(Press-News.org) About The Study: Between 14 and 27 weeks’ gestation, novice users with no prior training in ultrasonography estimated gestational age as accurately with the low-cost, point-of-care artificial intelligence (AI) tool as credentialed sonographers performing standard biometry on high-specification machines. These findings have immediate implications for obstetrical care in low-resource settings, advancing the World Health Organization goal of ultrasonography estimation of gestational age for all pregnant people.
Quote from corresponding author Jeffrey S. A. Stringer, MD:
“Our study demonstrates that an AI-enabled, portable ultrasound device can estimate gestational age as accurately as an expert sonographer using an expensive, high-specification machine. This high degree of accuracy was obtained even though the users of the device had no formal training in sonography.
“The most important takeaway is the potential democratization of a critical prenatal diagnostic tool. By enabling accurate gestational age estimation without the need for expensive equipment or specialized training, this technology could significantly expand access to quality prenatal care in resource-limited settings worldwide.
“This research could transform prenatal care delivery globally. In areas where ultrasound was previously unavailable, patients can now receive timely, accurate gestational age estimates, crucial for identifying high-risk pregnancies and guiding appropriate care. Health care providers in remote or underserved areas can offer expert-level diagnostics without extensive training, potentially leading to improved maternal and neonatal outcomes on a large scale.”
Contact information for Jeffrey S. A. Stringer, MD: email jeffrey_stringer@med.unc.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.10770)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/10.1001/jama.2024.10770?guestAccessKey=35480dc0-b13a-4c82-ae68-19aa19d01fab&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=080124
END
Diagnostic accuracy of an integrated AI tool to estimate gestational age from blind ultrasound sweeps
JAMA
2024-08-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Aspirin use and incidence of colorectal cancer according to lifestyle risk
2024-08-01
About The Study: Aspirin use was associated with a greater absolute reduction in risk of colorectal cancer among individuals with less healthy lifestyles in this cohort study. The findings of the study suggest that lifestyle risk factors may be useful to identify individuals who may have a more favorable risk-benefit profile for cancer prevention with aspirin.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Andrew T. Chan, MD, MPH (achan@mgh.harvard.edu) and Long H. Nguyen, MD, MS (lnguyen24@mgh.harvard.edu).
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2024.2503)
Editor’s ...
State abortion policy and moral distress among clinicians providing abortion after the Dobbs decision
2024-08-01
About The Study: In this purposive national survey study of clinicians providing abortion, moral distress was elevated among all clinicians and more than twice as high among those practicing in states that restrict abortion compared with those in states that protect abortion. The findings suggest that structural changes addressing bans on necessary health care, such as federal protections for abortion, are needed at institutional, state, and federal policy levels to combat widespread moral distress.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, ...
Universal background checks, permit requirements, and firearm homicide rates
2024-08-01
About The Study: This cross-sectional study found that universal background checks alone were not associated with firearm homicide rates, but a permit requirement for the purchase and possession of firearms was associated with substantially reduced rates of firearm homicide. The findings suggest that combining universal background checks and permit-to-purchase requirements is an effective strategy for firearm-related fatality reduction.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Michael Siegel, MD, MPH, email mike.siegel@tufts.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.25025)
Editor’s ...
Joseph Rogers, MD, named to American Board of Internal Medicine’s Cardiovascular Board
2024-08-01
Houston, Texas, July 24, 2024 – The Texas Heart Institute, a globally renowned cardiovascular health center, announced today that Joseph G. Rogers, MD, President and Chief Executive Officer for The Texas Heart Institute and Adjunct Professor in the Division of Cardiology at Duke University, has been appointed by the American Board of Internal Medicine (ABIM) to its Cardiovascular Board for a three-year term beginning July 1, 2024.
“I am honored to have been appointed to this esteemed group ...
Study examines effect of fish oil in older adults’ brains
2024-08-01
A clinical trial at Oregon Health & Science University suggests that a subset of older adults with a genetic predisposition to Alzheimer’s disease may benefit from fish oil supplements.
The study published today in the journal JAMA Network Open.
The results come amid claims that fish oil supplements can improve brain function in people with memory problems. The study found no statistically significant benefit for all older adults in general. However, among those enrolled in the study who also carry a gene associated with Alzheimer’s disease, it showed a reduction in the breakdown of nerve cells in the brain.
The study’s senior co-author from OHSU ...
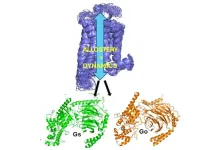
Conformational dynamics and allostery elucidate how GPCR couple to multiple G-proteins, offering mechanistic insights into coupling-promiscuity and novel drug discovery strategies
2024-08-01
In a groundbreaking study, a multinational research team led by Dr. Adnan Sljoka (RIKEN) and Prof. Akio Kitao (Tokyo Tech), in collaboration with Prof. Scott Prosser (University of Toronto), has carried out experimental and computational studies to elucidate the mechanisms behind G protein selectivity and efficacy in the human adenosine A2A receptor (A2AR). A2AR is a member of major drug targets G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily, which engages the G protein and initiates cell signaling, influencing heart health, inflammation, cancer, and brain diseases. Scientists have ...
Proteins as the key to precision medicine: Finding unknown effects of existing drugs
2024-08-01
Fewer side effects, improved chances of healing: the goal of precision medicine is to provide patients with the most individualized treatment possible. This requires a precise understanding of what is happening at the cellular level. For the first time, researchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) have now succeeded in mapping the interactions of 144 active substances with around 8,000 proteins. The results could help to identify previously unknown potential benefits of existing drugs.
Practically all drugs either affect, produce or eliminate proteins – or are, in fact, proteins. But what exactly happens when a high or low dose is taken? And what is going ...
Cheese of the future: Consumers open to animal-free alternatives
2024-08-01
Companies and institutes are currently working on biotechnological processes for the production of dairy products without the use of cows: In so-called precision fermentation, egg and milk proteins are produced with the help of bacteria, yeasts or other fungi. This results in foods such as milk or cheese with a familiar flavour and texture. Supporters hope that this will lead to more sustainable food production, as nutrient-rich proteins can be produced using fewer resources. But will consumers accept such products? Researchers at the University of Göttingen have found that a large proportion of German consumers are willing to try and buy cheese produced in this way. ...
New Moffitt study explores how antifragility could revolutionize cancer treatment
2024-08-01
TAMPA, Fla. — Researchers constantly seek innovative approaches to tackle cancer. One concept gaining traction is antifragility, a property where systems not only withstand stress but improve because of it. In cancer research, this concept is particularly relevant for tumors that adapt and evolve in response to treatment. Understanding antifragility could lead to more effective therapies. In a new study published in npj Complexity, Moffitt Cancer Center researchers offer a new perspective on antifragility, proposing ...
Advances in 3D organ bioprinting: A step towards personalized medicine and solving organ shortages
2024-08-01
In a latest review published in Engineering, an international team of scientists from China and the United States has presented a comprehensive analysis of the latest advancements in 3D organ bioprinting. This innovative technology holds the potential to revolutionize regenerative medicine and tackle some of the most pressing issues in organ transplantation.
Organ damage or failure, whether resulting from injury, disease, or aging, poses a significant challenge due to the body’s limited natural regenerative capabilities. Traditional organ transplantation, while lifesaving, is fraught with difficulties including donor shortages and the risk of immune rejection. This has spurred a ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Roadmap for Europe’s biodiversity monitoring system
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
[Press-News.org] Diagnostic accuracy of an integrated AI tool to estimate gestational age from blind ultrasound sweepsJAMA