(Press-News.org) Companies and institutes are currently working on biotechnological processes for the production of dairy products without the use of cows: In so-called precision fermentation, egg and milk proteins are produced with the help of bacteria, yeasts or other fungi. This results in foods such as milk or cheese with a familiar flavour and texture. Supporters hope that this will lead to more sustainable food production, as nutrient-rich proteins can be produced using fewer resources. But will consumers accept such products? Researchers at the University of Göttingen have found that a large proportion of German consumers are willing to try and buy cheese produced in this way. The results of the study have been published in the international journal Future Foods.
The study, which was conducted in collaboration with LI Food – Landesinitiative Ernährungswirtschaft Niedersachsen and the German Institute of Food Technologies (DIL), is based on a representative online survey with around 2,000 participants. The researchers analysed how various aspects of information affect the acceptance of cheese produced in this way. They analysed the potential opportunities and risks of the technology, including its relation to sustainability, impact on agriculture and product quality.
In general, information has only a minor influence on whether consumers would try or buy cheese from precision fermentation. Only the reference to the technological genetic modification of the microorganisms required for the production process leads to a slightly significantly lower willingness to try the product.
Respondents were also confronted with the potential advantages and disadvantages of this technology. It was found that emphasising the consistently high quality of the products and advantages in terms of the environment and animal welfare in particular increased the willingness to try such cheese. The situation is different when consumers are informed about possible risks, for example that farmers could lose their source of income due to the new technology or that large companies could exert too much power on the market. These aspects reduced the willingness to buy and pay for such cheese the most.
“Our study shows that consumers in Germany are open to cheese from precision fermentation if they are informed about the benefits and high quality of the product. However, it is important to design the communication carefully to address concerns about the impact on traditional agriculture”, explains first author Dr Sarah Kühl, Chair for Marketing for Food and Agricultural Products at the University of Göttingen.
Corresponding products are already on the market in the USA; authorisation in Germany and the European Union is still pending. The technology as such is not new – it is already used in the production of medicines such as insulin.
Original publication: Kühl, S.; Schäfer, A.; Kircher, C.; Mehlhose, C (2024): Beyond the Cow: Consumer Perceptions and Information Impact on Acceptance of Precision Fermentation-produced Cheese in Germany. Future Foods, 10, 100411. DOI: 10.1016/j.fufo.2024.100411
Contact:
Dr Sarah Kühl
University of Göttingen
Faculty of Agricultural Sciences
Marketing for Food and Agricultural Products
Platz der Göttinger Sieben 5, 37073 Göttingen
Phone: +49 (0)551 39-26245
Mail: sarah.kuehl@uni-goettingen.de
Web: www.uni-goettingen.de/en/443621.html
END
Cheese of the future: Consumers open to animal-free alternatives
Researchers at the University of Göttingen investigate consumer acceptance
2024-08-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New Moffitt study explores how antifragility could revolutionize cancer treatment
2024-08-01
TAMPA, Fla. — Researchers constantly seek innovative approaches to tackle cancer. One concept gaining traction is antifragility, a property where systems not only withstand stress but improve because of it. In cancer research, this concept is particularly relevant for tumors that adapt and evolve in response to treatment. Understanding antifragility could lead to more effective therapies. In a new study published in npj Complexity, Moffitt Cancer Center researchers offer a new perspective on antifragility, proposing ...
Advances in 3D organ bioprinting: A step towards personalized medicine and solving organ shortages
2024-08-01
In a latest review published in Engineering, an international team of scientists from China and the United States has presented a comprehensive analysis of the latest advancements in 3D organ bioprinting. This innovative technology holds the potential to revolutionize regenerative medicine and tackle some of the most pressing issues in organ transplantation.
Organ damage or failure, whether resulting from injury, disease, or aging, poses a significant challenge due to the body’s limited natural regenerative capabilities. Traditional organ transplantation, while lifesaving, is fraught with difficulties including donor shortages and the risk of immune rejection. This has spurred a ...
China forges ahead with technological innovations in large-span arch bridge construction
2024-08-01
The field of bridge engineering is witnessing a transformative era, as China leads the way with its recent advancements in constructing large-span arch bridges. Jielian Zheng, the member of the Chinese Academy of Engineering from Guangxi University, has authored a research article in Engineering, titled “Recent Construction Technology Innovations and Practices for Large-Span Arch Bridges in China.” The article elucidates the significant strides made in the construction of concrete-filled steel tubular (CFST) and steel-reinforced concrete (SRC) ...
