies, the estimated changes in firearm mortality following implementation of individual policies were often small and uncertain.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding ...
About The Study: Sugar-sweetened beverage excise taxes were associated with lower body mass index percentile among youth in this cohort study. Policymakers should consider implementing sugar-sweetened beverage excise taxes to prevent or reduce youth overweight and obesity and, ultimately, chronic disease, particularly among children younger than 12 years.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Deborah Rohm Young, PhD, email deborah.r.young@kp.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.24822)
Editor’s ...
E. Kate Webb, PhD, a research fellow at McLean Hospital who works in the Neurobiology of Fear Laboratory and Neurobiology of Affective and Traumatic Experiences Laboratory, led an investigation into whether individual resources and neighborhood resources, like greenspace, might impact neurobiology and the trajectory of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms. Her research was published July 31st in JAMA Psychiatry.
What led you to examine the link between neighborhood characteristics and PTSD?
About 46 million people experience ...
Nearly half of the nation’s National Cancer Institute (NCI)-designated cancer centers required universal masking in key clinical areas during the winter 2023-2024 COVID-19 surge, according to a study by Tulane University researchers.
Overall, 41.8% of these 67 centers required some universal masking, according to the study, which published in JAMA Network Open. Further, 12 NCI-designated centers (18%) required universal masking in all areas. Masking policies were even more common in northeastern states and in centers with longer NCI designation, more funding and higher care rankings.
Those with cancer face higher risks from COVID-19 ...
Proteins are constantly performing a kind of dance. They move and contort their bodies to fulfill specific functions inside our bodies. The NMDAR protein executes an especially hard dance routine in our brains. One wrong step can lead to a range of neurological disorders. NMDAR binds to the neurotransmitter, glutamate, and another compound, glycine. These bindings control NMDAR’s dance steps. When their routine is over, the NMDAR opens. This open ion channel generates electrical signals critical for cognitive functions like memory.
The problem is that scientists couldn’t figure out the last step in NMDAR’s routine—until ...
At any given time, over 10 trillion microbes call our guts their home. From breaking down nutrients in our food to strengthening our immunity against pathogens, these microbes play an essential role in how we interact with the world. This includes – as shown in a new study by EMBL researchers and collaborators at the University of Split, Croatia – the way the body responds to carcinogens and develops cancer.
Carcinogens are chemicals that can cause ordinary cells to transform into cancer ...
BOSTON– A cross-representative survey of adults in the United States showed decreasing levels of trust in physicians and hospitals during the COVID-19 pandemic—and the lower the trust, the less likely an individual was to get vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 or influenza. The findings come from a survey study of more than 400,000 U.S. adults published in JAMA Network Open by a team co-led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system.
“Trust in ...