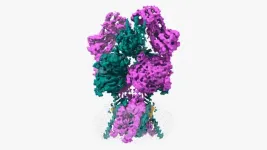
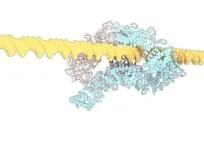
(Press-News.org) Proteins are constantly performing a kind of dance. They move and contort their bodies to fulfill specific functions inside our bodies. The NMDAR protein executes an especially hard dance routine in our brains. One wrong step can lead to a range of neurological disorders. NMDAR binds to the neurotransmitter, glutamate, and another compound, glycine. These bindings control NMDAR’s dance steps. When their routine is over, the NMDAR opens. This open ion channel generates electrical signals critical for cognitive functions like memory.
The problem is that scientists couldn’t figure out the last step in NMDAR’s routine—until now. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Professor Hiro Furukawa and his team have deciphered the critical dance move in which NMDAR rotates into an open formation. In other words, they’ve learned the NMDAR “Twist.”
To capture this key step, Furukawa and his team used a technique called electron cryo-microscopy (cryo-EM), which freezes and visualizes proteins in action. First, the team had to find a way to keep a type of NMDAR called GluN1-2B in its open pose long enough to image it. So, Furukawa teamed up with Professors Stephen Traynelis and Dennis Liotta at Emory University. Together, they discovered a molecule that favors NMDAR in an open position.
“It’s not the most stable conformation,” Furukawa explains. “There are many pieces dancing independently in NMDAR. They have to coordinate with each other. Everything has to go perfectly to open the ion channel. We need a precise amount of electrical signals at the right time for proper behaviors and cognitions.”
The cryo-EM images allow researchers to see precisely how the NMDAR’s atoms move during its “Twist.” This may one day lead to drug compounds that can teach the correct moves to NMDARs that have lost a step. Better drugs that target NMDARs might have applications for neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s and depression.
“Compounds bind to pockets within proteins and are imperfect, initially. This will allow us and chemists to find a way to fill those pockets more perfectly. That would improve the potency of the drug. Also, the shape of the pocket is unique. But there could be something similarly shaped in other proteins. That would cause side effects. So, specificity is key," Furukawa explains.
Indeed, there are many types of NMDARs in the brain. Another recent study from Furukawa’s lab offers the first view of the GluN1-3A NMDAR. Surprisingly, its dance moves are completely different. This routine results in unusual patterns of electrical signals.
In other words, we’re mastering the Twist. Next up: the headspin.
END
This protein does “The Twist”
2024-07-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Gut microbes implicated in bladder cancer
2024-07-31
At any given time, over 10 trillion microbes call our guts their home. From breaking down nutrients in our food to strengthening our immunity against pathogens, these microbes play an essential role in how we interact with the world. This includes – as shown in a new study by EMBL researchers and collaborators at the University of Split, Croatia – the way the body responds to carcinogens and develops cancer.
Carcinogens are chemicals that can cause ordinary cells to transform into cancer ...
Trust in physicians and hospitals declined over the course of the COVID-19 pandemic
2024-07-31
BOSTON– A cross-representative survey of adults in the United States showed decreasing levels of trust in physicians and hospitals during the COVID-19 pandemic—and the lower the trust, the less likely an individual was to get vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 or influenza. The findings come from a survey study of more than 400,000 U.S. adults published in JAMA Network Open by a team co-led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system.
“Trust in ...
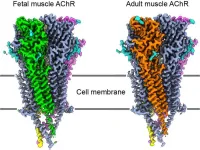
Unraveling a key junction underlying muscle contraction
2024-07-31
The connections between the nervous system and muscles develop differently across the kingdom of life. It takes newborn humans roughly a year to develop the proper muscular systems that support the ability to walk, while cows can walk mere minutes after birth and run not long after.
University of California San Diego researchers, using powerful new visualization technologies, now have a clear picture of why these two scenarios develop so differently. The results offer new insight into understanding muscle contraction in humans that may help in developing future treatments for muscular diseases.
