(Press-News.org) About The Study: In this comparative effectiveness study of state firearm policies, the joint effect estimates of combinations of firearm laws were calculated, showing that restrictive firearm policies were associated with substantial reductions in firearm mortality. Although policymakers would benefit from knowing the effects of individual policies, the estimated changes in firearm mortality following implementation of individual policies were often small and uncertain.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Terry L. Schell, PhD, email tschell@rand.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.22948)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.22948?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=073124
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
State policies regulating firearms and changes in firearm mortality
JAMA Network Open
2024-07-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
City-level sugar-sweetened beverage taxes and youth body mass index percentile
2024-07-31
About The Study: Sugar-sweetened beverage excise taxes were associated with lower body mass index percentile among youth in this cohort study. Policymakers should consider implementing sugar-sweetened beverage excise taxes to prevent or reduce youth overweight and obesity and, ultimately, chronic disease, particularly among children younger than 12 years.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Deborah Rohm Young, PhD, email deborah.r.young@kp.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.24822)
Editor’s ...
Impact of neighborhood resources on resilience after trauma
2024-07-31
E. Kate Webb, PhD, a research fellow at McLean Hospital who works in the Neurobiology of Fear Laboratory and Neurobiology of Affective and Traumatic Experiences Laboratory, led an investigation into whether individual resources and neighborhood resources, like greenspace, might impact neurobiology and the trajectory of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms. Her research was published July 31st in JAMA Psychiatry.
What led you to examine the link between neighborhood characteristics and PTSD?
About 46 million people experience ...
Study finds nearly half of top cancer centers required universal masking during last winter’s COVID-19 surge
2024-07-31
Nearly half of the nation’s National Cancer Institute (NCI)-designated cancer centers required universal masking in key clinical areas during the winter 2023-2024 COVID-19 surge, according to a study by Tulane University researchers.
Overall, 41.8% of these 67 centers required some universal masking, according to the study, which published in JAMA Network Open. Further, 12 NCI-designated centers (18%) required universal masking in all areas. Masking policies were even more common in northeastern states and in centers with longer NCI designation, more funding and higher care rankings.
Those with cancer face higher risks from COVID-19 ...
This protein does “The Twist”
2024-07-31
Proteins are constantly performing a kind of dance. They move and contort their bodies to fulfill specific functions inside our bodies. The NMDAR protein executes an especially hard dance routine in our brains. One wrong step can lead to a range of neurological disorders. NMDAR binds to the neurotransmitter, glutamate, and another compound, glycine. These bindings control NMDAR’s dance steps. When their routine is over, the NMDAR opens. This open ion channel generates electrical signals critical for cognitive functions like memory.
The problem is that scientists couldn’t figure out the last step in NMDAR’s routine—until ...
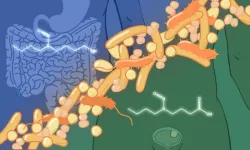
Gut microbes implicated in bladder cancer
2024-07-31
At any given time, over 10 trillion microbes call our guts their home. From breaking down nutrients in our food to strengthening our immunity against pathogens, these microbes play an essential role in how we interact with the world. This includes – as shown in a new study by EMBL researchers and collaborators at the University of Split, Croatia – the way the body responds to carcinogens and develops cancer.
Carcinogens are chemicals that can cause ordinary cells to transform into cancer ...
Trust in physicians and hospitals declined over the course of the COVID-19 pandemic
2024-07-31
BOSTON– A cross-representative survey of adults in the United States showed decreasing levels of trust in physicians and hospitals during the COVID-19 pandemic—and the lower the trust, the less likely an individual was to get vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 or influenza. The findings come from a survey study of more than 400,000 U.S. adults published in JAMA Network Open by a team co-led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system.
“Trust in ...
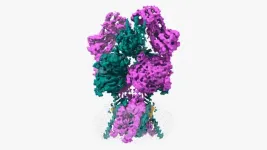
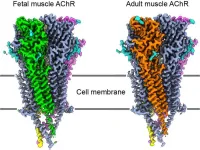
Unraveling a key junction underlying muscle contraction
2024-07-31
The connections between the nervous system and muscles develop differently across the kingdom of life. It takes newborn humans roughly a year to develop the proper muscular systems that support the ability to walk, while cows can walk mere minutes after birth and run not long after.
University of California San Diego researchers, using powerful new visualization technologies, now have a clear picture of why these two scenarios develop so differently. The results offer new insight into understanding muscle contraction in humans that may help in developing future treatments for muscular diseases.
“In this study we set out to understand ...
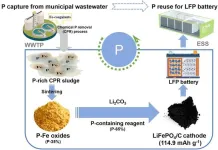
New method recovers phosphorus from wastewater to power the future of lithium-iron phosphate batteries
2024-07-31
In a recent study published in Engineering, a research team from the Shenzhen Engineering Research Laboratory for Sludge and Food Waste Treatment and Resource Recovery has introduced a pioneering method to tackle the critical global issue of phosphorus (P) scarcity. Their innovative approach leverages municipal wastewater to produce phosphorus vital for the manufacture of lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries, a key component in the rapidly growing electric vehicle market.
As the demand for LiFePO4 batteries ...
SwRI awarded $35.7 million to support cryptologic systems for U.S. Navy
2024-07-31
SAN ANTONIO — July 31, 2024 —Southwest Research Institute will provide engineering and equipment support for advanced cryptologic technology for shipboard and airborne platforms as part of a $35.7 million contract with the U.S. Navy. The five-year contract will deliver services from June 2024 through June 2029, with the option for the U.S. Navy to add $14 million and extend the contract through 2031.
SwRI develops electronic warfare (EW) technology to detect, intercept and disrupt a range of signals on the electromagnetic spectrum, supporting efforts to thwart ...
With biodiversity under threat, scientists suggest the need for a new biorepository—on the moon
2024-07-31
With numerous species facing extinction, an international team of researchers has proposed an innovative solution to protect the planet's biodiversity: a lunar biorepository. This concept, detailed in a recent article in the journal BioScience, is aimed at creating a passive, long-lasting storage facility for cryopreserved samples of Earth's most at-risk animal species.
Led by Dr. Mary Hagedorn of the Smithsonian's National Zoo and Conservation Biology Institute, the team envisions taking advantage of the Moon's naturally cold temperatures, particularly in permanently shadowed regions near the poles, where temperatures remain consistently below –196 degrees ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
[Press-News.org] State policies regulating firearms and changes in firearm mortalityJAMA Network Open