(Press-News.org) An estimated 16% of people worldwide live with a significant disability that impacts their daily life. Of this population, only about 40% engage in aerobic activity. Due to this lack of exercise, people with disabilities (PWD) are more likely to suffer from chronic conditions such as heart disease, stroke, diabetes, or cancer and are at higher risk of mental illnesses like depression and anxiety.
“Many PWD struggle with psychological issues such as low self-esteem and negative body image, which can further reduce their motivation to participate in exercise activities, especially in public places like gyms,” said Alexandra Jamieson, research scientist at The University of Texas at Arlington Research Institute (UTARI) and lead author of a new peer-reviewed study on adaptive exercise technologies for PWD. Former UTARI student researcher Helara D. Wijesundara is also an author on the paper.
Even PWD who are interested in exercising face challenges, as most commercial gyms lack adaptive equipment and properly trained staff to ensure their safety. Jamieson found that although some nonprofit organizations aim to promote fitness for PWD, there are few commercial efforts to reach the wider community to encourage exercise.
“The biggest barriers to fitness are accessibility and cost,” said Jamieson. “Standard gyms are not legally required to have adaptive machines for users of differing abilities. Plus, there is generally a lack of data about the demand for these adaptive machines that would help gyms justify the higher costs of adding them.”
She also noted that transportation to and from the gym can be an issue for PWD. Although ride-sharing and disabled transit options exist, they are not always reliable, and many are not equipped for PWD.
Home gyms are a popular option for PWD, but a lot of adaptative exercise equipment is produced by smaller manufacturers and has higher production costs, making it cost-prohibitive for individuals to purchase it. Jamieson suggests expanding government assistance programs around acquiring adaptative exercise machines for home use.
“Medicaid does have purchasing assistance programs for PWD to buy assistive technology, but they are not well known and only cover exercise machines that are deemed medically necessary by an individual’s doctor,” she said. Raising public awareness among physicians and PWD about how to apply for assistance to acquire adaptive exercise equipment could be a way to help.
To improve adaptive exercise options, Jamieson is working with colleagues from UTARI, the Department of Kinesiology, and the Department of Art to create an adaptive exergame machine, a type of accessible exercise equipment with a video game component that keeps users engaged while monitoring their activity. The team is currently recruiting individuals to participate in a pilot study of the technology. Please contact Jamieson if you would like additional information.
END
Barriers complicate exercise for disability community
More resources and outreach necessary to encourage continued physical activity
2024-08-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Venezuelan crisis has negatively affected country’s Internet
2024-08-01
As the Venezuelan crisis intensifies, researchers and policy experts have worked to understand its ramifications on the country’s politics, economics, health services, water security, infrastructure and more.
Now, Northwestern University computer scientists have comprehensively examined the effects of the crisis on a previously unexplored area: the Internet.
In a new study, the researchers found the crisis has significantly — and negatively — affected Venezuela’s Internet infrastructure and connectivity. Compared to the ...
COSPAR 2024: Embracing team spirit in space research
2024-08-01
The Committee on Space Research (COSPAR) has successfully concluded its 45th COSPAR Scientific Assembly in Busan, Korea, held from 13 to 21 July. This prestigious event brought together more than 3,000 experts and leaders from 55 countries in all major fields of space science, under the theme “Team Spirit in Space Research”. This biennial event, actively supported by major space organizations, is a benchmark for fostering dialogue and collaboration within the global space science community.
Bringing space leaders together
Of particular note this time was the showcasing of ...
'Cowpuppy' takes readers into secret world of cows
2024-08-01
During the height of the COVID-19 pandemic Gregory Berns, a neuroscientist at Emory University, moved from Atlanta to a farm an hour south of the city. His reinvention from city dweller to farmer led to his upcoming book “Cowpuppy: An Unexpected friendship and a Scientist’s Journey into the Secret World of Cows.”
Set for publication by Harper Collins on August 20, the book describes Berns’ crash course to becoming a cattleman and his ongoing fascination with the interior world of cows.
Berns originally bought a few cows to keep the grass in the ...
