(Press-News.org) About The Study: In this purposive national survey study of clinicians providing abortion, moral distress was elevated among all clinicians and more than twice as high among those practicing in states that restrict abortion compared with those in states that protect abortion. The findings suggest that structural changes addressing bans on necessary health care, such as federal protections for abortion, are needed at institutional, state, and federal policy levels to combat widespread moral distress.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Katherine Rivlin, M.D., M.Sc., email krivlin@bsd.uchicago.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.26248)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.26248?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=080124
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
State abortion policy and moral distress among clinicians providing abortion after the Dobbs decision
JAMA Network Open
2024-08-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Universal background checks, permit requirements, and firearm homicide rates
2024-08-01
About The Study: This cross-sectional study found that universal background checks alone were not associated with firearm homicide rates, but a permit requirement for the purchase and possession of firearms was associated with substantially reduced rates of firearm homicide. The findings suggest that combining universal background checks and permit-to-purchase requirements is an effective strategy for firearm-related fatality reduction.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Michael Siegel, MD, MPH, email mike.siegel@tufts.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.25025)
Editor’s ...
Joseph Rogers, MD, named to American Board of Internal Medicine’s Cardiovascular Board
2024-08-01
Houston, Texas, July 24, 2024 – The Texas Heart Institute, a globally renowned cardiovascular health center, announced today that Joseph G. Rogers, MD, President and Chief Executive Officer for The Texas Heart Institute and Adjunct Professor in the Division of Cardiology at Duke University, has been appointed by the American Board of Internal Medicine (ABIM) to its Cardiovascular Board for a three-year term beginning July 1, 2024.
“I am honored to have been appointed to this esteemed group ...
Study examines effect of fish oil in older adults’ brains
2024-08-01
A clinical trial at Oregon Health & Science University suggests that a subset of older adults with a genetic predisposition to Alzheimer’s disease may benefit from fish oil supplements.
The study published today in the journal JAMA Network Open.
The results come amid claims that fish oil supplements can improve brain function in people with memory problems. The study found no statistically significant benefit for all older adults in general. However, among those enrolled in the study who also carry a gene associated with Alzheimer’s disease, it showed a reduction in the breakdown of nerve cells in the brain.
The study’s senior co-author from OHSU ...
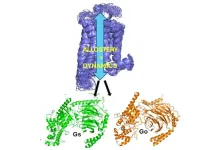
Conformational dynamics and allostery elucidate how GPCR couple to multiple G-proteins, offering mechanistic insights into coupling-promiscuity and novel drug discovery strategies
2024-08-01
In a groundbreaking study, a multinational research team led by Dr. Adnan Sljoka (RIKEN) and Prof. Akio Kitao (Tokyo Tech), in collaboration with Prof. Scott Prosser (University of Toronto), has carried out experimental and computational studies to elucidate the mechanisms behind G protein selectivity and efficacy in the human adenosine A2A receptor (A2AR). A2AR is a member of major drug targets G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily, which engages the G protein and initiates cell signaling, influencing heart health, inflammation, cancer, and brain diseases. Scientists have ...
Proteins as the key to precision medicine: Finding unknown effects of existing drugs
2024-08-01
Fewer side effects, improved chances of healing: the goal of precision medicine is to provide patients with the most individualized treatment possible. This requires a precise understanding of what is happening at the cellular level. For the first time, researchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) have now succeeded in mapping the interactions of 144 active substances with around 8,000 proteins. The results could help to identify previously unknown potential benefits of existing drugs.
Practically all drugs either affect, produce or eliminate proteins – or are, in fact, proteins. But what exactly happens when a high or low dose is taken? And what is going ...
Cheese of the future: Consumers open to animal-free alternatives
2024-08-01
Companies and institutes are currently working on biotechnological processes for the production of dairy products without the use of cows: In so-called precision fermentation, egg and milk proteins are produced with the help of bacteria, yeasts or other fungi. This results in foods such as milk or cheese with a familiar flavour and texture. Supporters hope that this will lead to more sustainable food production, as nutrient-rich proteins can be produced using fewer resources. But will consumers accept such products? Researchers at the University of Göttingen have found that a large proportion of German consumers are willing to try and buy cheese produced in this way. ...
New Moffitt study explores how antifragility could revolutionize cancer treatment
2024-08-01
TAMPA, Fla. — Researchers constantly seek innovative approaches to tackle cancer. One concept gaining traction is antifragility, a property where systems not only withstand stress but improve because of it. In cancer research, this concept is particularly relevant for tumors that adapt and evolve in response to treatment. Understanding antifragility could lead to more effective therapies. In a new study published in npj Complexity, Moffitt Cancer Center researchers offer a new perspective on antifragility, proposing ...
Advances in 3D organ bioprinting: A step towards personalized medicine and solving organ shortages
2024-08-01
In a latest review published in Engineering, an international team of scientists from China and the United States has presented a comprehensive analysis of the latest advancements in 3D organ bioprinting. This innovative technology holds the potential to revolutionize regenerative medicine and tackle some of the most pressing issues in organ transplantation.
Organ damage or failure, whether resulting from injury, disease, or aging, poses a significant challenge due to the body’s limited natural regenerative capabilities. Traditional organ transplantation, while lifesaving, is fraught with difficulties including donor shortages and the risk of immune rejection. This has spurred a ...
China forges ahead with technological innovations in large-span arch bridge construction
2024-08-01
The field of bridge engineering is witnessing a transformative era, as China leads the way with its recent advancements in constructing large-span arch bridges. Jielian Zheng, the member of the Chinese Academy of Engineering from Guangxi University, has authored a research article in Engineering, titled “Recent Construction Technology Innovations and Practices for Large-Span Arch Bridges in China.” The article elucidates the significant strides made in the construction of concrete-filled steel tubular (CFST) and steel-reinforced concrete (SRC) ...
External mentorship key in encouraging trainees to pursue classical hematology
2024-08-01
(WASHINGTON, August 1, 2024) — In a year-long pilot program, external mentorship increased confidence, furthered career development, and facilitated networking opportunities for trainees in classical hematology, according to a study published in Blood Advances.
Classical hematology, the study of non-cancerous blood disorders such as sickle cell anemia and thrombotic and hemorrhagic disorders, is projected to face a significant workforce shortage in the coming years. The American Society of Hematology’s (ASH) previous surveys of hematology/oncology program ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
UCLA researchers engineer CAR-T cells to target hard-to-treat solid tumors
New study reveals asynchronous land–ocean responses to ancient ocean anoxia
Ctenophore research points to earlier origins of brain-like structures
[Press-News.org] State abortion policy and moral distress among clinicians providing abortion after the Dobbs decisionJAMA Network Open