External mentorship key in encouraging trainees to pursue classical hematology
2024-08-01
(WASHINGTON, August 1, 2024) — In a year-long pilot program, external mentorship increased confidence, furthered career development, and facilitated networking opportunities for trainees in classical hematology, according to a study published in Blood Advances.
Classical hematology, the study of non-cancerous blood disorders such as sickle cell anemia and thrombotic and hemorrhagic disorders, is projected to face a significant workforce shortage in the coming years. The American Society of Hematology’s (ASH) previous surveys of hematology/oncology program ...
Tiny flyers with large impact: Blowflies carry bird flu virus
2024-08-01
Fukuoka, Japan – Researchers from Kyushu University have discovered that blowflies, a family of flies strongly attracted to decaying flesh and feces, are carrying the bird flu virus in southern Japan. Their findings, published in Scientific Reports, introduce a potential new route of transmission for bird flu and highlight the need to develop new countermeasures to prevent and control the disease in poultry farms.
Since 2020, bird flu has been spreading rapidly around the globe, leading to the death of millions of wild birds and the culling ...
Stock market turbulence linked to increased risk of heart attacks, strokes, and suicide: A groundbreaking study analyzes 12 million deaths
2024-08-01
In a recent study published in Engineering, a team of Chinese researchers has uncovered a startling correlation between stock market volatility and the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) and suicide. The research, which analyzed over 12 million deaths across China from 2013 to 2019, provides compelling evidence that the psychological stress induced by stock market fluctuations has severe and immediate health implications.
The study, titled “Stock Volatility Increases the Mortality Risk of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events and Suicide: A Case-Crossover Study of 12 Million Deaths,” is a wake-up call for investors, ...
Judging your own happiness could backfire
2024-08-01
Judging how happy you are could backfire and negatively impact life satisfaction and psychological well-being, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
In three experiments comprising more than 1,800 participants, researchers found that having concerns or judgments about one’s own level of happiness were associated with lower well-being, due in part to greater negativity and disappointment about positive events.
The research was published in the journal Emotion.
Thinking too much about one’s own level of happiness could be related to fears about not measuring up or not being as happy as other people, said lead researcher Felicia ...
Uncontrolled hypertension: The old ‘silent killer’ is alive and well
2024-08-01
In the United States and worldwide, cardiovascular disease is the leading avoidable cause of premature death and disability. Primarily heart attacks and stroke, cardiovascular disease accounts for more than 900,000 annual deaths nationally and about 10 million deaths globally.
Uncontrolled hypertension or high blood pressure is a major risk factor for stroke and heart attacks. Prevention and management of cardiovascular disease involves therapeutic lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise and adjunctive drug therapies of proven benefit.
In a commentary published in The American ...
Talking about regeneration
2024-08-01
Researchers including those from the University of Tokyo’s Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences transferred genes from simple organisms capable of regenerating their bodies into common fruit flies, more complex animals that cannot. They found the transferred gene suppressed an age-related intestinal issue in the flies. Their results suggest studying genes specific to animals with high regenerative capability may uncover new mechanisms for rejuvenating stem cell function and extending the healthy lifespan ...
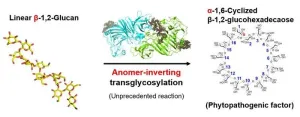
Breakthrough in plant disease: New enzyme could lead to anti-bacterial pesticides
2024-08-01
Plant diseases pose significant challenges to agricultural productivity, presenting formidable hurdles that require urgent attention. Left unchecked, these diseases can spread rapidly, inflicting widespread damage on crops and leading to reduced yields and substantial economic losses. Therefore, accurately identifying the pathogens responsible for these diseases is crucial. This identification allows for targeted interventions that minimize risks and effectively mitigate the agricultural impacts.
Xanthomonas species are notorious plant pathogens that affect a broad spectrum of hosts, including key crops like rice, wheat, and tomatoes. These pathogens augment ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
[Press-News.org] Cheese of the future: Consumers open to animal-free alternativesResearchers at the University of Göttingen investigate consumer acceptance