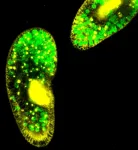
Warming stops tiny organisms working together
2024-08-01
Hotter conditions prevent two tiny organisms working together for mutual benefit, new research shows.
University of Exeter scientists studied a single-celled organism (Paramecium bursaria) which can absorb and host algae (Chlorella spp).
This pairing is common in freshwater worldwide, and their symbiotic relationship provides benefits including trading of nutrients and protection for the algae.
But when scientists made the water 5°C warmer, the partnership stopped working – and the results suggest the algae may even become parasitic.
The breakdown of such relationships could have a major impact on ecosystems.
“This ...
Gun permits may be more effective than background checks alone at reducing firearm homicides
2024-08-01
Despite widespread support, laws enforcing universal background checks at the time of firearm purchase may not be enough to move the needle on reducing shooting deaths in the United States. A Tufts University School of Medicine study, published August 1 in the journal JAMA Network Open, reports that states that require gun permits rather than relying solely on universal background checks see firearm homicide rates, on average, 18% lower than states with background check policies alone.
The analysis compared firearm homicide data from the 12 states with universal background check laws but no permit ...
Study finds regular aspirin use associated with greatest reduction in colorectal cancer among those most at risk
2024-08-01
Regular aspirin may help lower risk of colorectal cancer in people with greater lifestyle-related risk factors for the disease, according to a study led by researchers at Mass General Brigham. The study, published in JAMA Oncology, could encourage a more nuanced approach to preventive aspirin use.
“We sought to identify individuals who are more likely to benefit from aspirin to facilitate more personalized prevention strategies,” said co-senior author Andrew Chan, MD, MPH, Director of Epidemiology for the Mass General Cancer Center and gastroenterology Director of the Center for ...
Diagnostic accuracy of an integrated AI tool to estimate gestational age from blind ultrasound sweeps
2024-08-01
About The Study: Between 14 and 27 weeks’ gestation, novice users with no prior training in ultrasonography estimated gestational age as accurately with the low-cost, point-of-care artificial intelligence (AI) tool as credentialed sonographers performing standard biometry on high-specification machines. These findings have immediate implications for obstetrical care in low-resource settings, advancing the World Health Organization goal of ultrasonography estimation of gestational age for all pregnant people.
Quote from corresponding author Jeffrey ...
Aspirin use and incidence of colorectal cancer according to lifestyle risk
2024-08-01
About The Study: Aspirin use was associated with a greater absolute reduction in risk of colorectal cancer among individuals with less healthy lifestyles in this cohort study. The findings of the study suggest that lifestyle risk factors may be useful to identify individuals who may have a more favorable risk-benefit profile for cancer prevention with aspirin.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Andrew T. Chan, MD, MPH (achan@mgh.harvard.edu) and Long H. Nguyen, MD, MS (lnguyen24@mgh.harvard.edu).
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2024.2503)
Editor’s ...
State abortion policy and moral distress among clinicians providing abortion after the Dobbs decision
2024-08-01
About The Study: In this purposive national survey study of clinicians providing abortion, moral distress was elevated among all clinicians and more than twice as high among those practicing in states that restrict abortion compared with those in states that protect abortion. The findings suggest that structural changes addressing bans on necessary health care, such as federal protections for abortion, are needed at institutional, state, and federal policy levels to combat widespread moral distress.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, ...
Universal background checks, permit requirements, and firearm homicide rates
2024-08-01
About The Study: This cross-sectional study found that universal background checks alone were not associated with firearm homicide rates, but a permit requirement for the purchase and possession of firearms was associated with substantially reduced rates of firearm homicide. The findings suggest that combining universal background checks and permit-to-purchase requirements is an effective strategy for firearm-related fatality reduction.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Michael Siegel, MD, MPH, email mike.siegel@tufts.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.25025)
Editor’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Stem cells from human baby teeth show promise for treating cerebral palsy
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
UF research finds a gentler way to treat aggressive gum disease
[Press-News.org] Barriers complicate exercise for disability communityMore resources and outreach necessary to encourage continued physical activity