“In this study we set out to understand ...
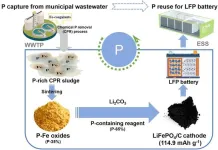
New method recovers phosphorus from wastewater to power the future of lithium-iron phosphate batteries
2024-07-31
In a recent study published in Engineering, a research team from the Shenzhen Engineering Research Laboratory for Sludge and Food Waste Treatment and Resource Recovery has introduced a pioneering method to tackle the critical global issue of phosphorus (P) scarcity. Their innovative approach leverages municipal wastewater to produce phosphorus vital for the manufacture of lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries, a key component in the rapidly growing electric vehicle market.
As the demand for LiFePO4 batteries ...
SwRI awarded $35.7 million to support cryptologic systems for U.S. Navy
2024-07-31
SAN ANTONIO — July 31, 2024 —Southwest Research Institute will provide engineering and equipment support for advanced cryptologic technology for shipboard and airborne platforms as part of a $35.7 million contract with the U.S. Navy. The five-year contract will deliver services from June 2024 through June 2029, with the option for the U.S. Navy to add $14 million and extend the contract through 2031.
SwRI develops electronic warfare (EW) technology to detect, intercept and disrupt a range of signals on the electromagnetic spectrum, supporting efforts to thwart ...
With biodiversity under threat, scientists suggest the need for a new biorepository—on the moon
2024-07-31
With numerous species facing extinction, an international team of researchers has proposed an innovative solution to protect the planet's biodiversity: a lunar biorepository. This concept, detailed in a recent article in the journal BioScience, is aimed at creating a passive, long-lasting storage facility for cryopreserved samples of Earth's most at-risk animal species.
Led by Dr. Mary Hagedorn of the Smithsonian's National Zoo and Conservation Biology Institute, the team envisions taking advantage of the Moon's naturally cold temperatures, particularly in permanently shadowed regions near the poles, where temperatures remain consistently below –196 degrees ...
Strong El Nino makes European winters easier to forecast
2024-07-31
Heavy rain and flooding in Brazil in November could tell forecasters whether December, January and February in Britain will be cold and dry or mild and wet.
This is because forecasting European winter weather patterns months in advance is made simpler during years of strong El Niño or La Niña events in the tropical Pacific Ocean, a new study has found.
A strong El Nino or La Nina in the Pacific Ocean can bring big changes in temperatures, wind patterns and rainfall patterns to South America. When ...
MD Anderson and collaborators to launch project studying T cells on International Space Station
2024-07-31
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and collaborators are initiating a research project that will send T cells to the International Space Station (ISS) to study the effects of prolonged microgravity on cell differentiation, activation, memory and exhaustion. These results will be further analyzed on Earth to uncover signaling pathways and identify potential immune targets that can improve treatment strategies for patients with cancer and other diseases.
To accomplish this work, MD Anderson researchers ...
Chameleon testbed secures $12 million in funding for phase 4: Expanding frontiers in computer science research
2024-07-31
Chameleon, led by Senior Scientist Kate Keahey from Argonne National Laboratory, has been a cornerstone of CS research and education for nearly a decade. The platform has served over 10,000 users, contributing to more than 700 research publications. Chameleon has now secured an additional $12 million in funding from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) to roll out its next four-year phase. With this new funding, Chameleon will continue to innovate and support its growing community, enabling groundbreaking discoveries in CS systems research.
ABOUT CHAMELEON: A PLATFORM FOR INNOVATION
Chameleon is a large-scale, deeply reconfigurable experimental ...
For bigger muscles push close to failure, for strength, maybe not
2024-07-31
When performing resistance training such as lifting weights, there’s a lot of interest in how close you push yourself to failure – the point where you can’t do another rep – and how it affects your results.
While research has looked at this concept in different ways, to date, no meta-analysis has explored the pattern (i.e., linear or non-linear) of how the distance from failure (measured by repetitions in reserve) affects changes in muscle strength and size.
As such, it’s ...